Abstract
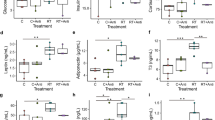
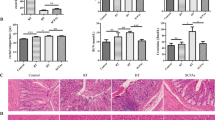
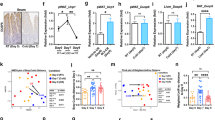
Heat stress induces multi-organ damage and serious physiological dysfunction in mammals, and gut bacteria may translocate to extra-intestinal tissues under heat stress pathology. However, whether gut bacteria translocate to the key metabolic organs and impair function as a result of heat stress remains unknown. Using a heat stress-induced mouse model, heat stress inhibited epididymal white adipose tissue (eWAT) expansion and induced lipid metabolic disorder but did not damage other organs, such as the heart, liver, spleen, or muscle. Microbial profiling analysis revealed that heat stress shifted the bacterial community in the cecum and eWAT but not in the inguinal white adipose tissue, blood, heart, liver, spleen, or muscle. Notably, gut-vascular barrier function was impaired, and the levels of some bacteria, particularly Lactobacillus, were higher in the eWAT, as confirmed by catalyzed reporter deposition fluorescence in situ hybridization (CARD-FISH) staining when mice were under heat stress. Moreover, integrated multi-omics analysis showed that the eWAT microbiota was associated with host lipid metabolism, and the expression of genes involved in the lipid metabolism in eWAT was upregulated under heat stress. A follow-up microbial supplementation study after introducing Lactobacillus plantarum to heat-stressed mice revealed that the probiotic ameliorated heat stress-induced loss of eWAT and dyslipidemia and reduced gut bacterial translocation to the eWAT by improving gut barrier function. Overall, our findings suggest that gut bacteria, particularly Lactobacillus spp., play a crucial role in heat stress-induced lipid metabolism disorder and that there is therapeutic potential for using probiotics, such as Lactobacillus plantarum.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article or its supporting information files.
References
Agus, A., Clément, K., and Sokol, H. (2021). Gut microbiota-derived metabolites as central regulators in metabolic disorders. Gut 70, 1174–1182.
Alexander, J.W., Gianotti, L., Pyles, T., Carey, M.A., and Babcock, G.F. (1991). Distribution and survival of Escherichia coli translocating from the intestine after thermal injury. Ann Surg 213, 558–567.
Amar, J., Lange, C., Payros, G., Garret, C., Chabo, C., Lantieri, O., Courtney, M., Marre, M., Charles, M.A., Balkau, B., et al. (2013). Blood microbiota dysbiosis is associated with the onset of cardiovascular events in a large general population: the D.E.S.I.R. study. PLoS ONE 8, e54461.
Amato, K.R., Yeoman, C.J., Kent, A., Righini, N., Carbonero, F., Estrada, A., Rex Gaskins, H., Stumpf, R.M., Yildirim, S., Torralba, M., et al. (2013). Habitat degradation impacts black howler monkey (Alouatta pigra) gastrointestinal microbiomes. ISME J 7, 1344–1353.
Anhê, F.F., Jensen, B.A.H., Varin, T.V., Servant, F., Van Blerk, S., Richard, D., Marceau, S., Surette, M., Biertho, L., Lelouvier, B., et al. (2020). Type 2 diabetes influences bacterial tissue compartmentalisation in human obesity. Nat Metab 2, 233–242.
Anhê, F.F., Nachbar, R.T., Varin, T.V., Trottier, J., Dudonné, S., Le Barz, M., Feutry, P., Pilon, G., Barbier, O., Desjardins, Y., et al. (2019). Treatment with camu camu (Myrciaria dubia) prevents obesity by altering the gut microbiota and increasing energy expenditure in diet-induced obese mice. Gut 68, 453–464.
Bertocchi, A., Carloni, S., Ravenda, P.S., Bertalot, G., Spadoni, I., Lo Cascio, A., Gandini, S., Lizier, M., Braga, D., Asnicar, F., et al. (2021). Gut vascular barrier impairment leads to intestinal bacteria dissemination and colorectal cancer metastasis to liver. Cancer Cell 39, 708–724.e11.
Bhaswant, M., Poudyal, H., and Brown, L. (2015). Mechanisms of enhanced insulin secretion and sensitivity with n-3 unsaturated fatty acids. J Nutral Biochem 26, 571–584.
