Abstract
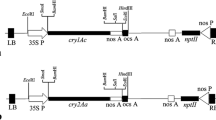
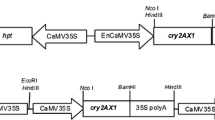
The cry1Ah gene was one of novel insecticidal genes cloned from Bacillus thuringiensis isolate BT8. Two plant expression vectors containing cry1Ah gene were constructed. The first intron of maize ubiqutin1 gene was inserted between the maize Ubiquitin promoter and cry1Ah gene in one of the plant expressing vectors (pUUOAH). The two vectors were introduced into maize immature embryonic calli by microprojectile bombardment, and the reproductively plants were acquired. PCR and Southern blot analysis showed that foreign genes had been integrated into maize genome and inherited to the next generation stably. The ELISA assay to T1 and T2 generation plants showed that the expression of Cry1Ah protein in the construct containing the ubi1 intron (pUUOAH) was 20% higher than that of the intronless construct (pUOAH). Bioassay results showed that the transgenic maize harboring cry1Ah gene had high resistance to the Asian corn borers and the insecticidal activity of the transgenic maize containing the ubi1 intron was higher than that of the intronless construct. These results indicated that the maize ubi1 intron can enhance the expression of the Bt cry1Ah gene in transgenic maize efficiently
Similar content being viewed by others
References
James C. Global Status of Commercialized Biotech/GM Crops: 2006. ISAAA Brief No. 35. ISAAA: Ithaca, 2006
James C. Global Status of Commercialized Biotech/GM Crops: 2007. ISAAA Brief No. 37. ISAAA: Ithaca, 2007
Shelton A M, Zhao J Z, Roush R T. Economic, ecological, food safety, and social consequences of the deployment of Bt transgenic plants. Annu Rev Entomol, 2002, 47: 845–881
Castle L A, Wu G S, McElroy D. Agricultural input traits: past, present and future. Curr Opin Biotech, 2006, 17:105–112
Xue J, Liang G, Crickmore N, et al. Cloning and characterization of a novel Cry1A toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis with high toxicity to the Asian corn borer and other lepidopteran insects. FEMS Microbiol Lett, 2008, 280(1): 95–101
Callis J, Fromm M, Walbot V. Introns increase gene expression in cultured maize cells. Genes Dev, 1987, 1: 1183–1200
Jeong Y M, Mun J H, Kim H, et al. An upstream region in the first intron of petunia actin depolymerizing factor 1 affects tissue-specific expression in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant J, 2007, 50: 230–239
Maniatis T, Reed R. An extensive network of coupling among gene expression machines. Nature, 2002, 416: 499–506
Proudfoot N J, Furger A, Dye M J. Integrating mRNA processing with transcription. Cell, 2002, 108: 501–512
Zhang X J, Liu J Q, Zhao Q, et al. Transfer of high Lysine gene into maize by microprojectile bombardment and detection of transgenic plants (in Chinese). J Agricult Biotechnol, 1999, 7: 363–367
Soyle J J, Doyle J L, Hortorium B H. Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus, 1996, 12(1): 13
Sambrook J, Russell D. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. 3rd ed. Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 2001
Ferre J, Van R J. Biochemistry and genetics of insect resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis. Annu Rev Entomol, 2002, 47: 501–533
Bates S L, Zhao J Z, Roush R T, et al. Insect resistance management in GMcrops: Past, present and future. Nat Biotechnol, 2005, 23(1): 57–62
Vain P, Finer K R, Engler D E, et al. Intron-mediated enhancement of gene expression in maize and bluegrass. Plant Cell Rep, 1996, 15: 489–494
Lorkovi Z J, Wieczorek Kirk D A, Lambermon M H L, et al. Pre-mRNA splicing in higher plants. Trends Plant Sci, 2000, 5(4): 160–167
Vries J, Herzfeld T, Wackernagel W. Transfer of plastid DNA from tobacco to the soil bacterium Acinetobactersp by natural transformation. Mol Microbiol, 2004, 53(1): 323–334
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 30500039), National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2003CB114201) and Basic Scientific Research Foundation for Chinese Central Academy (Biotechnology Research Institute, CAAS)
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Lang, Z., Zhang, J. et al. Ubi1 intron-mediated enhancement of the expression of Bt cry1Ah gene in transgenic maize (Zea mays L.). Chin. Sci. Bull. 53, 3185–3190 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-008-0379-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-008-0379-1