Abstract
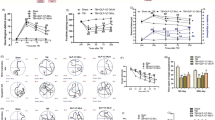
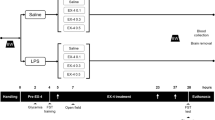
Mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) represents a major and increasing public health concern and is both the most frequent cause of mortality and disability in young adults and a chief cause of morbidity in the elderly. Albeit mTBI patients do not show clear structural brain defects and, generally, do not require hospitalization, they frequently suffer from long-lasting cognitive, behavioral, and emotional problems. No effective pharmaceutical therapy is available, and existing treatment chiefly involves intensive care management after injury. The diffuse neural cell death evident after mTBI is considered mediated by oxidative stress and glutamate-induced excitotoxicity. Prior studies of the long-acting GLP-1 receptor agonist, exendin-4 (Ex-4), an incretin mimetic approved for type 2 diabetes mellitus treatment, demonstrated its neurotrophic/protective activity in cellular and animal models of stroke, Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases, and, consequent to commonalities in mechanisms underpinning these disorders, Ex-4 was assessed in a mouse mTBI model. In neuronal cultures in this study, Ex-4 ameliorated H2O2-induced oxidative stress and glutamate toxicity. To evaluate in vivo translation, we administered steady-state Ex-4 (3.5 pM/kg/min) or saline to control and mTBI mice over 7 days starting 48 h prior to or 1 h post-sham or mTBI (30 g weight drop under anesthesia). Ex-4 proved well-tolerated and fully ameliorated mTBI-induced deficits in novel object recognition 7 and 30 days post-trauma. Less mTBI-induced impairment was evident in Y-maze, elevated plus maze, and passive avoidance paradigms, but when impairment was apparent Ex-4 induced amelioration. Together, these results suggest that Ex-4 may act as a neurotrophic/neuroprotective drug to minimize mTBI impairment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcalay RN, Giladi E, Pick CG, Gozes I (2004) Intranasal administration of NAP, a neuroprotective peptide, decreases anxiety-like behavior in aging mice in the elevated plus maze. Neurosci Lett 361:128–131
Arundine M, Aarts M, Lau A, Tymianski M (2004) Vulnerability of central neurons to secondary insults after in vitro mechanical stretch. J Neurosci 24:8106–8123
Arundine M, Tymianski M (2004) Molecular mechanisms of glutamate-dependent neurodegeneration in ischemia and traumatic brain injury. Cell Mol Life Sci 61:657–668
Banks WA, During MJ, Niehoff ML (2004) Brain uptake of the glucagon-like peptide-1 antagonist exendin(9-39) after intranasal administration. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 309:469–475
Baratz R, Rubovitch V, Frenk H, Pick CG (2010a) The influence of alcohol on behavioral recovery after mTBI in mice. J Neurotrauma 27:555–563
Baratz R, Tweedie D, Rubovitch V, Luo W, Yoon JS, Hoffer BJ, Greig NH, Pick CG (2010b) Tumor necrosis factor-α synthesis inhibitor, 3,6′-dithiothalidomide, reverses behavioral impairments induced by minimal traumatic brain injury in mice. J Neurochem 118:1032–1042
Barnett AH (2012) The role of GLP-1 mimetics and basal insulin analogues in type 2 diabetes mellitus: guidance from studies of liraglutide. Diabetes Obes Metab 14:304–314
Bauer R, Fritz H (2004) Pathophysiology of traumatic injury in the developing brain: an introduction and short update. Exp Toxicol Pathol 56:65–73
Belzung C, Griebel G (2001) Measuring normal and pathological anxiety-like behaviour in mice: a review. Behav Brain Res 125:141–149
Berrigan L, Marshall S, McCullagh S, Velikonja D, Bayley M (2011) Quality of clinical practice guidelines for persons who have sustained mild traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj 25:742–751
Bertilsson G, Patrone C, Zachrisson O, Andersson A, Dannaeus K, Heidrich J, Kortesmaa J, Mercer A, Nielsen E, Rönnholm H, Wikström L (2008) Peptide hormone exendin-4 stimulates subventricular zone neurogenesis in the adult rodent brain and induces recovery in an animal model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci Res 86:326–338