Bishehsari, F., Voigt, R.M., and Keshavarzian, A. (2020). Circadian rhythms and the gut microbiota: from the metabolic syndrome to cancer. Nat Rev Endocrinol 16, 731–739.
Bokulich, N.A., Kaehler, B.D., Rideout, J.R., Dillon, M., Bolyen, E., Knight, R., Huttley, G.A., and Gregory Caporaso, J. (2018). Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME 2’s q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome 6, 90.
Bouchama, A., and Knochel, J.P. (2002). Heat stroke. N Engl J Med 346, 1978–1988.
Callahan, B.J., McMurdie, P.J., Rosen, M.J., Han, A.W., Johnson, A.J.A., and Holmes, S.P. (2016). DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods 13, 581–583.
Cani, P.D., Van Hul, M., Lefort, C., Depommier, C., Rastelli, M., and Everard, A. (2019). Microbial regulation of organismal energy homeostasis. Nat Metab 1, 34–46.
Cani, P.D. (2018). Human gut microbiome: hopes, threats and promises. Gut 67, 1716–1725.
Chen, C., Fang, S., Wei, H., He, M., Fu, H., Xiong, X., Zhou, Y., Wu, J., Gao, J., Yang, H., et al. (2021). Prevotella copri increases fat accumulation in pigs fed with formula diets. Microbiome 9, 175.
Chen, Y., Jiang, W., Liu, X., Du, Y., Liu, L., Ordovas, J.M., Lai, C.Q., and Shen, L. (2020a). Curcumin supplementation improves heat-stress-induced cardiac injury of mice: physiological and molecular mechanisms. J Nutr Biochem 78, 108331.
Chen, X., Li, P., Liu, M., Zheng, H., He, Y., Chen, M.X., Tang, W., Yue, X., Huang, Y., Zhuang, L., et al. (2020b). Gut dysbiosis induces the development of pre-eclampsia through bacterial translocation. Gut 69, 513–522.
Chen, F., Yin, Y., Chua, B.T., and Li, P. (2020c). CIDE family proteins control lipid homeostasis and the development of metabolic diseases. Traffic 21, 94–105.
Chouchani, E.T., and Kajimura, S. (2019). Metabolic adaptation and maladaptation in adipose tissue. Nat Metab 1, 189–200.
Crandall, C.G., and Wilson, T.E. (2015). Human cardiovascular responses to passive heat stress. Compr Physiol 5, 17–43.
Cui, J., Arbab-Zadeh, A., Prasad, A., Durand, S., Levine, B.D., and Crandall, C.G. (2005). Effects of heat stress on thermoregulatory responses in congestive heart failure patients. Circulation 112, 2286–2292.
Daims, H., Brühl, A., Amann, R., Schleifer, K.H., and Wagner, M. (1999). The domain-specific probe EUB338 is insufficient for the detection of all bacteria: development and evaluation of a more comprehensive probe set. Syst Appl Microbiol 22, 434–444.
Deprince, A., Haas, J.T., and Staels, B. (2020). Dysregulated lipid metabolism links NAFLD to cardiovascular disease. Mol Metab 42, 101092.
Ding, N., Zhang, X., Zhang, X.D., Jing, J., Liu, S.S., Mu, Y.P., Peng, L.L., Yan, Y.J., Xiao, G.M., Bi, X.Y., et al. (2020). Impairment of spermatogenesis and sperm motility by the high-fat diet-induced dysbiosis of gut microbes. Gut 69, 1608–1619.
Ding, S., Yan, W., Fang, J., Jiang, H., and Liu, G. (2021). Potential role of Lactobacillus plantarum in colitis induced by dextran sulfate sodium through altering gut microbiota and host metabolism in murine model. Sci China Life Sci 64, 1906–1916.
Ebi, K.L., Capon, A., Berry, P., Broderick, C., de Dear, R., Havenith, G., Honda, Y., Kovats, R.S., Ma, W., Malik, A., et al. (2021). Hot weather and heat extremes: health risks. Lancet 398, 698–708.
Gabler, N.K., Koltes, D., Schaumberger, S., Murugesan, G.R., and Reisinger, N. (2018). Diurnal heat stress reduces pig intestinal integrity and increases endotoxin translocation. Transl anim Sci 2, 1–10.
