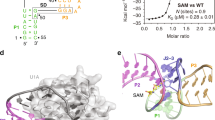
Abstract
Riboswitches are highly conserved RNA elements that located in the 5′-UTR of mRNAs, which undergo real-time structure conformational change to achieve the regulation of downstream gene expression by sensing their cognate ligands. S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) is a ubiquitous methyl donor for transmethylation reactions in all living organisms. SAM riboswitch is one of the most abundant riboswitches that bind to SAM with high affinity and selectivity, serving as regulatory modules in multiple metabolic pathways. To date, seven SAM-specific riboswitch classes that belong to four families, one SAM/SAH riboswitch and one SAH riboswitch have been identified. Each SAM riboswitch family has a well-organized tertiary core scaffold to support their unique ligand-specific binding pocket. In this review, we summarize the current research progress on the distribution, structure, ligand recognition and gene regulation mechanism of these SAM-related riboswitch families, and further discuss their evolutionary prospects and potential applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blount, K.F., and Breaker, R.R. (2006). Riboswitches as antibacterial drug targets. Nat Biotechnol 24, 1558–1564.
Boyapati, V.K., Huang, W., Spedale, J., and Aboul-Ela, F. (2012). Basis for ligand discrimination between ON and OFF state riboswitch conformations: the case of the SAM-I riboswitch. RNA 18, 1230–1243.
Breaker, R.R. (2022). The biochemical landscape of riboswitch ligands. Biochemistry 61, 137–149.
Breaker, R.R. (2012). Riboswitches and the RNA world. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives Biol 4, a003566.
Caron, M.P., Bastet, L., Lussier, A., Simoneau-Roy, M., Massé, E., and Lafontaine, D.A. (2012). Dual-acting riboswitch control of translation initiation and mRNA decay. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109, E3444–E3453.
Cheah, M.T., Wachter, A., Sudarsan, N., and Breaker, R.R. (2007). Control of alternative RNA splicing and gene expression by eukaryotic riboswitches. Nature 447, 497–500.
Chen, B., LeBlanc, R., and Dayie, T.K. (2016). SAM-II riboswitch samples at least two conformations in solution in the absence of ligand: implications for recognition. Angew Chem Int Ed 55, 2724–2727.
Chen, B., Zuo, X., Wang, Y.X., and Dayie, T.K. (2012). Multiple conformations of SAM-II riboswitch detected with SAXS and NMR spectroscopy. Nucleic Acids Res 40, 3117–3130.
Corbino, K.A., Barrick, J.E., Lim, J., Welz, R., Tucker, B.J., Puskarz, I., Mandal, M., Rudnick, N.D., and Breaker, R.R. (2005). Evidence for a second class of S-adenosylmethionine riboswitches and other regulatory RNA motifs in alpha-proteobacteria. Genome Biol 6, R70.
Dai, P., Wang, X., and Liu, M.F. (2020). A dual role of the PIWI/piRNA machinery in regulating mRNAs during mouse spermiogenesis. Sci China Life Sci 63, 447–449.
Deigan, K.E., and Ferré-D’Amaré, A.R. (2011). Riboswitches: discovery of drugs that target bacterial gene-regulatory RNAs. Acc Chem Res 44, 1329–1338.
Doshi, U., Kelley, J.M., and Hamelberg, D. (2011). Atomic-level insights into metabolite recognition and specificity of the SAM-II riboswitch. RNA 18, 300–307.
Edwards, A.L., Reyes, F.E., Héroux, A., and Batey, R.T. (2010). Structural basis for recognition of S-adenosylhomocysteine by riboswitches. RNA 16, 2144–2155.
Eschbach, S.H., St-Pierre, P., Penedo, J.C., and Lafontaine, D.A. (2012). Folding of the SAM-I riboswitch. RNA Biol 9, 535–541.
Fontecave, M., Atta, M., and Mulliez, E. (2004). S-adenosylmethionine: nothing goes to waste. Trends Biochem Sci 29, 243–249.
