Abstract
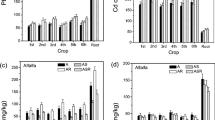
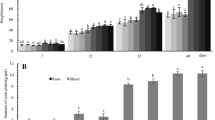
Corn steep liquor-assisted microbial remediation has been proposed as a promising strategy to remediate cadmium (Cd)-contaminated soil. In this study, we determined Bacillus subtilis (K2) with a high cadmium (Cd) accumulation ability and Cd resistance. However, studies on this strategy used in the Cd uptake of Chinese cabbage are lacking, and the effect of the combined incorporation of corn steep liquor and K2 on the functions and microbial interactions of soil microbiomes is unclear. Here, we study the Cd uptake and transportation in Chinese cabbage by the combination of K2 and corn steep liquor (K2 + C7) in a Cd-contaminated soil and corresponding microbial regulation mechanisms. Results showed that compared to inoculant K2 treatment alone, a reduction of Cd concentration in the shoots by 14.4% and the dry weight biomass of the shoots and the roots in Chinese cabbage increased by 21.6% and 30.8%, respectively, under K2 + C7 treatment. Meanwhile, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels were decreased by enhancing POD and SOD activity, thereby reversing Cd-induced oxidative damage. Importantly, inoculation of K2 would decrease the diversity of the microbial community while enhancing the abundance of dominant species. These findings provide a promising strategy for reducing the Cd accumulation in Chinese cabbage and recovering soil ecological functions.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its Supplementary Information files, or available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Bader BR, Taban SK, Fahmi AH, Abood MA, Hamdi GJ (2021) Potassium availability in soil amended with organic matter and phosphorous fertiliser under water stress during maize (Zea mays L) growth. J Saudi Soc Agric Sci 20:390–394
Canellas LP, Olivares F, Agriculture B (2014) Physiological responses to humic substances as plant growth promoter. Chem Biol Technol Agric 1:1–11
Chen Y, Ma J, Li Y, Weng L (2019) Enhanced cadmium immobilization in saturated media by gradual stabilization of goethite in the presence of humic acid with increasing pH. Sci Total Environ 648:358–366
Chen C, Lan Y, Mi R, Xu M, Liu Y, Wu J, Zhang Y, Long L, Yang GJC (2023) Effects of intercropping ryegrass with hollyhock and inoculation with Bacillus thuringiensis on enhancing phytoremediation of Cd-contaminated soils. Chemosphere 311:136974
Coles CA, Yong RN (2006) Humic acid preparation, properties and interactions with metals lead and cadmium. Eng Geol 85:26–32
Colla G, Rouphael Y, Canaguier R, Svecova E, Cardarelli M (2014) Biostimulant action of a plant-derived protein hydrolysate produced through enzymatic hydrolysis. Front Plant Sci 5:448
Dominguez-Solis JR, Lopez-Martin MC, Ager FJ, Ynsa MD, Romero LC, Gotor C (2004) Increased cysteine availability is essential for cadmium tolerance and accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Biotechnol J 2:469–476
Etesami H (2018) Bacterial mediated alleviation of heavy metal stress and decreased accumulation of metals in plant tissues: mechanisms and future prospects. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:175–191
Fang H, Li W, Tu S, Ding Y, Wang R, Rensing C, Li Y, Feng R (2019) Differences in cadmium absorption by 71 leaf vegetable varieties from different families and genera and their health risk assessment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 184:109593