Bomfim TR, Forny-Germano L, Sathler LB, Brito-Moreira J, Houzel JC, Decker H, Silverman MA, Kazi H, Melo HM, McClean PL, Holscher C, Arnold SE, Talbot K, Klein WL, Munoz DP, Ferreira ST, De Felice FG (2012) An anti-diabetes agent protects the mouse brain from defective insulin signaling caused by Alzheimer’s disease-associated Aβ oligomers. J Clin Invest 122:1339–1353
Bramlett HM, Green E, Dietrich WD (1997) Hippocampally dependent and independent chronic spatial navigational deficits following parasagittal fluid percussion brain injury in the rat. Brain Res 762:195–202
Calara F, Taylor K, Han J, Zabala E, Carr EM, Wintle M, Fineman M (2005) A randomized, open-label, crossover study examining the effect of injection site on bioavailability of exenatide (synthetic Exendin-4). Clin Ther 27:210–215
Chaudhuri A, Ghanim H, Vora M, Sia CL, Korzeniewski K, Dhindsa S, Makdissi A, Dandona P (2012) Exenatide exerts a potent antiinflammatory effect. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97:198–207
Dix SL, Aggleton JP (1999) Extending the spontaneous preference test of recognition: evidence of object-location and object-context recognition. Behav Brain Res 99:191–200
Dixon C, Kochanek P, Yan H, Schiding J, Griffith R, Baum E, Marion D, DeKosky ST (1999) One-year study of spatial memory performance, brain morphology, and cholinergic markers after moderate controlled cortical impact in rats. J Neurotrauma 16:109–122
Drucker DJ, Buse JB, Taylor K, Kendall DM, Trautmann M, Zhuang D, Porter L, and for the DURATION-1 Study Group (2008) Exenatide once weekly versus twice daily for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: a randomised, open-label, non-inferiority study. Lancet 372:1240–1250
During MJ, Cao L, Zuzga DS, Francis JS, Fitzsimons HL, Jiao X, Bland RJ, Klugmann M, Banks WA, Drucker DJ, Haile CN (2003) Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor is involved in learning and neuroprotection. Nat Med 9:1173–1179
Erreger K, Davis AR, Poe AM, Greig NH, Stanwood GD, Galli A (2012) Exendin-4 decreases amphetamine-induced locomotor activity. Physiol Behav 106:574–578
Faden AI, Demediuk P, Panter SS, Vink R (1989) The role of excitatory amino acids and NMDA receptors in traumatic brain injury. Science 244:798–800
Faul M, Xu L, Wald MM, Coronado VG (2010) Traumatic brain injury in the United States: emergency department visits, hospitalizations and deaths 2002–2006. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, Atlanta
Fleminger S, Oliver D, Lovestone S, Rabe-Hesketh S, Giora A (2003) Head injury as a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease: the evidence 10 years on; a partial replication. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:857–862
Foda MA, Marmarou A (1994) A new model of diffuse brain injury in rats. Part II: morphological characterization. J Neurosurg 80:301–313
Frankola KA, Greig NH, Luo W, Tweedie D (2011) Targeting TNF-α to elucidate and ameliorate neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 10:391–403
Gallwitz B (2011) Glucagon-like peptide-1 analogues for type 2 diabetes mellitus: current and emerging agents. Drugs 71:1675–1688
Garber AJ (2011) Long-acting glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists: a review of their efficacy and tolerability. Diabetes Care 34(Suppl 2):S279–S284
Garner J, Brett SJ (2007) Mechanisms of injury by explosive devices. Anesthesiol Clin 25:147–160
Grant P, Lipscomb D, Quin J (2011) Psychological and quality of life changes in patients using GLP-1 analogues. J Diabetes Complications 25:244–246
Hamilton A, Hölscher C (2009) Receptors for the incretin glucagon-like peptide-1 are expressed on neurons in the central nervous system. Neuroreport 20:1161–1166
