Abstract
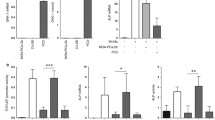
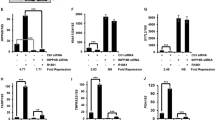
Most prostate cancers are insensitive to growth-inhibitory effect of TGF-β, while PI3K-PKB signaling is highly activated in prostate cancers. We investigated whether the PI3K-PKB signaling contributes to TGF-β insensitivity in PTEN-null prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Cell growth analysis showed that inhibition of PI3K-PKB pathway by LY294002 enhanced growth inhibition and cell cycle arrest induced by TGF-β. Furthermore, activation of PI3K-PKB pathway by insulin or overexpression of PKB decreased the transcriptional activity of TGF-β, as measured by the TGF-β/Smad3-responsive CAGA-luciferase reporter, while inhibition of PI3K-PKB pathway by introducing PTEN, inactive PKB mutant or using LY294002 promoted TGF-β-induced expression of CAGA-luciferase. Co-immunoprecipitation studies further demonstrated that Smad3 interacted with PKB through its linker region and MH2 domain. This interaction was facilitated by insulin and disrupted by TGF-β signaling activation. Our results suggest that the PI3K-PKB pathway may play an important role in rendering cell resistance to the antiproliferative effect of TGF-β and regulating cell response to TGF-β.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Massague J. TGFbeta signaling: Receptors, transducers, and Mad proteins. Cell, 1996, 85(7): 947–950
Siegel P M, Massague J. Cytostatic and apoptotic actions of TGF-beta in homeostasis and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer, 2003, 3(11): 807–821
Kreisberg J I, Malik S N, Prihoda T J, et al. Phosphorylation of Akt (Ser473) is an excellent predictor of poor clinical outcome in prostate cancer. Cancer Res, 2004, 64(15): 5232–5236
Bello-DeOcampo D, Tindall D J. TGF-betal/Smad signaling in prostate cancer. Curr Drug Targets, 2003, 4(3): 197–207
Chen R H, Su Y H, Chuang R L, et al. Suppression of transforming growth factor-beta-induced apoptosis through a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-dependent pathway. Oncogene, 1998, 17(15): 1959–1968
Song K, Cornelius S C, Reiss M, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-I inhibits transcriptional responses of transforming growth factor-beta by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-dependent suppression of the activation of Smad3 but not Smad2. J Biol Chem, 2003, 278(40): 38342–38351
Vlietstra R J, van Alewijk D C, Hermans K G, et al. Frequent inactivation of PTEN in prostate cancer cell lines and xenografts. Cancer Res, 1998, 58(13): 2720–2723
Remy I, Montmarquette A, Michnick S W. PKB/Akt modulates TGF-beta signalling through a direct interaction with Smad3. Nat Cell Biol, 2004, 6(4): 358–365
Conery A R, Cao Y, Thompson E A, et al. Akt interacts directly with Smad3 to regulate the sensitivity to TGF-beta induced apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol, 2004, 6(4): 366–372
Wu R Y, Zhang Y, Feng X H, et al. Heteromeric and homomeric interactions correlate with signaling activity and functional cooperativity of Smad3 and Smad4/DPC4. Mol Cell Biol, 1997, 17(5): 2521–2528
Coffer P J, Jin J, Woodgett J R. Protein kinase B (c-Akt): A multifunctional mediator of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation. Biochem J, 1998, 335(Pt 1): 1–13
Teicher B A. Malignant cells, directors of the malignant process: Role of transforming growth factor-beta. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 2001, 20(1–2): 133–143
van der Poel H G. Mammalian target of rapamycin and 3-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway inhibition enhances growth inhibition of transforming growth factor-betal in prostate cancer cells. J Urol, 2004, 172(4 Pt 1): 1333–1337
Dai C, Liu Y. Hepatocyte growth factor antagonizes the profibrotic action of TGF-betal in mesangial cells by stabilizing Smad transcriptional corepressor TGIF. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2004, 15(6): 1402–1412
Yang J, Dai C, Liu Y. Hepatocyte growth factor suppresses renal interstitial myofibroblast activation and intercepts Smad signal transduction. Am J Pathol 2003, 163(2): 621–632
Afrakhte M, Moren A, Jossan S, et al. Induction of inhibitory Smad6 and Smad7 mRNA by TGF-beta family members. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 1998, 249(2): 505–511
Derynck R, Zhang Y E. Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signalling. Nature, 2003, 425(6958): 577–584
van der Poel H G, Hanrahan C, Zhong H, et al. Rapamycin induces Smad activity in prostate cancer cell lines. Urol Res, 2003, 30(6): 380–386
Hjelmeland A B, Hjelmeland M D, Shi Q, et al. Loss of phosphatase and tensin homologue increases transforming growth factor {beta}-mediated invasion with enhanced SMAD3 transcriptional activity. Cancer Res, 2005, 65(24): 11276–11281
Song K, Wang H, Krebs T L, et al. Novel roles of Akt and mTOR in suppressing TGF-beta/ALK5-mediated Smad3 activation. Embo J, 2006, 25(1): 58–69
Kang H Y, Lin H K, Hu Y C, et al. From transforming growth factor-beta signaling to androgen action: Identification of Smad3 as an androgen receptor coregulator in prostate cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2001, 98(6): 3018–3023
Hayes S A, Zarnegar M, Sharma M, et al. SMAD3 represses androgen receptor-mediated transcription. Cancer Res, 2001, 61(5): 2112–2118
Chipuk J E, Cornelius S C, Pultz N J, et al. The androgen receptor represses transforming growth factor-beta signaling through interaction with Smad3. J Biol Chem, 2002, 277(2): 1240–1248
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Xin, D. & Guo, Y. PKB negatively modulates TGF-β responsiveness in prostate carcinoma PC-3 cells through its interaction with Smad3. CHINESE SCI BULL 51, 1563–1570 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-006-2016-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-006-2016-1