Feng X, Wang Q, Sun Y, Zhang S, Wang F (2022) Microplastics change soil properties, heavy metal availability and bacterial community in a Pb-Zn-contaminated soil. J Hazard 424:127364
Fitzpatrick TB, Chapman LM (2020) The importance of thiamine (vitamin B1) in plant health: from crop yield to biofortification. J Biol Chem 295:12002–12013
Gauvry E, Mathot A-G, Couvert O, Leguérinel I, Coroller L (2021) Effects of temperature, pH and water activity on the growth and the sporulation abilities of Bacillus subtilis BSB1. Int J Food Microbiol 337:108915
Guo J, Qin S, Rengel Z, Gao W, Nie Z, Liu H, Li C, Zhao PJE (2019) Cadmium stress increases antioxidant enzyme activities and decreases endogenous hormone concentrations more in Cd-tolerant than Cd-sensitive wheat varieties. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 172:380–387
Haghighi M, Kafi M, Fang P, Gui-Xiao LJ, Research OP (2010) Humic Acid Decreased Hazardous of Cadmium Toxicity on Lettuce (L.). J Fruit Ornam Plant Res 72:49–61
Haghighi M, Saadat S, Abbey L (2020) Effect of exogenous amino acids application on growth and nutritional value of cabbage under drought stress. Sci Hortic 272:109561
Halim M, Conte P, Piccolo A (2003) Potential availability of heavy metals to phytoextraction from contaminated soils induced by exogenous humic substances. Chemosphere 52:265–275
Han H, Wang X, Yao L, Chen ZJE, Botany E (2020) Lettuce-derived rhizosphere polyamine-producing bacteria and their potential to reduce Cd and Pb accumulation in lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). Environ Exp Bot 178:104161
Han H, Wu X, Hui R, Xia X, Chen Z, Yao L, Yang J (2022) Synergistic effects of Cd-loving Bacillus sp. N3 and iron oxides on immobilizing Cd and reducing wheat uptake of Cd. Environ Pollut 305:119303
Hashem A, Tabassum B, Abd_Allah EF (2019) Bacillus subtilis: a plant-growth promoting rhizobacterium that also impacts biotic stress. Saudi J Biol Sci 26:1291–1297
Hofer A, Hauer S, Kroll P, Fricke J, Herwig C (2018) In-depth characterization of the raw material corn steep liquor and its bioavailability in bioprocesses of Penicillium chrysogenum. Process Biochem 70:20–28
Huang L, Wang Q, Zhou Q, Ma L, Wu Y, Liu Q, Wang S, Feng Y (2020) Cadmium uptake from soil and transport by leafy vegetables: a meta-analysis. Environ Pollut 264:114677
Hussain A, Ali S, Rizwan M, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Yasmeen T, Hayat MT, Hussain I, Ali Q, Hussain SM (2019) Morphological and physiological responses of plants to cadmium toxicity, cadmium toxicity and tolerance in plants, Academic Press, pp 47–72
Irfan M, Dawar K, Fahad S, Mehmood I, Alamri S, Siddiqui MH, Saud S, Khattak JZK, Ali S, Hassan S, Nawaz T, Hammad HM, Banout J, Nasim W (2022) Exploring the potential effect of Achnatherum splendens L.–derived biochar treated with phosphoric acid on bioavailability of cadmium and wheat growth in contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:37676–37684
Jézéquel K, Lebeau T (2008) Soil bioaugmentation by free and immobilized bacteria to reduce potentially phytoavailable cadmium. Bioresour Technol 99:690–698
Ji L, Tian C, Kuramae E (2023) Phosphorus-mediated succession of microbial nitrogen, carbon, and sulfur functions in rice driven saline-alkali soil remediation. Soil Biol Biochem 184:109125
Ke T, Guo G, Liu J, Zhang C, Tao Y, Wang P, Xu Y, Chen L (2021) Improvement of the Cu and Cd phytostabilization efficiency of perennial ryegrass through the inoculation of three metal-resistant PGPR strains. Environ Pollut 271:116314
