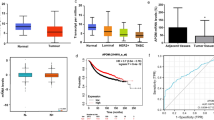
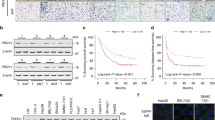
Abstract
Breast cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors with high mortality and poor prognosis in women. There is an urgent need to discover new therapeutic targets for breast cancer metastasis. Herein, we identified that Apolipoprotein C1 (APOC1) was up-regulated in primary tumor of breast cancer patient that recurrence and metastasis by immunohistochemistry (IHC). Kaplan-Meier Plotter database showed that high levels of APOC1 in breast cancer patients were strongly associated with worse overall survival (OS) and relapse-free survival (RFS). Mechanistically, APOC1 silencing significantly inhibits MAPK/ERK kinase pathway and restrains the NF-κB to decrease the transcription of target genes related to growth and metastasis in vitro. Based on this regulatory mechanism, we developed these findings into potential therapeutic drugs, glutathione (GSH) responsive nano-particles (NPs) were used for systemic APOC1 siRNA delivery, NPs (siAPOC1) silenced APOC1 expression, and subsequently resulted in positive anti-tumor effects in orthotopic and liver metastasis models in vivo. Taken together, GSH responsive NP-mediated siAPOC1 delivery was proved to be effective in regulating growth and metastasis in multiple tumor models. These findings show that APOC1 could be a potential biomarker to predict the prognosis of breast cancer patients and NP-mediated APOC1 silencing could be new strategies for exploration of new treatments for breast cancer metastasis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blache, U., Horton, E.R., Xia, T., Schoof, E.M., Blicher, L.H., Schönenberger, A., Snedeker, J.G., Martin, I., Erler, J.T., and Ehrbar, M. (2019). Mesenchymal stromal cell activation by breast cancer secretomes in bioengineered 3D microenvironments. Life Sci Alliance 2, e201900304.
Bomgaars, L., Geyer, J.R., Franklin, J., Dahl, G., Park, J., Winick, N.J., Klenke, R., Berg, S.L., and Blaney, S.M. (2004). Phase I trial of intrathecal liposomal cytarabine in children with neoplastic meningitis. J Clin Oncol 22, 3916–3921.
Bouillet, B., Gautier, T., Blache, D., Pais de Barros, J.P., Duvillard, L., Petit, J.M., Lagrost, L., and Vergès, B. (2014). Glycation of apolipoprotein C1 impairs its CETP inhibitory property: pathophysiological relevance in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 37, 1148–1156.
Bus, P., Pierneef, L., Bor, R., Wolterbeek, R., van Es, L.A., Rensen, P.C., de Heer, E., Havekes, L.M., Bruijn, J.A., Berbée, J.F., et al. (2017). Apolipoprotein C-I plays a role in the pathogenesis of glomerulosclerosis. J Pathol 241, 589–599.
Cai, Z., Wang, J., Li, Y., Shi, Q., Jin, L., Li, S., Zhu, M., Wang, Q., Wong, L.L., Yang, W., et al. (2023). Overexpressed Cyclin D1 and CDK4 proteins are responsible for the resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitor in breast cancer that can be reversed by PI3K/mTOR inhibitors. Sci China Life Sci 66, 94–109.
Cao, S., Saw, P.E., Shen, Q., Li, R., Liu, Y., and Xu, X. (2022). Reduction-responsive RNAi nanoplatform to reprogram tumor lipid metabolism and repolarize macrophage for combination pancreatic cancer therapy. Biomaterials 280, 121264.
Casagrande, N., Celegato, M., Borghese, C., Mongiat, M., Colombatti, A., and Aldinucci, D. (2014). Preclinical activity of the liposomal cisplatin lipoplatin in ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res 20, 5496–5506.
Chen, J., Yang, J., and Ding, J. (2022). Rational construction of polycystine-based nanoparticles for biomedical applications. J Mater Chem B 10, 7173–7182.
Cheng, R., Feng, F., Meng, F., Deng, C., Feijen, J., and Zhong, Z. (2011). Glutathione-responsive nano-vehicles as a promising platform for targeted intracellular drug and gene delivery. J Control Release 152, 2–12.
