Abstract
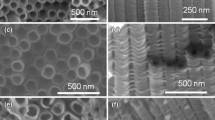
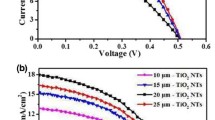
To substitute the non-regular nano-crystalline semiconductor for a novel kind of ordered microstructure is a very important aspect in the domain of dye-sensitized solar cell. One of the researching hotspots is the highly-ordered TiO2 nanotube architecture. As a new type of titania nano-material, titania nanotube arrays have drawn extraordinary attention due to its distinctive morphology, notable photoelectrical and hydro-sensitive performance. At 100% sun the new kind of TiO2 nanotube arrays solar cell exhibits an overall conversion efficiency of 5.44%. This paper introduces the preparation methods of titania nanotube arrays, the existing problems and recent progress in titania nanotube arrays solar cell.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Regan B O, Grätzel M. A low-cost, high-efficiency solar cell based on dye-sensitized colloidal TiO2 films. Nature, 1991, 353(4): 737–739
Grätzel M. Conversion of sunlight to electric power by nanocrystalline dye-sensitized solar cells. J Photochem Photobiol A: Chem, 2004, 164: 3–14
Yang S M, Li F Y, Huang C H. Dye sensitized nanocrystalline solar cells. Chemistry Online (in Chinese), 2002, (5): 292–296
Grätzel M. Dye-sensitized solar cells. J Photochem Photobiol C: Photochem Rev, 2003, 4: 145–153
Grätzel M. Photovoltaic performance and long-term stability of dye-sensitized meosocopic solar cells. C R Chimie, 2006, 9(5–6): 578–583
Grätzel M. The advent of mesoscopic injection solar cells. Prog Photovoltaics, 2006, 14(5): 429–442
Wang M, Yang L, and Zhou X W, et al. A new type quasi-solid state electrolyte for dye-sensitized solar cells. Chin Sci Bull, 2006, 51(13): 1551–1556
Zhang Z, Zhou B X, Ge W J, et al. Charge recombination in dye-sensitized nanoporous TiO2 solar cell. Chin Sci Bull, 2005, 50(21): 2408–2412
Gong D W, Grimes C A, Varghese O K, et al. Titanium oxide nanotube arrays prepared by anodic oxidation. J Mater Res, 2001, 16(12): 3331–3334
Varghese O K, Gong D W, Paulose M, et al. Extreme changes in the electrical resistance of titania nanotubes with hydrogen exposure. Adv Mater, 2003, 15(7–8): 624–627
Paulose M, Shankar K, Yoriya S, et al. Anodic growth of highly ordered TiO2 nanotube arrays to 134 μm in length. J Phys Chem B, 2006, 10(33): 16179–16184
Varghese O K, Paulose M, Shankar K, et al. Water-photolysis properties of micron-length highly-ordered titania nanotube-arrays. J Nanosci Nanotech, 2005, 5(7): 1158–1165
Quan X, Yang S G, Ruan X L, et al. Preparation of titania nanotubes and their environmental applications as electrode. Environ Sci & Technol, 2005, 39(10): 3770–3775
Xie Y B, Li X Z. Preparation and characterization of TiO2/Ti film electrodes by anodization at low voltage for photoelectrocatalytic application. J Appl Electrochem, 2006, 36(6): 663–668
Jiang F, Zheng S R, Zheng Z, et al. Photo-degradation of Acid-red 3B dye catalyzed by TiO2 nanotubes. J Environ Sci, 2006, 18(4): 783–787
Macak J M, Tsuchiya H, Ghicov A, et al. Dye-sensitized anodic TiO2 nanotubes. Electrochem Commun, 2005, 7(11): 1133–1137
Ohsaki Y, Masaki N, Kitamura T, et al. Dye-sensitized TiO2 nanotube solar cells: fabrication and electronic characterization. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2005, (7): 4157–4163
Mor G K, Karthik S, Maggie Paulose, et al. Use of highly-ordered TiO2 nanotube arrays in dye-sensitized solar cells. Nano Lett, 2006, 6(2): 215–218
Paulose M, Shankar K, Varghese O K, et al. Application of highly-ordered TiO2 nanotube-arrays in heterojunction dye-sensitized solar cells. J Phys D: Appl Phys, 2006, 39(12): 2498–2503
Mor G K, Varghese O K, Paulose M, et al. A review on highly ordered, vertically oriented TiO2 nanotube arrays: fabrication, material properties, and solar energy applications. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells, 2006, 90(14): 2011–2075
Paulose M, Shankar K, Varghese O K, et al. Backside illuminated dye-sensitized solar cells based on titania nanotube array electrodes. Nanotech, 2006, 17(5): 1446–1448