Khan MI, Afzal MJ, Bashir S, Naveed M, Anum S, Cheema SA, Wakeel A, Sanaullah M, Ali MH, Chen ZJA (2021) Improving nutrient uptake, growth, yield and protein content in chickpea by the co-addition of phosphorus fertilizers, organic manures, and bacillus sp. MN-54. Agron 11:436
Kim S, Lee D, Lim D, Lim S, Park S, Kang C, Yu J, Lee TJAR (2020) Paramylon production from heterotrophic cultivation of Euglena gracilis in two different industrial byproducts: corn steep liquor and brewer’s spent grain. Algal Res 47:101826
Kragelund C, Kong Y, Van der Waarde J, Thelen K, Eikelboom D, Tandoi V, Thomsen TR, Nielsen PHJM (2006) Ecophysiology of different filamentous Alphaproteobacteria in industrial wastewater treatment plants. Microbiol 152:3003–3012
Le PT, Pontarotti P, Raoult DJ (2014): Alphaproteobacteria species as a source and target of lateral sequence transfers. Trends Microbiol 22:147–156
Li Q, Xing Y, Huang B, Chen X, Ji L, Fu X, Li T, Wang J, Chen G, Zhang QJ (2022) Rhizospheric mechanisms of Bacillus subtilis bioaugmentation-assisted phytostabilization of cadmium contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 825:154136
Liu J, Wang Y, Liu X, Xu J (2021) Occurrence and health risks of heavy metals in plastic-shed soils and vegetables across China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 321:107632
Liu Z, Li S, Liu N, Huang G, Zhou Q (2022) Soil microbial community driven by soil moisture and nitrogen in milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.)–rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) intercropping. Agric 12:1538
Ma H, Wei M, Wang Z, Hou S, Li X, Xu HJ (2020) Bioremediation of cadmium polluted soil using a novel cadmium immobilizing plant growth promotion strain Bacillus sp. TZ5 loaded on biochar. J Hazard Mater 388:122065
Marc Y, Baert L, Buss da Silva N, Postollec F, Huchet V, Baranyi J, Ellouze M (2021) The effect of pH on the growth rate of Bacillus cereus sensu lato: quantifying strain variability and modelling the combined effects of temperature and pH. Int J Food Microbiol 360:109420
Márquez MC, Sánchez-Porro C, Ventosa AJE-fSB (2011) Halophilic and haloalkaliphilic, aerobic endosporeforming bacteria in soil. Endospore-forming Soil Bact 309–339
McCauley A, Jones C, Jacobsen J (2009) Soil pH and organic matter. Nutr Manag module 8:1–12
Nazli F, Wang X, Ahmad M, Hussain A, Bushra, Dar A, Nasim M, Jamil M, Panpluem N (2021) Efficacy of indole acetic acid and exopolysaccharides-producing Bacillus safensis strain FN13 for inducing Cd-stress tolerance and plant growth promotion in Brassica juncea (L.). Appl Sci 11:4160
Ng CWW, Yan WH, Tsim KWK, San So P, Xia YT (2022) Effects of Bacillus subtilis and Pseudomonas fluorescens as the soil amendment. Heliyon 11:11674
Panosyan H, Hakobyan A, Birkeland N-K, Trchounian A, microbiology a (2018) Bacilli community of saline–alkaline soils from the Ararat Plain (Armenia) assessed by molecular and culture-based methods. Syst Appl Microbiol 41:232–240
Podosokorskaya OA, Kochetkova TV, Novikov AA, Toshchakov SV, Elcheninov AG, Kublanov IV, Microbiology A (2020) Tenuifilum thalassicum gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel moderate thermophilic anaerobic bacterium from a Kunashir Island shallow hot spring representing a new family Tenuifilaceae fam. nov. in the class Bacteroidia. Syst Appl Microbiol 43:126126
Qi WY, Chen H, Wang Z, Xing SF, Song C, Yan Z, Wang SG (2023) Biochar-immobilized Bacillus megaterium enhances Cd immobilization in soil and promotes Brassica chinensis growth. J Hazard Mater 458:131921