Galarraga, M., Campión, J., Muñoz-Barrutia, A., Boqué, N., Moreno, H., Martínez, J.A., Milagro, F., and Ortiz-de-Solórzano, C. (2012). Adiposoft: automated software for the analysis of white adipose tissue cellularity in histological sections. J Lipid Res 53, 2791–2796.
Geng, Y., Ma, Q., Liu, Y.N., Peng, N., Yuan, F.F., Li, X.G., Li, M., Wu, Y. S., Li, B., Song, W., et al. (2015). Heatstroke induces liver injury via IL-1β and HMGB1-induced pyroptosis. J Hepatol 63, 622–633.
Gomes, A.C., Hoffmann, C., and Mota, J.F. (2018). The human gut microbiota: metabolism and perspective in obesity. Gut Microbes 1–18.
Guimarães, K.S.L., Braga, V.A., Noronha, S.I.S.R., Costa, W.K.A., Makki, K., Cruz, J.C., Brandão, L.R., Chianca Junior, D.A., Meugnier, E., Leulier, F., et al. (2020). Lactiplantibacillus plantarum WJL administration during pregnancy and lactation improves lipid profile, insulin sensitivity and gut microbiota diversity in dyslipidemic dams and protects male offspring against cardiovascular dysfunction in later life. Food Funct 11, 8939–8950.
Ha, C.W.Y., Martin, A., Sepich-Poore, G.D., Shi, B., Wang, Y., Gouin, K., Humphrey, G., Sanders, K., Ratnayake, Y., Chan, K.S.L., et al. (2020). Translocation of viable gut microbiota to mesenteric adipose drives formation of creeping fat in humans. Cell 183, 666–683.e17.
Hall, D.M., Buettner, G.R., Oberley, L.W., Xu, L., Matthes, R.D., and Gisolfi, C.V. (2001). Mechanisms of circulatory and intestinal barrier dysfunction during whole body hyperthermia. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 280, H509–H521.
Han, Q., Wang, J., Li, W., Chen, Z.J., and Du, Y. (2021). Androgen-induced gut dysbiosis disrupts glucolipid metabolism and endocrinal functions in polycystic ovary syndrome. Microbiome 9, 101.
He, Z., Wu, J., Gong, J., Ke, J., Ding, T., Zhao, W., Cheng, W.M., Luo, Z., He, Q., Zeng, W., et al. (2021). Microbiota in mesenteric adipose tissue from Crohn’s disease promote colitis in mice. Microbiome 9, 228.
Huang, W., Ma, T., Liu, Y., Kwok, L. Y., Li, Y., Jin, H., Zhao, F., Shen, X., Shi, X., Sun, Z., et al. (2022). Spraying compound probiotics improves growth performance and immunity and modulates gut microbiota and blood metabolites of suckling piglets. Sci China Life Sci 66, 1092–1107.
Huber, J., Löffler, M., Bilban, M., Reimers, M., Kadl, A., Todoric, J., Zeyda, M., Geyeregger, R., Schreiner, M., Weichhart, T., et al. (2007). Prevention of high-fat diet-induced adipose tissue remodeling in obese diabetic mice by n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Int J Obes 31, 1004–1013.
Jensen, B.A., and Marette, A. (2020). Microbial translocation in type 2 diabetes: when bacterial invaders overcome host defence in human obesity. Gut 69, 1724–1726.
Kjellstrom, T., Briggs, D., Freyberg, C., Lemke, B., Otto, M., and Hyatt, O. (2016). Heat, human performance, and occupational health: a key issue for the assessment of global climate change impacts. Annu Rev Public Health 37, 97–112.
Knights, D., Kuczynski, J., Charlson, E.S., Zaneveld, J., Mozer, M.C., Collman, R.G., Bushman, F.D., Knight, R., and Kelley, S.T. (2011). Bayesian community-wide culture-independent microbial source tracking. Nat Methods 8, 761–763.
Koch, F., Thom, U., Albrecht, E., Weikard, R., Nolte, W., Kuhla, B., and Kuehn, C. (2019). Heat stress directly impairs gut integrity and recruits distinct immune cell populations into the bovine intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116, 10333–10338.
Kovats, R.S., and Hajat, S. (2008). Heat stress and public health: a critical review. Annu Rev Public Health 29, 41–55.