Wang H, Yip C T, Cheung K Y, et al. Titania-nanotube-array-based photovoltaic cells. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 89(2): 023508/1-023508/3
Zhu K, Neale N R, Miedaner A, et al. Enhanced charge-collection efficiencies and light scattering in dye-sensitized solar cells using oriented TiO2 nanotubes arrays. Nano Lett, 2007, 7(1): 69–74
Ma Y T, Lin Y, Xiao X R, et al. Synthesis of TiO2 nanotubes film and its light scattering property. Chin Sci Bull, 2005, 50(18): 1985–1990
Miyauchi M, Tokudome H, Toda Y, et al. Electron field emission from TiO2 nanotube arrays synthesized by hydrothermal reaction. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 89: 043114/1-043114/3
Cheng L F, Zhang X T, Liu B, et al. Template synthesis and characterization of WO3/TiO2 composite nanotubes. Nanotechnology, 2005, 16(8): 1341–1345
Lee S, Jeon C, Park Y. Fabrication of TiO2 tubules by template synthesis and hydrolysis with water vapor. Chem Mater, 2004, 16(22): 4292–4295
Lee J H, Leu I C, Hsu M C, et al. Fabrication of aligned TiO2 one-dimensional nanostructured arrays using a one-step templating solution approach. J Phys Chem B Lett, 2005, 109(27): 13056–13059
Jung J H, Kobayashi H, Kjeld J C, et al. Creation of novel helical ribbon and double-layered nanotube TiO2 structures. Chem Mater, 2002, 14(4): 1445–1447
Hoyer P. Formation of a titanium dioxide nanotube array. Langmuir, 1996, 12: 1411–1413
Wu S, Jiang Q Z, Ma Z F, et al. TiO2 nanotubes prepared by microwave method. Chin J Inorg Chem (in Chinese), 2006, 22(2): 341–345
Mor G K, Varghese O K, Paulose M, et al. Fabrication of tapered, conical-shaped titania nanotubes. J Mater Res, 2003, 18(11): 2588–2589
Jan M M, Saule A, Andrei G, et al. Smooth anodic TiO2 nanotubes: annealing and structure. Phys Stat Sol, 2006, 203(10): R67–R69
Macak J M, Tsuchiy H, Taveira L, et al. Smooth anodic TiO2 nanotubes. Angew Chem Int ed, 2005, 44(45): 7463–7465
Hiroaki T, Schmuki P. Self-organized high aspect ratio porous hafnium oxide prepared by electrochemical anodization. Electrochem Commun, 2005, 7(1): 49–52
Macak J M, Tsuchiya H, Schmuki P. High-aspect-ratio TiO2 nanotubes by anodization of titanium. Angew Chem Int ed, 2005, 44(14): 2100–2102
Lai Y K, Sun L, Zuo J, et al. Electrochemical fabrication and formation mechanism of TiO2 nanotube arrays on metallic titanium surface. Acta Phys-Chim Sin, 2004, 20(9): 1063–1066
Beranek R, Hildebrand H, Schmuki P. Self-organized porous titanium oxide prepared in H2SO4/HF electrolytes. Electrochem Solid-state Lett, 2003, 6(3): B12–B14
Tsuchiya H, Macak J M, Taveira L, et al. Self-organized TiO2 nanotubes prepared in ammonium fluoride containing acetic acid electrolytes. Electrochem Commun, 2005, 7(6): 576–580
Bauer S, Kleber S, Schmuki P. TiO2 nanotubes: tailoring the geometry in H3PO4/HF electrolytes. Electrochem Commun, 2006, 8(8): 1321–1325
Ghicov A, Tsuchiya H, Macak J M, et al. Titanium oxide nanotubes prepared in phosphate electrolytes. Electrochem Commun, 2005, 7(5): 505–509
Cai Q Y, Paulose M, Varghese O K, et al. The effect of electrolyte composition on the fabrication of self-organized titanium oxide nanotube arrays by anodic oxidation. J Mater Res, 2005, 20(1): 230–236
Zhao J L, Wang X H, Chen R Z, et al. Fabrication of titanium oxide nanotube arrays by anodic oxidation. Solid State Commun, 2005, 134(10): 705–710
Zheng Q, Zhou B X, Bai J, et al. Titanium oxide nanotube arrays and their applications. Progress in Chemistry (in Chinese), 2007, 19(1): 117–122
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 20677039), Shanghai Commission for Science and Technology (Grant No. 05nm05004), and the Program of New Century Excellent Talents in University (Grant No. NCET-04-0406)
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Zhou, B., Xiong, B. et al. TiO2 nanotube arrays and TiO2-nanotube-array based dye-sensitized solar cell. CHINESE SCI BULL 52, 1585–1589 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-007-0254-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-007-0254-5