Cui, C., Xue, Y.N., Wu, M., Zhang, Y., Yu, P., Liu, L., Zhuo, R.X., and Huang, S.W. (2013). Cellular uptake, intracellular trafficking, and antitumor efficacy of doxorubicin-loaded reduction-sensitive micelles. Biomaterials 34, 3858–3869.
Din, F., Aman, W., Ullah, I., Qureshi, O.S., Mustapha, O., Shafique, S., and Zeb, A. (2017). Effective use of nanocarriers as drug delivery systems for the treatment of selected tumors. Int J Nanomed Volume 12, 7291–7309.
Eccles, S.A., and Welch, D.R. (2007). Metastasis: recent discoveries and novel treatment strategies. Lancet 369, 1742–1757.
Fares, J., Fares, M.Y., Khachfe, H.H., Salhab, H.A., and Fares, Y. (2020). Molecular principles of metastasis: a hallmark of cancer revisited. Sig Transduct Target Ther 5, 28.
Feng, X., Xu, W., Liu, J., Li, D., Li, G., Ding, J., and Chen, X. (2021). Polypeptide nanoformulation-induced immunogenic cell death and remission of immunosuppression for enhanced chemoimmunotherapy. Sci Bull 66, 362–373.
Feng, X., Xu, W., Xu, X., Li, G., Ding, J., and Chen, X. (2020). Cystine proportion regulates fate of polypeptide nanogel as nanocarrier for chemotherapeutics. Sci China Chem 64, 293–301.
Gaitanis, A., and Staal, S. (2010). Liposomal doxorubicin and nab-pacli-taxel: nanoparticle cancer chemotherapy in current clinical use. In: Grobmyer, S., and Moudgil, B., eds. Cancer Nanotechnology. Methods in Molecular Biology. New York: Humana Press. 385–392.
Ghoda, L., Lin, X., and Greene, W.C. (1997). The 90-kDa ribosomal S6 kinase (pp90rsk) phosphorylates the N-terminal regulatory domain of IκBα and stimulates its degradation in vitro. J Biol Chem 272, 21281–21288.
Guan, X. (2015). Cancer metastases: challenges and opportunities. Acta Pharm Sin B 5, 402–418.
Han, Y., Fan, M., Han, D., Ge, K., Chang, J., and Zhang, J. (2022). Bacteria-based nanosystems for enhanced antitumor therapy. Sci China Life Sci 65, 438–441.
Jiang, B., Jia, X., Ji, T., Zhou, M., He, J., Wang, K., Tian, J., Yan, X., and Fan, K. (2022). Ferritin nanocages for early theranostics of tumors via inflammation-enhanced active targeting. Sci China Life Sci 65, 328–340.
Jong, M.C., Hofker, M.H., and Havekes, L.M. (1999). Role of ApoCs in lipoprotein metabolism: functional differences between ApoC1, ApoC2, and ApoC3. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 19, 472–484.
Karin, M., and Delhase, M. (2000). The IκB kinase (IKK) and NF-κB: key elements of proinflammatory signalling. Semin Immunol 12, 85–98.
Ko, H.L., Wang, Y.S., Fong, W.L., Chi, M.S., Chi, K.H., and Kao, S.J. (2014). Apolipoprotein C1 (APOC1) as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for lung cancer: a marker phase I trial. Thorac Cancer 5, 500–508.
Kulkarni, J.A., Witzigmann, D., Chen, S., Cullis, P.R., and van der Meel, R. (2019). Lipid nanoparticle technology for clinical translation of siRNA therapeutics. Acc Chem Res 52, 2435–2444.
Lambert, A.W., Pattabiraman, D.R., and Weinberg, R.A. (2017). Emerging biological principles of metastasis. Cell 168, 670–691.
Leduc, V., Jasmin-Bélanger, S., and Poirier, J. (2010). APOE and cholesterol homeostasis in Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Mol Med 16, 469–477.
Leone, B.A., Romero, A., Rabinovich, M.G., Vallejo, C.T., Bianco, A., Perez, J.E., Machiavelli, M., Rodriguez, R., and Alvarez, L.A. (1988). Stage IV breast cancer: clinical course and survival of patients with osseous versus extraosseous metastases at initial diagnosis. Am J Clin Oncol 11, 618–622.