Lelouvier, B., Servant, F., Paíssé, S., Brunet, A., Benyahya, S., Serino, M., Valle, C., Ortiz, M.R., Puig, J., Courtney, M., et al. (2016). Changes in blood microbiota profiles associated with liver fibrosis in obese patients: a pilot analysis. Hepatology 64, 2015–2027.
Le Roy, T., Moens de Hase, E., Van Hul, M., Paquot, A., Pelicaen, R., Régnier, M., Depommier, C., Druart, C., Everard, A., Maiter, D., et al. (2022). Dysosmobacter welbionis is a newly isolated human commensal bacterium preventing diet-induced obesity and metabolic disorders in mice. Gut 71, 534–543.
Li, H., Liu, F., Lu, J., Shi, J., Guan, J., Yan, F., Li, B., and Huo, G. (2020). Probiotic mixture of Lactobacillus plantarum strains improves lipid metabolism and gut microbiota structure in high fat diet-fed mice. Front Microbiol 11, 512.
Li, Y., Ma, Z., Jiang, S., Hu, W., Li, T., Di, S., Wang, D., and Yang, Y. (2017). A global perspective on FOXO1 in lipid metabolism and lipid-related diseases. Prog Lipid Res 66, 42–49.
Liu, Y., Gao, Y., Ma, F., Sun, M., Mu, G., and Tuo, Y. (2020a). The ameliorative effect of Lactobacillus plantarum Y44 oral administration on inflammation and lipid metabolism in obese mice fed with a high fat diet. Food Funct 11, 5024–5039.
Liu, M., Zhang, L., Chu, X.H., Ma, R., Wang, Y.W., Liu, Q., Zhang, N.Y., Karrow, N.A., and Sun, L.H. (2020b). Effects of deoxynivalenol on the porcine growth performance and intestinal microbiota and potential remediation by a modified HSCAS binder. Food Chem Toxicol 141, 111373.
Liu, M., Zhang, L., Mo, Y., Li, J., Yang, J., Wang, J., Karrow, N.A., Wu, H., and Sun, L. (2023). Ferroptosis is involved in deoxynivalenol-induced intestinal damage in pigs. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 14, 29.
Lozupone, C.A., Hamady, M., Kelley, S.T., and Knight, R. (2007). Quantitative and qualitative β diversity measures lead to different insights into factors that structure microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 73, 1576–1585.
Ma, N., Guo, P., Chen, J., Qi, Z., Liu, C., Shen, J., Sun, Y., Chen, X., Chen, G.Q., and Ma, X. (2022). Poly-β-hydroxybutyrate alleviated diarrhea and colitis via Lactobacillus johnsonii biofilm-mediated maturation of sulfomucin. Sci China Life Sci 66, 1569–1588.
Machado, A., Almeida, C., Carvalho, A., Boyen, F., Haesebrouck, F., Rodrigues, L., Cerca, N., and Azevedo, N.F. (2013). Fluorescence in situ hybridization method using a peptide nucleic acid probe for identification of Lactobacillus spp. in milk samples. Int J Food Microbiol 162, 64–70.
Massier, L., Chakaroun, R., Tabei, S., Crane, A., Didt, K.D., Fallmann, J., von Bergen, M., Haange, S.B., Heyne, H., Stumvoll, M., et al. (2020). Adipose tissue derived bacteria are associated with inflammation in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Gut 69, 1796–1806.
McDonald, D., Price, M.N., Goodrich, J., Nawrocki, E.P., DeSantis, T.Z., Probst, A., Andersen, G.L., Knight, R., and Hugenholtz, P. (2012). An improved Greengenes taxonomy with explicit ranks for ecological and evolutionary analyses of bacteria and archaea. ISME J 6, 610–618.
Monnerat, G., Seara, F.A.C., Evaristo, J.A.M., Carneiro, G., Evaristo, G.P.C., Domont, G., Nascimento, J.H.M., Mill, J.G., Nogueira, F.C.S., and Campos de Carvalho, A.C. (2018). Aging-related compensated hypogonadism: role of metabolomic analysis in physiopathological and therapeutic evaluation. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 183, 39–50.
Mouries, J., Brescia, P., Silvestri, A., Spadoni, I., Sorribas, M., Wiest, R., Mileti, E., Galbiati, M., Invernizzi, P., Adorini, L., et al. (2019). Microbiota-driven gut vascular barrier disruption is a prerequisite for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis development. J Hepatol 71, 1216–1228.