Fuchs, R.T., Grundy, F.J., and Henkin, T.M. (2006). The SMK box is a new SAM-binding RNA for translational regulation of SAM synthetase. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13, 226–233.
Gilbert, S.D., Rambo, R.P., Van Tyne, D., and Batey, R.T. (2008). Structure of the SAM-II riboswitch bound to S-adenosylmethionine. Nat Struct Mol Biol 15, 177–182.
Gong, C., Cheng, Z., Yang, Y., Shen, J., Zhu, Y., Ling, L., Lin, W., Yu, Z., Li, Z., Tan, W., et al. (2022). A 10-miRNA risk score-based prediction model for pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Sci China Life Sci, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2104-3.
Gong, S., Wang, Y., Wang, Z., Wang, Y., and Zhang, W. (2016). Reversible-switch mechanism of the SAM-III riboswitch. J Phys Chem B 120, 12305–12311.
Grundy, F.J., and Henkin, T.M. (1998). The S box regulon: a new global transcription termination control system for methionine and cysteine biosynthesis genes in gram-positive bacteria. Mol Microbiol 30, 737–749.
Haller, A., Rieder, U., Aigner, M., Blanchard, S.C., and Micura, R. (2011a). Conformational capture of the SAM-II riboswitch. Nat Chem Biol 7, 393–400.
Haller, A., Soulière, M.F., and Micura, R. (2011b). The dynamic nature of RNA as key to understanding riboswitch mechanisms. Acc Chem Res 44, 1339–1348.
Halliday, N.M., Hardie, K.R., Williams, P., Winzer, K., and Barrett, D.A. (2010). Quantitative liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry profiling of activated methyl cycle metabolites involved in LuxS-dependent quorum sensing in Escherichia coli. Anal Biochem 403, 20–29.
Hickey, S.F., and Hammond, M.C. (2014). Structure-guided design of fluorescent S-adenosylmethionine analogs for a high-throughput screen to target SAM-I riboswitch RNAs. Chem Biol 21, 345–356.
Hilbers, C.W., Michiels, P.J.A., and Heus, H.A. (1998). New developments in structure determination of pseudoknots. Biopolymers 48, 137–153.
Howe, J.A., Wang, H., Fischmann, T.O., Balibar, C.J., Xiao, L., Galgoci, A. M., Malinverni, J.C., Mayhood, T., Villafania, A., Nahvi, A., et al. (2015). Selective small-molecule inhibition of an RNA structural element. Nature 526, 672–677.
Huang, L., Liao, T.W., Wang, J., Ha, T., and Lilley, D.M.J. (2020). Crystal structure and ligand-induced folding of the SAM/SAH riboswitch. Nucleic Acids Res 46, 6869–6879.
Huang, L., and Lilley, D.M.J. (2018). Structure and ligand binding of the SAM-V riboswitch. Nucleic Acids Res 46, 6869–6879.
Huang, W., Kim, J., Jha, S., and Aboul-Ela, F. (2012). Conformational heterogeneity of the SAM-I riboswitch transcriptional ON state: a chaperone-like role for S-adenosyl methionine. J Mol Biol 418, 331–349.
Jiang, H., Gao, Y., Zhang, L., Chen, D., Gan, J., and Murchie, A.I.H. (2021). The identification and characterization of a selected SAM-dependent methyltransferase ribozyme that is present in natural sequences. Nat Catal 4, 872–881.
Kim, H., and Jaffrey, S.R. (2019). A fluorogenic RNA-based sensor activated by metabolite-induced RNA dimerization. Cell Chem Biol 26, 1725–1731.e6.
Klein, D.J., and Ferre-D’Amare, A.R. (2006). Structural basis of glmS ribozyme activation by glucosamine-6-phosphate. Science 313, 1752–1756.
Kozbial, P.Z., and Mushegian, A.R. (2005). Natural history of S-adenosylmethionine-binding proteins. BMC Struct Biol 5, 19.
