Abstract
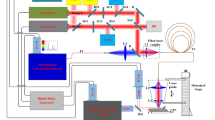
Relatively large measurement uncertainty severely hindered wide application for laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS), therefore it is of great importance to understand the mechanism of signal uncertainty generation, including initiation and propagation. It has been found that the fluctuation of plasma morphology was the main reason for signal uncertainty. However, it still remains unclear what mechanism leads to laser-induced plasma morphology fluctuation. In the present work, we employed three fast-imaging cameras to capture three successive plasma images from a same laser-induced Titanium alloy plasma, which enables us to understand more clearly of the plasma evolution process especially for the early plasma evolution stage when plasma and surrounding gases interact drastically. Seen from the images, the plasma experienced an increasing morphological fluctuation as delay time increased, transforming from a “stable plasma” before the delay time of 100 ns to a “fluctuating plasma” after the delay time of 300 ns. Notably, the frontier part of plasma showed a significant downward motion from the delay time of 150 ns to 200 ns and crashed with the lower part of the plasma, making the plasma flatter and later even splitting the plasma into two parts, which was considered as a critical process for the transformation of “stable plasma” to “unstable plasma”. By calculating the correlation coefficient of plasma image pairs at successive delay times, it was found that the higher the similarity between two plasma at early stage, the more similar at later stage; this implied that the tiny plasma fluctuation earlier than the critical delay time (150–200 ns) was amplified, causing a large plasma fluctuation at the later stage as well as LIBS measurement uncertainty. The initiation of slight fluctuation was linked with Rayleigh-Taylor Instability (RTI) due to the drastic material interpenetration at the plasma-ambient gas interface at earlier stage (before 50 ns). That is, the uncertainty generation of LIBS was proposed as: plasma morphology fluctuation was inevitably trigged by RTI at the early stage and the tiny fluctuation was amplified by the back pressed downward process of plasma frontier material, leading to severe morphology fluctuation as well as LIBS signal uncertainty.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. W. Hahn and N. Omenetto, Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS), Part I: Review of basic diagnostics and plasma-particle interactions: Still-challenging issues within the analytical plasma community, Appl. Spectrosc. 64(12), 335A (2010)
D. W. Hahn and N. Omenetto, Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS), Part II: Review of instrumental and methodological approaches to material analysis and applications to different fields, Appl. Spectrosc. 66(4), 347 (2012)
D. A. Cremers and L. J. Radziemski, Handbook of Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy, Wiley, 2013
Z. Wang, T. B. Yuan, Z. Y. Hou, W. D. Zhou, J. D. Lu, H. B. Ding, and X. Y. Zeng, Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy in China, Front. Phys. 9, 419 (2014)
J. D. Winefordner, I. B. Gornushkin, T. Correll, E. Gibb, B. W. Smith, and N. Omenetto, Comparing several atomic spectrometric methods to the super stars: Special emphasis on laser induced breakdown spectrometry, LIBS, a future super star, J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 19(9), 1061 (2004)
J. M. Mermet, P. Mauchien, and J. L. Lacour, Processing of shot-to-shot raw data to improve precision in laser-induced breakdown spectrometry microprobe, Spectrochim. Acta B At. Spectrosc. 63(10), 999 (2008)
Z. Hou, Z. Wang, T. Yuan, J. Liu, Z. Li, and W. Ni, A hybrid quantification model and its application for coal analysis using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy, J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 31(3), 722 (2016)
E. Tognoni and G. Cristoforetti, Signal and noise in laser induced breakdown spectroscopy: An introductory review, Opt. Laser Technol. 79, 164 (2016)
X. Zeng, X. Mao, S. S. Mao, J. H. Yoo, R. Greif, and R. E. Russo, Laser-plasma interactions in fused silica cavities, J. Appl. Phys. 95, 816 (2004)
J. Yu, Q. Ma, V. Motto-Ros, W. Lei, X. Wang, and X. S. Bai, Generation and expansion of laser-induced plasma as a spectroscopic emission source, Front. Phys. 7(6), 649 (2012)
X. Bai, Q. Ma, M. Perrier, V. Motto-Ros, D. Sabourdy, L. Nguyen, A. Jalocha, and J. Yu, Experimental study of laser-induced plasma: Influence of laser fluence and pulse duration, Spectrochim. Acta B At. Spectrosc. 87, 27 (2013)
R. Wisbrun, I. Schechter, R. Niessner, H. Schroeder, and K. L. Kompa, Detector for trace elemental analysis of solid environmental samples by laser plasma spectroscopy, Anal. Chem. 66(18), 2964 (1994)
Z. Wang, Z. Hou, S. Lui, D. Jiang, J. Liu, and Z. Li, Utilization of moderate cylindrical confinement for precision improvement of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy signal, Opt. Express 20(S6), A1011 (2012)
Z. Hou, Z. Wang, J. Liu, W. Ni, and Z. Li, Signal quality improvement using cylindrical confinement for laser induced breakdown spectroscopy, Opt. Express 21(13), 15974 (2013)
Y. Fu, Z. Hou, and Z. Wang, Physical insights of cavity confinement enhancing effect in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy, Opt. Express 24(3), 3055 (2016)