Harkavyi A, Abuirmeileh A, Lever R, Kingsbury A, Biggs C et al (2008) Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor stimulation reverses key deficits in distinct rodent models of Parkinson’s disease. J Neuroinflammation 5:19
Hellewell SC, Yan E, Bye N, Agyapomaa D, Morganti-Kossmann C (2010) Post traumatic hypoxia exacerbates brain tissue damage: analysis of axonal injury and glial responses. J Neurotrauma 27:1997–2010
Hesdorffer DC, Rauch SL, Tamminga CA (2009) Long-term psychiatric outcomes following traumatic brain injury: a review of the literature. J Head Trauma Rehabil 24:452–459
Hinzman JM, Thomas TC, Burmeister JJ, Quintero JE, Huettl P, Pomerleau F, Gerhardt GA, Lifshitz J (2010) Diffuse brain injury elevates tonic glutamate levels and potassium-evoked glutamate release in discrete brain regions at two days post-injury: an enzyme-based microelectrode array study. J Neurotrauma 27:889–899
Hinzman JM, Thomas TC, Quintero JE, Gerhardt GA, Lifshitz J (2012) Disruptions in the regulation of extracellular glutamate by neurons and glia in the rat striatum two days after diffuse brain injury. J Neurotrauma 29:1197–1208
Hoare SR (2005) Mechanisms of peptide and nonpeptide ligand binding to class B G-protein-coupled receptors. Drug Discov Today 10:417–427
Holscher C (2010) Incretin analogues that have been developed to treat type 2 diabetes hold promise as a novel treatment strategy for Alzheimer’s disease. Recent Pat CNS Drug Discov 5:109–117
Hossmann KA (1994) Glutamate-mediated injury in focal cerebral ischemia: the excitotoxin hypothesis revised. Brain Pathol 4:23–36
Howard PK, Shapiro SE (2011) Diagnosing and treating mild traumatic brain injury in children. Adv Emerg Nurs J 33:274–278
Hunter K, Holscher C (2012) Drugs developed to treat diabetes, liraglutide and lixisenatide, cross the blood brain barrier and enhance neurogenesis. BMC Neurosci 13:33
Hyder AA, Wunderlich CA, Puvanachandra P, Gururaj G, Kobusingye OC (2007) The impact of traumatic brain injuries: a global perspective. NeuroRehabilitation 22:341–353
Ikonomovic M, Uryu K, Abrahamson E, Ciallella J, Trojanowski J, Lee V, Clark R, Marion D, Wisniewski S, DeKosky S (2004) Alzheimer’s pathology in human temporal cortex surgically excised after severe brain injury. Exp Neurol 190:192–203
Kastin AJ, Akerstrom V, Pan W (2002) Interactions of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) with the blood–brain barrier. J Mol Neurosci 18:7–14
Kastin AJ, Akerstrom V (2003) Entry of exendin-4 into brain is rapid but may be limited at high doses. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 27:313–318
Lafon-Cazal M, Pietri S, Culcasi M et al (1993) NMDA-dependent superoxide production and neurotoxicity. Nature 364:535–537
Lau A, Tymianski M (2010) Glutamate receptors, neurotoxicity and neurodegeneration. Pflugers Arch 460:525–542
Laurer HL, Lezlinger PM, Mclintoch TK (2000) Models of traumatic brain injury. Eur J Trauma 26:95–100
Levin HS (1998) Cognitive function outcomes after traumatic brain injury. Curr Opin Neurol 11:643–646
Li Y, Chigurupati S, Holloway HW, Mughal M, Tweedie D, Bruestle DA, Mattson MP, Wang Y, Harvey BK, Ray B, Lahiri DK, Greig NH (2012) Exendin-4 ameliorates motor neuron degeneration in cellular and animal models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PLoS One 7(2):e32008
Li Y, Duffy KB, Ottinger MA, Ray B, Bailey JA, Holloway HW, Tweedie D, Perry T, Mattson MP, Kapogiannis D, Sambamurti K, Lahiri DK, Greig NH (2010a) GLP-1 receptor stimulation reduces amyloid-beta peptide accumulation and cytotoxicity in cellular and animal models of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 19:1205–1219
Li Y, Perry T, Kindy MS, Harvey BK, Tweedie D, Holloway HW, Powers K, Shen H, Egan JM, Sambamurti K, Brossi A, Lahiri DK, Mattson MP, Hoffer BJ, Wang Y, Greig NH (2009) GLP-1 receptor stimulation preserves primary cortical and dopaminergic neurons in cellular and rodent models of stroke and Parkinsonism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:1285–1290