Kusakabe, Y., Ishihara, M., Umeda, T., Kuroda, D., Nakanishi, M., Kitade, Y., Gouda, H., Nakamura, K.T., and Tanaka, N. (2015). Structural insights into the reaction mechanism of S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine hydrolase. Sci Rep 5, 16641.
Li, X., Zhang, J.L., Lei, Y.N., Liu, X.Q., Xue, W., Zhang, Y., Nan, F., Gao, X., Zhang, J., Wei, J., et al. (2021). Linking circular intronic RNA degradation and function in transcription by RNase H1. Sci China Life Sci 64, 1795–1809.
Lim, J., Winkler, W.C., Nakamura, S., Scott, V., and Breaker, R.R. (2006). Molecular-recognition characteristics of SAM-binding riboswitches. Angew Chem Int Ed 45, 964–968.
Lu, C., Ding, F., Chowdhury, A., Pradhan, V., Tomsic, J., Holmes, W.M., Henkin, T.M., and Ke, A. (2010). SAM recognition and conformational switching mechanism in the Bacillus subtilis yitJ S box/SAM-I riboswitch. J Mol Biol 404, 803–818.
Lu, C., Smith, A.M., Ding, F., Chowdhury, A., Henkin, T.M., and Ke, A. (2011). Variable sequences outside the SAM-binding core critically influence the conformational dynamics of the SAM-III/SMK box riboswitch. J Mol Biol 409, 786–799.
Lu, C., Smith, A.M., Fuchs, R.T., Ding, F., Rajashankar, K., Henkin, T.M., and Ke, A. (2008). Crystal structures of the SAM-III/SMK riboswitch reveal the SAM-dependent translation inhibition mechanism. Nat Struct Mol Biol 15, 1076–1083.
Manz, C., Kobitski, A.Y., Samanta, A., Jäschke, A., and Nienhaus, G.U. (2018). The multi-state energy landscape of the SAM-I riboswitch: a single-molecule Förster resonance energy transfer spectroscopy study. J Chem Phys 148, 123324.
Manz, C., Kobitski, A.Y., Samanta, A., Keller, B.G., Jäschke, A., and Nienhaus, G.U. (2017). Single-molecule FRET reveals the energy landscape of the full-length SAM-I riboswitch. Nat Chem Biol 13, 1172–1178.
Meyer, M.M., Ames, T.D., Smith, D.P., Weinberg, Z., Schwalbach, M.S., Giovannoni, S.J., and Breaker, R.R. (2009). Identification of candidate structured RNAs in the marine organism ‘Candidatus Pelagibacter ubique’. BMC Genomics 10, 268.
Mirihana Arachchilage, G., Sherlock, M.E., Weinberg, Z., and Breaker, R. R. (2018). SAM-VI RNAs selectively bind S-adenosylmethionine and exhibit similarities to SAM-III riboswitches. RNA Biol 15, 371–378.
Montange, R.K., and Batey, R.T. (2006). Structure of the S-adenosylmethionine riboswitch regulatory mRNA element. Nature 441, 1172–1175.
Montange, R.K., Mondragón, E., van Tyne, D., Garst, A.D., Ceres, P., and Batey, R.T. (2010). Discrimination between closely related cellular metabolites by the SAM-I riboswitch. J Mol Biol 396, 761–772.
Paige, J.S., Nguyen-Duc, T., Song, W., and Jaffrey, S.R. (2012). Fluorescence imaging of cellular metabolites with RNA. Science 335, 1194.
Parveen, N., and Cornell, K.A. (2011). Methylthioadenosine/S-adenosylhomocysteine nucleosidase, a critical enzyme for bacterial metabolism. Mol Microbiol 79, 7–20.
Penchovsky, R., Pavlova, N., and Kaloudas, D. (2021). RSwitch: a novel bioinformatics database on riboswitches as antibacterial drug targets. IEEE ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinf 18, 804–808.