Nejman, D., Livyatan, I., Fuks, G., Gavert, N., Zwang, Y., Geller, L.T., Rotter-Maskowitz, A., Weiser, R., Mallel, G., Gigi, E., et al. (2020). The human tumor microbiome is composed of tumor type-specific intracellular bacteria. Science 368, 973–980.
Odi, R., Invernizzi, R.W., Gallily, T., Bialer, M., and Perucca, E. (2021). Fenfluramine repurposing from weight loss to epilepsy: what we do and do not know. Pharmacol Ther 226, 107866.
Oh, D.Y., Talukdar, S., Bae, E.J., Imamura, T., Morinaga, H., Fan, W.Q., Li, P., Lu, W.J., Watkins, S.M., and Olefsky, J.M. (2010). GPR120 is an omega-3 fatty acid receptor mediating potent anti-inflammatory and insulin-sensitizing effects. Cell 142, 687–698.
Paíssé, S., Valle, C., Servant, F., Courtney, M., Burcelin, R., Amar, J., and Lelouvier, B. (2016). Comprehensive description of blood microbiome from healthy donors assessed by 16S targeted metagenomic sequencing. Transfusion 56, 1138–1147.
Pan, Z., Hu, Y., Huang, Z., Han, N., Li, Y., Zhuang, X., Yin, J., Peng, H., Gao, Q., Zhang, W., et al. (2022). Alterations in gut microbiota and metabolites associated with altitude-induced cardiac hypertrophy in rats during hypobaric hypoxia challenge. Sci China Life Sci 65, 2093–2113.
Patni, N., and Garg, A. (2015). Congenital generalized lipodystrophies— new insights into metabolic dysfunction. Nat Rev Endocrinol 11, 522–534.
Pearce, S.C., Lonergan, S.M., Huff-Lonergan, E., Baumgard, L.H., and Gabler, N.K. (2015). Acute heat stress and reduced nutrient intake alter intestinal proteomic profile and gene expression in pigs. PLoS ONE 10, e0143099.
Quan, L.H., Zhang, C., Dong, M., Jiang, J., Xu, H., Yan, C., Liu, X., Zhou, H., Zhang, H., Chen, L., et al. (2020). Myristoleic acid produced by enterococci reduces obesity through brown adipose tissue activation. Gut 69, 1239–1247.
Schindelin, J., Arganda-Carreras, I., Frise, E., Kaynig, V., Longair, M., Pietzsch, T., Preibisch, S., Rueden, C., Saalfeld, S., Schmid, B., et al. (2012). Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat Methods 9, 676–682.
Sorensen, C., and Garcia-Trabanino, R. (2019). A new era of climate medicine—addressing heat-triggered renal disease. N Engl J Med 381, 693–696.
Spadoni, I., Pietrelli, A., Pesole, G., and Rescigno, M. (2016). Gene expression profile of endothelial cells during perturbation of the gut vascular barrier. Gut Microbes 7, 540–548.
Spadoni, I., Zagato, E., Bertocchi, A., Paolinelli, R., Hot, E., Di Sabatino, A., Caprioli, F., Bottiglieri, L., Oldani, A., Viale, G., et al. (2015). A gut-vascular barrier controls the systemic dissemination of bacteria. Science 350, 830–834.
Sun, D., Bai, R., Zhou, W., Yao, Z., Liu, Y., Tang, S., Ge, X., Luo, L., Luo, C., Hu, G., et al. (2021). Angiogenin maintains gut microbe homeostasis by balancing α-Proteobacteria and Lachnospiraceae. Gut 70, 666–676.
Tang, W.H.W., Kitai, T., and Hazen, S.L. (2017). Gut microbiota in cardiovascular health and disease. Circ Res 120, 1183–1196.
Tanoue, T., Morita, S., Plichta, D.R., Skelly, A.N., Suda, W., Sugiura, Y., Narushima, S., Vlamakis, H., Motoo, I., Sugita, K., et al. (2019). A defined commensal consortium elicits CD8 T cells and anti-cancer immunity. Nature 565, 600–605.