V. N. Rai, A. K. Rai, F. Y. Yueh, and J. P. Singh, Optical emission from laser-induced breakdown plasma of solid and liquid samples in the presence of a magnetic field, Appl. Opt. 42(12), 2085 (2003)
L. B. Guo, W. Hu, B. Y. Zhang, X. N. He, C. M. Li, Y. S. Zhou, Z. X. Cai, X. Y. Zeng, and Y. F. Lu, Enhancement of optical emission from laser-induced plasmas by combined spatial and magnetic confinement, Opt. Express 19(15), 14067 (2011)
Z. Wang, Y. Deguchi, R. Liu, A. Ikutomo, Z. Zhang, D. Chong, J. Yan, J. Liu, and F.J. Shiou, Emission characteristics of laser-induced plasma using collinear long and short dual-pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS), Appl. Spectrosc. 71, 2187 (2017)
Y. Fu, Z. Hou, T. Li, Z. Li, and Z. Wang, Investigation of intrinsic origins of the signal uncertainty for laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy, Spectrochim. Acta B At. Spectrosc. 155, 67 (2019)
Z. Hou, Z. Wang, J. Liu, W. Ni, and Z. Li, Combination of cylindrical confinement and spark discharge for signal improvement using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy, Opt. Express 22(11), 12909 (2014)
X. Li, Z. Wang, Y. Fu, Z. Li, J. Liu, and W. Ni, Application of a spectrum standardization method for carbon analysis in coal using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS), Appl. Spectrosc. 68, 955 (2014)
X. Li, Z. Wang, X. Mao, and R. E. Russo, Spatially and temporally resolved spectral emission of laser-induced plasmas confined by cylindrical cavities, J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 29(11), 2127 (2014)
H. Yin, Z. Hou, T. Yuan, Z. Wang, W. Ni, and Z. Li, Application of spatial confinement for gas analysis using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy to improve signal stability, J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 30(4), 922 (2015)
T. Li, S. Sheta, Z. Hou, J. Dong, and Z. Wang, Impacts of a collection system on laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy signal detection, Appl. Opt. 57(21), 6120 (2018)
S. B. Wen, X. Mao, R. Greif, and R. E. Russo, Laser ablation induced vapor plume expansion into a background gas (II): Experimental analysis, J. Appl. Phys. 101, 023115 (2007)
S. B. Wen, X. Mao, R. Greif, and R. E. Russo, Expansion of the laser ablation vapor plume into a background gas (I): Analysis, J. Appl. Phys. 101, 023114 (2007)
C. G. Parigger, C. M. Helstern, B. S. Jordan, D. M. Surmick, and R. Splinter, Laser-plasma spatiotemporal cyanide spectroscopy and applications, Molecules 25, 615 (2020)
C. G. Parigger, D. M. Surmick, and G. Gautam, Self-absorption characteristics of measured laser-induced plasma line shapes, J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 810, 012012 (2017)
S. S. Harilal, C. V. Bindhu, M. S. Tillack, F. Najmabadi, and A. C. Gaeris, Internal structure and expansion dynamics of laser ablation plumes into ambient gases, J. Appl. Phys. 93, 2380 (2003)
S. S. Harilal, G. V. Miloshevsky, P. K. Diwakar, N. L. La-Haye, and A. Hassanein, Experimental and computational study of complex shockwave dynamics in laser ablation plumes in argon atmosphere, Phys. Plasmas. 19, 083504 (2012)
V. Y. Baranov, O. N. Derkach, V. G. Grishina, M. F. Kanevskii, and A. Y. Sebrant, Dynamics and stability of an expanding laser-induced plasma in a low-density gas, Phys. Rev. E 8(2), 1324 (1993)
P. S. R. Abhilasha, P. S. R. Prasad, and R. K. Thareja, Laser-produced carbon plasma in an ambient gas, Phys. Rev. E 48(4), 2929 (1993)
A. K. Sharma and R. K. Thareja, Characterization of laser-produced aluminum plasma in ambient atmosphere of nitrogen using fast photography, Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 4490 (2004)
D. W. Koopman, H. J. Siebeneck, and G. Jellison, Turbulent interaction fronts in counterstreaming laser-produced plasma studies, Phys. Fluids 22, 526, (1979)
A. Neogi and R. K. Thareja, Laser-produced carbon plasma expanding in vacuum, low pressure ambient gas and nonuniform magnetic field, Phys. Plasmas. 6, 365 (1999)
K. Rifai, F. Vidal, and T. W. Johnston, Theoretical investigation of the Rayleigh-Taylor instability in laserproduced plasmas driving into background gases, Phys. Plasmas. 14, 082311 (2007)
R. A. Marin, C. A. Gonzales, and H. Riascos, Rayleigh-Taylor analysis in a laser-induced plasma, J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 370, 012063 (2012)
H. J. Kull, Theory of the Rayleigh-Taylor instability, Phys. Rep. 206(5), 197 (1991)
L. J. Radziemski, Lasers-Induced Plasmas and Applications, Taylor & Francis, 1989
T. Lü, Y. Hu, J. Meng, Z. Li, C. Zhang, X. Zhang, and E. Tuyizere, Secondary shock wave: Implication for laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, J. Appl. Phys. 124, 073101 (2018)
B. Campanella, S. Legnaioli, S. Pagnotta, F. Poggialini, and V. Palleschi, Shock waves in laser-induced plasmas, Atoms 7(2), 57 (2019)
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61675110) and the National Key Research and Development Program Key Projects of China (No. 2016YFC0302102). We thank Patrick Hong for the paper improvement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article can also be found at http://journal.hep.com.cn/fop/EN/10.1007/s11467-020-1006-0.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, YT., Gu, WL., Hou, ZY. et al. Mechanism of signal uncertainty generation for laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Front. Phys. 16, 22502 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-020-1006-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-020-1006-0