Li, Q., Qin, T., Bi, Z., Hong, H., Ding, L., Chen, J., Wu, W., Lin, X., Fu, W., Zheng, F., et al. (2020a). Rac1 activates non-oxidative pentose phosphate pathway to induce chemoresistance of breast cancer. Nat Commun 11, 1456.
Li, Y., Wu, L., Zeng, L., Zhang, Z., Wang, W., Zhang, C., and Lin, N. (2020b). ApoC1 promotes the metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma via activation of STAT3. Oncogene 39, 6203–6217.
Liu, B., Sun, L., Liu, Q., Gong, C., Yao, Y., Lv, X., Lin, L., Yao, H., Su, F., Li, D., et al. (2015). A cytoplasmic NF-κB interacting long noncoding RNA blocks IκB phosphorylation and suppresses breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Cell 27, 370–381.
Loibl, S., Poortmans, P., Morrow, M., Denkert, C., and Curigliano, G. (2021). Breast cancer. Lancet 397, 1750–1769.
McKay, G.J., Savage, D.A., Patterson, C.C., Lewis, G., McKnight, A.J., and Maxwell, A.P. (2013). Association analysis of dyslipidemia-related genes in diabetic nephropathy. PLoS ONE 8, e58472.
Mills, R.C. 3rd (2017). Breast cancer survivors, common markers of inflammation, and exercise: a narrative review. Breast Cancer 11, 117822341774397.
Mooyaart, A.L., Valk, E.J.J., van Es, L.A., Bruijn, J.A., de Heer, E., Freedman, B.I., Dekkers, O.M., and Baelde, H.J. (2011). Genetic associations in diabetic nephropathy: a meta-analysis. Diabetologia 54, 544–553.
Ren, H., Chen, Z., Yang, L., Xiong, W., Yang, H., Xu, K., Zhai, E., Ding, L., He, Y., and Song, X. (2019). Apolipoprotein C1 (APOC1) promotes tumor progression via MAPK signaling pathways in colorectal cancer. Cancer Manag Res Volume 11, 4917–4930.
Riggio, A.I., Varley, K.E., and Welm, A.L. (2021). The lingering mysteries of metastatic recurrence in breast cancer. Br J Cancer 124, 13–26.
Saw, P.E., and Song, E.W. (2020). siRNA therapeutics: a clinical reality. Sci China Life Sci 63, 485–500.
Setten, R.L., Rossi, J.J., and Han, S. (2019). The current state and future directions of RNAi-based therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 18, 421–446.
Shi, J., Kantoff, P.W., Wooster, R., and Farokhzad, O.C. (2017). Cancer nanomedicine: progress, challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer 17, 20–37.
Stagg, R.J., Venook, A.P., Chase, J.L., Lewis, B.J., Warren, R.S., Roh, M., Mulvihill, S.J., Grobman, B.J., Rayner, A.A., and Hohn, D.C. (1991). Alternating hepatic intra-arterial floxuridine and fluorouracil: a less toxic regimen for treatment of liver metastases from colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 83, 423–428.
Steeg, P.S. (2006). Tumor metastasis: mechanistic insights and clinical challenges. Nat Med 12, 895–904.
Sung, H., Ferlay, J., Siegel, R.L., Laversanne, M., Soerjomataram, I., Jemal, A., and Bray, F. (2021). Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71, 209–249.
Tong, S., Zhu, H., and Bao, G. (2019). Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for disease detection and therapy. Mater Today 31, 86–99.
Valastyan, S., and Weinberg, R.A. (2011). Tumor metastasis: molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell 147, 275–292.
Wang, J., Luo, B., Li, X., Lu, W., Yang, J., Hu, Y., Huang, P., and Wen, S. (2017). Inhibition of cancer growth in vitro and in vivo by a novel ROS-modulating agent with ability to eliminate stem-like cancer cells. Cell Death Dis 8, e2887.
Wei, L., Chen, J., and Ding, J. (2021). Sequentially stimuli-responsive anticancer nanomedicines. Nanomedicine 16, 261–264.