Wang, J., Ji, H., Wang, S., Liu, H., Zhang, W., Zhang, D., and Wang, Y. (2018). Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum promotes intestinal barrier function by strengthening the epithelium and modulating gut microbiota. Front Microbiol 9, 1953.
Wang, X., Andersson, R., Soltesz, V., Guo, W., and Bengmark, S. (1993). Water-soluble ethylhydroxyethyl cellulose prevents bacterial translocation induced by major liver resection in the rat. Ann Surg 217, 155–167.
Wen, C., Li, S., Wang, J., Zhu, Y., Zong, X., Wang, Y., and Jin, M. (2021). Heat stress alters the intestinal microbiota and metabolomic profiles in mice. Front Microbiol 12, 706772.
Yamaguchi, T., Shimizu, K., Kokubu, Y., Nishijima, M., Takeda, S., Ogura, H., and Kawabata, K. (2019). Effect of heat stress on blood-brain barrier integrity in iPS cell-derived microvascular endothelial cell models. PLoS ONE 14, e0222113.
Yu, P., Wang, Y., Yang, W.T., Li, Z., Zhang, X.J., Zhou, L., and Gui, J.F. (2021). Upregulation of the PPAR signaling pathway and accumulation of lipids are related to the morphological and structural transformation of the dragon-eye goldfish eye. Sci China Life Sci 64, 1031–1049.
Yu, G., Xu, C., Zhang, D., Ju, F., and Ni, Y. (2022). MetOrigin: discriminating the origins of microbial metabolites for integrative analysis of the gut microbiome and metabolome. iMeta 1.
Zhai, Q., Feng, S., Arjan, N., and Chen, W. (2019). A next generation probiotic, Akkermansia muciniphila. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 59, 3227–3236.
Zhang, C., Zhao, X.H., Yang, L., Chen, X.Y., Jiang, R.S., Jin, S.H., and Geng, Z.Y. (2017). Resveratrol alleviates heat stress-induced impairment of intestinal morphology, microflora, and barrier integrity in broilers. Poultry Sci 96, 4325–4332.
Zhao, F., Whiting, S., Lambourne, S., Aitken, R.J., and Sun, Y. (2021a). Melatonin alleviates heat stress-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in human spermatozoa. Free Radic Biol Med 164, 410–416.
Zhao, L., Deng, J., Xu, Z.J., Zhang, W.P., Khalil, M.M., Karrow, N.A., and Sun, L.H. (2021b). Mitigation of aflatoxin B1 hepatoxicity by dietary Hedyotis diffusa is associated with activation of NRF2/ARE signaling in chicks. Antioxidants 10, 878.
Zhao, L., Liu, M., Sun, H., Yang, J.C., Huang, Y.X., Huang, J.Q., Lei, X., and Sun, L.H. (2023). Selenium deficiency-induced multiple tissue damage with dysregulation of immune and redox homeostasis in broiler chicks under heat stress. Sci China Life Sci doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2226-1.
Zheng, C., Chen, T., Lu, J., Wei, K., Tian, H., Liu, W., Xu, T., Wang, X., Wang, S., Yang, R., et al. (2021). Adjuvant treatment and molecular mechanism of probiotic compounds in patients with gastric cancer after gastrectomy. Food Funct 12, 6294–6308.
Zhuang, P., Li, H., Jia, W., Shou, Q., Zhu, Y., Mao, L., Wang, W., Wu, F., Chen, X., Wan, X., et al. (2021). Eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids attenuate hyperglycemia through the microbiome-gut-organs axis in db/db mice. Microbiome 9, 185.
Zou, J., Chassaing, B., Singh, V., Pellizzon, M., Ricci, M., Fythe, M.D., Kumar, M.V., and Gewirtz, A.T. (2018). Fiber-mediated nourishment of gut microbiota protects against diet-induced obesity by restoring IL-22-mediated colonic health. Cell Host Microbe 23, 41–53.e4.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Key Research and Development Program of China Project (2022YFD1300402), fundamental research funds for the Central Universities (2662022DKPY004, 2662023DKPY002), and the Top-Notch Young Talent Supporting Program (to LH Sun).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Compliance and ethics The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, ZC., Yang, JC., Huang, YX. et al. Translocation of gut microbes to epididymal white adipose tissue drives lipid metabolism disorder under heat stress. Sci. China Life Sci. 66, 2877–2895 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2320-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2320-y