Abstract
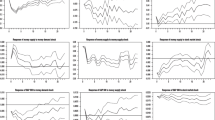
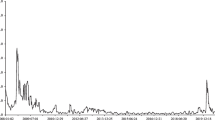
This paper examines the impact of anticipated and unanticipated interest rate changes on aggregate and sectoral stock returns in the United Kingdom. The monetary policy shock is generated from the change in the 3-month sterling LIBOR futures contract. Results from time-series and panel analysis indicate an important structural break in the relationship between stock returns and monetary policy shifts. Specifically, whereas before the credit crunch, the stock market response to both expected and unexpected interest rate changes is negative and significant; the relationship becomes positive during the credit crisis. The latter finding highlights the inability, so far, of monetary policymakers to reverse, via interest rate cuts, the negative trend observed in stock prices since the onset of the credit crisis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arellano, M., Bond, S.: Some tests of specification for panel data: Monte Carlo evidence and an application to employment equations. Rev. Econ. Studies 58, 277–297 (1991)
Bentzen, E., Hansen, P., Lunde, A., Zebedee, A.: The Greenspan years: an analysis of the magnitude and speed of the equity market response to FOMC announcements. Finan. Mark. Portf. Manag. 22, 3–20 (2008)
Bernanke, B., Kuttner, K.: What explains the stock market’s reaction to Federal Reserve policy? J. Finance 60, 1221–1257 (2005)
Bredin, D., Hyde, S., Nitzsche, D., O’Reilly, G.: UK stock returns and the impact of domestic monetary policy shocks. J. Bus. Finan. Account. 34, 872–888 (2007)
Campbell, J.Y., Lo, A., MacKinlay, C.: The Econometrics of Financial Markets. Princeton University Press, Princeton (1997)
Hildebrand, P.: Monetary policy and financial markets. Finan. Mark. Portf. Manag. 20, 7–18 (2006)
Konrad, E.: The impact of monetary policy surprises on asset return volatility: the case of Germany. Finan. Mark. Portf. Manag. 23, 111–135 (2009)
Kuttner, K.: Monetary policy surprises and interest rates: evidence from the Fed Funds Futures Market. J. Mon. Econ. 47, 523–544 (2001)
Lildholdt, P., Wetherilt, A.: Anticipation of monetary policy in UK financial markets. Bank of England Working Paper 241 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gregoriou, A., Kontonikas, A., MacDonald, R. et al. Monetary policy shocks and stock returns: evidence from the British market. Financ Mark Portf Manag 23, 401–410 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11408-009-0113-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11408-009-0113-2