Poiata, E., Meyer, M.M., Ames, T.D., and Breaker, R.R. (2009). A variant riboswitch aptamer class for S-adenosylmethionine common in marine bacteria. RNA 15, 2046–2056.
Price, I.R., Grigg, J.C., and Ke, A. (2014). Common themes and differences in SAM recognition among SAM riboswitches. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Gene Regulatory Mech 1839, 931–938.
Priyakumar, U.D. (2010). Atomistic details of the ligand discrimination mechanism of SMK/SAM-III Riboswitch. J Phys Chem B 114, 9920–9925.
Saw, P.E., and Song, E.W. (2020). siRNA therapeutics: a clinical reality. Sci China Life Sci 63, 485–500.
Saw, P.E., Xu, X., Chen, J., and Song, E.W. (2021). Non-coding RNAs: the new central dogma of cancer biology. Sci China Life Sci 64, 22–50.
Schroeder, K.T., Daldrop, P., and Lilley, D.M.J. (2011). RNA tertiary interactions in a riboswitch stabilize the structure of a kink turn. Structure 19, 1233–1240.
Serganov, A., and Nudler, E. (2013). A decade of riboswitches. Cell 152, 17–24.
Smith, A.M., Fuchs, R.T., Grundy, F.J., and Henkin, T.M. (2010). The SAM-responsive SMK box is a reversible riboswitch. Mol Microbiol 78, 1393–1402.
Stoddard, C.D., Montange, R.K., Hennelly, S.P., Rambo, R.P., Sanbonmatsu, K.Y., and Batey, R.T. (2010). Free state conformational sampling of the SAM-I riboswitch aptamer domain. Structure 18, 787–797.
Struck, A.W., Thompson, M.L., Wong, L.S., and Micklefield, J. (2012). S-adenosyl-methionine-dependent methyltransferases: highly versatile enzymes in biocatalysis, biosynthesis and other biotechnological applications. ChemBioChem 13, 2642–2655.
Sun, A., Gasser, C., Li, F., Chen, H., Mair, S., Krasheninina, O., Micura, R., and Ren, A. (2019). SAM-VI riboswitch structure and signature for ligand discrimination. Nat Commun 10, 5728.
Suresh, G., Srinivasan, H., Nanda, S., and Priyakumar, U.D. (2016). Ligand-induced stabilization of a duplex-like architecture is crucial for the switching mechanism of the SAM-III riboswitch. Biochemistry 55, 3349–3360.
Tang, D.J., Du, X., Shi, Q., Zhang, J.L., He, Y.P., Chen, Y.M., Ming, Z., Wang, D., Zhong, W.Y., Liang, Y.W., et al. (2020). A SAM-I riboswitch with the ability to sense and respond to uncharged initiator tRNA. Nat Commun 11, 2794.
Trausch, J.J., Xu, Z., Edwards, A.L., Reyes, F.E., Ross, P.E., Knight, R., and Batey, R.T. (2014). Structural basis for diversity in the SAM clan of riboswitches. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, 6624–6629.
Truong, J., Hsieh, Y.F., Truong, L., Jia, G., and Hammond, M.C. (2018). Designing fluorescent biosensors using circular permutations of riboswitches. Methods 143, 102–109.
Tucker, B.J., and Breaker, R.R. (2005). Riboswitches as versatile gene control elements. Curr Opin Struct Biol 15, 342–348.
Wachter, A. (2010). Riboswitch-mediated control of gene expression in eukaryotes. RNA Biol 7, 67–76.
Wachter, A., Tunc-Ozdemir, M., Grove, B.C., Green, P.J., Shintani, D.K., and Breaker, R.R. (2007). Riboswitch control of gene expression in plants by splicing and alternative 3′ end processing of mRNAs. Plant Cell 19, 3437–3450.
Wang, J.X., and Breaker, R.R. (2008). Riboswitches that sense S-adenosylmethionine and S-adenosylhomocysteine. Biochem Cell Biol 86, 157–168.