Wei, S., and Siegal, G.P. (2018). Surviving at a distant site: The organotropism of metastatic breast cancer. Semin Diagn Pathol 35, 108–111.
Whitehead, K.A., Langer, R., and Anderson, D.G. (2009). Knocking down barriers: advances in siRNA delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8, 129–138.
Xu, X., Wu, J., Liu, S., Saw, P.E., Tao, W., Li, Y., Krygsman, L., Yegnasubramanian, S., De Marzo, A.M., Shi, J., et al. (2018). Redox-responsive nanoparticle-mediated systemic RNAi for effective cancer therapy. Small 14, 1802565.
Xu, X., Wu, J., Liu, Y., Saw, P.E., Tao, W., Yu, M., Zope, H., Si, M., Victorious, A., Rasmussen, J., et al. (2017). Multifunctional envelope-type siRNA delivery nanoparticle platform for prostate cancer therapy. ACS Nano 11, 2618–2627.
Xu, X., Wu, J., Liu, Y., Yu, M., Zhao, L., Zhu, X., Bhasin, S., Li, Q., Ha, E., Shi, J., et al. (2016). Ultra-pH-responsive and tumor-penetrating nanoplatform for targeted siRNA delivery with robust anti-cancer efficacy. Angew Chem Int Ed 55, 7091–7094.
Yang, G., Liu, Y., Chen, J., Ding, J., and Chen, X. (2022a). Self-adaptive nanomaterials for rational drug delivery in cancer therapy. Acc Mater Res 3, 1232–1247.
Yang, J., Su, T., Zou, H., Yang, G., Ding, J., and Chen, X. (2022b). Spatiotemporally targeted polypeptide nanoantidotes improve chemotherapy tolerance of cisplatin. Angew Chem Int Ed 61, e202211136.
Yi, J., Ren, L., Wu, J., Li, W., Zheng, X., Du, G., and Wang, J. (2019). Apolipoprotein C1 (APOC1) as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for gastric cancer. Ann Transl Med 7, 380.
Yin, H., Kanasty, R.L., Eltoukhy, A.A., Vegas, A.J., Dorkin, J.R., and Anderson, D.G. (2014). Non-viral vectors for gene-based therapy. Nat Rev Genet 15, 541–555.
Younis, M.A., Tawfeek, H.M., Abdellatif, A.A.H., Abdel-Aleem, J.A., and Harashima, H. (2022). Clinical translation of nanomedicines: challenges, opportunities, and keys. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 181, 114083.
Zhang, C., and Zhang, B. (2023). RNA therapeutics: updates and future potential. Sci China Life Sci 66, 12–30.
Zhang, Z., Cheng, W., Pan, Y., and Jia, L. (2020). An anticancer agent-loaded PLGA nanomedicine with glutathione-response and targeted delivery for the treatment of lung cancer. J Mater Chem B 8, 655–665.
Zheng, P., Ding, B., Shi, R., Jiang, Z., Xu, W., Li, G., Ding, J., and Chen, X. (2021). A multichannel Ca2+ nanomodulator for multilevel mitochondrial destruction-mediated cancer therapy. Adv Mater 33, 2007426.
Zhou, Z., Liu, X., Zhu, D., Wang, Y., Zhang, Z., Zhou, X., Qiu, N., Chen, X., and Shen, Y. (2017). Nonviral cancer gene therapy: delivery cascade and vector nanoproperty integration. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 115, 115–154.
Zuckerman, J.E., and Davis, M.E. (2015). Clinical experiences with systemically administered siRNA-based therapeutics in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 14, 843–856.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81570764), Guangzhou Science and Technology Project (201807010069), Shenzhen Science and Technology Project (JCYJ20190807154205627), Guangdong Natural Science Fund (2020A1515010365), and Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Precision Medicine and Clinical Translation Research of Hakka Population (2018B030322003KF01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S., Zhang, F., Liang, Y. et al. Nanoparticle (NP)-mediated APOC1 silencing to inhibit MAPK/ERK and NF-κB pathway and suppress breast cancer growth and metastasis. Sci. China Life Sci. 66, 2451–2465 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2329-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2329-7