Li Y, Tweedie D, Mattson MP, Holloway HW, Greig NH (2010b) Enhancing the GLP-1 receptor signaling pathway leads to proliferation and neuroprotection in human neuroblastoma cells. J Neurochem 113:1621–1631
Lovshin JA, Drucker DJ (2009) Incretin-based therapies for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol 5:262–269
Lyeth BG, Jenkins L, Hamm J, Dixon C, Phillips L, Clifton G, Young H, Hayes R (1990) Prolonged memory impairment in the absence of hippocampal cell death following traumatic brain injury in the rat. Brain Res 526:249–258
McIntosh TK, Juhler M, Wieloch T (1998) Novel pharmacologic strategies in the treatment of experimental traumatic brain injury: 1998. J Neurotrauma 15:731–769
Magnoni S, Brody DL (2010) New perspectives on amyloid-β dynamics after acute brain injury. Arch Neurol 67:1068–1073
Marklund N, Hillered L (2011) Animal modeling of traumatic brain injury in preclinical drug development: where do we go from here? Br J Pharmacol 164:1207–1229
Marmarou A, Foda MA, van den Brink W, Campbell J, Kita H, Demetriadou K (1994) A new model of diffuse brain injury in rats. Part I: pathophysiology and biomechanics. J Neurosurg 80:291–300
Marshall S, Bayley M, McCullagh S, Velikonja D, Berrigan L (2012) Clinical practice guidelines for mild traumatic brain injury and persistent symptoms. Can Fam Physician 58:257–267
Maas AI, Steyerberg EW, Butcher I, Dammers R, Lu J, Marmarou A, Mushkudiani NA, McHugh GS, Murray GD (2007) Prognostic value of computerized tomography scan characteristics in traumatic brain injury: results from the IMPACT study. J Neurotrauma 24:303–314
Maas AI, Stocchetti N, Bullock R (2008) Moderate and severe traumatic brain injury in adults. Lancet Neurol 7:728–741
Messier C (1997) Object recognition in mice: improvement of memory by glucose. Neurobiol Learn Mem 67:172–175
Milman A, Rosenberg A, Weizman R, Pick CG (2005) Mild traumatic brain injury induces persistent cognitive deficits and behavioral disturbances in mice. J Neurotrauma 22:1003–1010
Moppett IK (2007) Traumatic brain injury: assessment, resuscitation and early management. Br J Anaesth 99:18–31
Oddy M, Humphrey M (1980) Social recovery during the year following severe head injury. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 43:798–802
Oddy M, Humphrey M, Uttley D (1978) Subjective impairment and social recovery after closed head injury. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 41:611–616
Oddy M, Coughlan T, Tyerman A, Jenkins D (1985) Social adjustment after closed head injury: a further follow-up seven years after injury. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 48:564–568
Pawaskar M, Li Q, Reynolds MW (2012) Metabolic outcomes of elderly patient populations initiating exenatide BID versus insulin glargine in an ambulatory care setting. Curr Med Res Opin 28:991–997
Perry T, Greig NH (2003) The glucagon-like peptides: a double-edged therapeutic sword? Trends Pharmacol Sci 24:377–383
Perry T, Haughey NJ, Mattson MP, Egan JM, Greig NH (2002) Protection and reversal of excitotoxic neuronal damage by glucagon-like peptide-1 and exendin-4. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 302:881–888
Perry T, Lahiri DK, Sambamurti K, Chen D, Mattson MP, Egan JM, Greig NH (2003) Glucagon-like peptide-1 decreases endogenous amyloid-beta peptide (Abeta) levels and protects hippocampal neurons from death induced by Abeta and iron. J Neurosci Res 72:603–612
Porter D, Faivre E, Flatt PR, Hölscher C, Gault VA (2012) Actions of incretin metabolites on locomotor activity, cognitive function and in vivo hippocampal synaptic plasticity in high fat fed mice. Peptides 35:1–8
Raghupathi R, Graham DI, McIntosh TK (2000) Apoptosis after traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 17:927–938
Reynolds IJ, Hastings TG (1995) Glutamate induces the production of reactive oxygen species in cultured forebrain neurons following NMDA receptor activation. J Neurosci 15:3318–27