Wang, J.X., Lee, E.R., Morales, D.R., Lim, J., and Breaker, R.R. (2008). Riboswitches that sense S-adenosylhomocysteine and activate genes involved in coenzyme recycling. Mol Cell 29, 691–702.
Wei, P.P., Han, B.W., and Chen, Y.Q. (2013). Role of long non-coding RNAs in normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Sci China Life Sci 56, 867–875.
Weickhmann, A.K., Keller, H., Wurm, J.P., Strebitzer, E., Juen, M.A., Kremser, J., Weinberg, Z., Kreutz, C., Duchardt-Ferner, E., and Wöhnert, J. (2019). The structure of the SAM/SAH-binding riboswitch. Nucleic Acids Res 47, 2654–2665.
Weinberg, Z., Barrick, J.E., Yao, Z., Roth, A., Kim, J.N., Gore, J., Wang, J. X., Lee, E.R., Block, K.F., Sudarsan, N., et al. (2007). Identification of 22 candidate structured RNAs in bacteria using the CMfinder comparative genomics pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res 35, 4809–4819.
Weinberg, Z., Regulski, E.E., Hammond, M.C., Barrick, J.E., Yao, Z., Ruzzo, W.L., and Breaker, R.R. (2008). The aptamer core of SAM-IV riboswitches mimics the ligand-binding site of SAM-I riboswitches. RNA 14, 822–828.
Weinberg, Z., Wang, J.X., Bogue, J., Yang, J., Corbino, K., Moy, R.H., and Breaker, R.R. (2010). Comparative genomics reveals 104 candidate structured RNAs from bacteria, archaea, and their metagenomes. Genome Biol 11, R31.
Winkler, W.C., Nahvi, A., Roth, A., Collins, J.A., and Breaker, R.R. (2004). Control of gene expression by a natural metabolite-responsive ribozyme. Nature 428, 281–286.
Winkler, W.C., Nahvi, A., Sudarsan, N., Barrick, J.E., and Breaker, R.R. (2003). An mRNA structure that controls gene expression by binding S-adenosylmethionine. Nat Struct Mol Biol 10, 701–707.
Xu, B., Zhu, Y., Cao, C., Chen, H., Jin, Q., Li, G., Ma, J., Yang, S.L., Zhao, J., Zhu, J., et al. (2022). Recent advances in RNA structurome. Sci China Life Sci 65, 1285–1324.
Xue, X., Yongjun, W., and Zhihong, L. (2015). Folding of SAM-II riboswitch explored by replica-exchange molecular dynamics simulation. J Theor Biol 365, 265–269.
Xue, Y., Chen, R., Qu, L., and Cao, X. (2020). Noncoding RNA: from dark matter to bright star. Sci China Life Sci 63, 463–468.
Yang, J., Li, J., Wang, J., Sheng, G., Wang, M., Zhao, H., Yang, Y., and Wang, Y. (2020). Crystal structure of Cas1 in complex with branched DNA. Sci China Life Sci 63, 516–528.
Yao, Z., Barrick, J., Weinberg, Z., Neph, S., Breaker, R., Tompa, M., and Ruzzo, W.L. (2007). A computational pipeline for high-throughput discovery of cis-regulatory noncoding RNA in prokaryotes. PLoS Comput Biol 3, e126.
Zhang, K., Li, S., Kappel, K., Pintilie, G., Su, Z., Mou, T.C., Schmid, M.F., Das, R., and Chiu, W. (2019). Cryo-EM structure of a 40 kDa SAM-IV riboswitch RNA at 3.7 Å resolution. Nat Commun 10, 5511.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32022039, 31870810, 91940302, 91640104), the National Key Research and Development Project of China (2021YFC2300300), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2022M713637), the Outstanding Youth Fund of Zhejiang Province (LR19C050003), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2017QN81010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Compliance and ethics
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, L., Song, Q., Xu, X. et al. Structure-based insights into recognition and regulation of SAM-sensing riboswitches. Sci. China Life Sci. 66, 31–50 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2188-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2188-7