Salcedo I, Tweedie D, Li Y, Greig NH (2012) Neuroprotective and neurotrophic actions of glucagon-like peptide-1: an emerging opportunity to treat neurodegenerative and cerebrovascular disorders. Br J Pharmacol 166:1586–1599
Sambamurti K, Greig NH, Lahiri DK (2002) Advances in the cellular and molecular biology of the beta-amyloid protein in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuromolecular Med 1:1–31
Schultz BA, Cifu DX, McNamee S, Nichols M, Carne W (2011) Assessment and treatment of common persistent sequelae following blast induced mild traumatic brain injury. NeuroRehabilitation 28:309–320
Sharma S, Rakoczy S, Brown-Borg H (2010) Assessment of spatial memory in mice. Life Sci 87:521–536
Shohami E, Beit-Yannai E, Horowitz M, Kohen R (1997) Oxidative stress in closed-head injury: brain antioxidant capacity as an indicator of functional outcome. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 17:1007–1019
Siesjo BK, Zhao Q, Pahlmark K, Siesjo P, Katsura K, Fol-bergrova J (1995) Glutamate, calcium and free radicals as mediators of ischemic brain damage. Ann Thorac Surg 59:1316–1320
Sivanandam TM, Thakur MK (2012) Traumatic brain injury: a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 36:1376–1381
Strawn JR, D’Alessio DA, Keck PE, Seeley RJ Jr (2008) Failure of glucagon-like peptide-1 to induce panic attacks or anxiety in patients with panic disorder. J Psychiatr Res 42:787–789
Susman M, DiRusso SM, Sullivan T, Risucci D, Nealon P, Cuff S, Haider A, Benzil D (2002) Traumatic brain injury in the elderly: increased mortality and worse functional outcome at discharge despite lower injury severity. J Trauma 53:219–223
Tagliaferri F, Compagnone C, Korsic M, Servadei F, Kraus J (2006) Systematic review of brain injury epidemiology in Europe. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 148:255–268
Tashlykov V, Katz Y, Volkov A, Gazit V, Schreiber S, Zohar O, Pick CG (2009) Minimal traumatic brain injury induce apoptotic cell death in mice. J Mol Neurosci 37:16–24
Tweedie D, Milman A, Holloway HW, Li Y, Harvey BK, Shen H, Pistell PJ, Lahiri DK, Hoffer BJ, Wang Y, Pick CG, Greig NH (2007) Apoptotic and behavioral sequelae of mild brain trauma in mice. J Neurosci Res 85:805–815
Uryu K, Chen X, Martinez D, Browne K, Johnson V, Graham D, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Smith DH (2007) Multiple proteins implicated in neurodegenerative disease accumulate in axons after brain trauma in humans. Exp Neurol 208:185–192
Zhang L, Rzigalinski BA, Ellis EF, Satin LS (1996) Reduction of voltage-dependent Mg2+ blockade of NMDA current in mechanically injured neurons. Science 274:1921–1923
Zipp F, Aktas O (2006) The brain as a target of inflammation: common pathways link inflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Neurosci 29:518–527
Zitnay GA (2005) Lessons from national and international TBI societies and funds like NBIRTT. Acta Neurochir Suppl 93:131–133
Zohar O, Rubovitch V, Milman A, Schreiber S, Pick CG (2011) Behavioral consequences of minimal traumatic brain injury in mice. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 71:36–45
Acknowledgments
This research was supported in part by the Intramural Research Program of both the National Institute on Aging, National Institutes of Health, and the Sackler School of Medicine, Tel-Aviv University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Nigel H. Greig, Chaim G. Pick, and Barry J. Hoffer contributed equally to this work as senior authors.
About this article
Cite this article
Rachmany, L., Tweedie, D., Li, Y. et al. Exendin-4 induced glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor activation reverses behavioral impairments of mild traumatic brain injury in mice. AGE 35, 1621–1636 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-012-9464-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-012-9464-0