Rahi AA, Younis U, Ahmed N, Ali MA, Fahad S, Sultan H, Zarei T, Danish S, Taban S, El Enshasy HA, Tamunaidu P, Alotaibi JM, Alharbi SA, Datta R (2022) Toxicity of cadmium and nickel in the context of applied activated carbon biochar for improvement in soil fertility. Saudi J Biol Sci 29:743–750
Rizvi A, Ahmed B, Zaidi A, Khan M (2019) Heavy metal mediated phytotoxic impact on winter wheat: oxidative stress and microbial management of toxicity by Bacillus subtilis BM2. RSC Adv 9:6125-6142
Romano I, Ventorino V, Pepe O (2020) Effectiveness of plant beneficial microbes: overview of the methodological approaches for the assessment of root colonization and persistence. Front Plant Sci 11:6
Sanga TR, Mwakalapa EB, Kalugendo K, Ponraj M, Maseka K (2023) Effects of cadmium uptake on growth and productivity of Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa subsp. pekinensis) and pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata Duchesne) vegetables. J Agric Food Chem 14:100744
Teixeira WF, Fagan EB, Soares LH, Umburanas RC, Reichardt K, Neto DD (2017) Foliar and seed application of amino acids affects the antioxidant metabolism of the soybean crop. Front Plant Sci 8:327
Vecino X, Moldes A, Martínez-Arcos A, Cid-Pérez B, López-Prieto A, Cruz J (2023) Biosurfactants produced from corn steep liquor and other nonconventional sources: their application in different industries, Biosurfactants. Elsevier, pp. 129–153
Wang G, Zhang Q, Du W, Ai F, Yin Y, Ji R, Guo H (2021) Microbial communities in the rhizosphere of different willow genotypes affect phytoremediation potential in Cd contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 769:145224
Wu Z, Wang F, Liu S, Du Y, Li F, Du R, Wen D, Zhao J (2016) Comparative responses to silicon and selenium in relation to cadmium uptake, compartmentation in roots, and xylem transport in flowering Chinese cabbage ( Brassica campestris L. ssp. chinensis var. utilis ) under cadmium stress. Environ Exp Bot 131:173–180
Wu Z, Zhao X, Sun X, Tan Q, Tang Y, Nie Z, Qu C, Chen Z, Hu CJC (2015) Antioxidant enzyme systems and the ascorbate glutathione cycle as contributing factors to cadmium accumulation and tolerance in two oilseed rape cultivars (Brassica napus L.) under moderate cadmium stress. Chemosphere 138:526–536
Xiao Z, Zou D, Zeng X, Zhang L, Liu F, Wang A, Zeng Q, Zhang G, Li L (2020) Cadmium accumulation in oilseed rape is promoted by intercropping with faba bean and ryegrass. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 205:111162
Xue W, Zhang X, Zhang C, Wang C, Huang Y, Liu ZJC (2023) Mitigating the toxicity of reactive oxygen species induced by cadmium via restoring citrate valve and improving the stability of enzyme structure in rice. 327:138511
Yang J, Guo H, Ma Y, Wang L, Wei D, Hua LJ (2010) Genotypic variations in the accumulation of Cd exhibited by different vegetables. J Environ Sci (China) 22:1246–1252
Yi S, Wu P, Bai F, Zhou D, Peng X, Zhang W, Guo WJW (2020) Environmental filtering drives plant community assembly processes in the riparian marsh of downstream Yellow River. China 40:287–298
Yu J-K, Moon Y-SJP (2021) Corn starch: quality and quantity improvement for industrial uses. Plants 11:92
Yu X, Zhao J, Ding Z, Xiong F, Liu X, Tian J, Wu N (2023) Cadmium-absorptive Bacillus vietnamensis 151–6 reduces the grain cadmium accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.): Potential for cadmium bioremediation. Ecotoxicol. Environ Saf 254:114760
Zafar-ul-Hye M, Naeem M, Danish S, Fahad S, Datta R, Abbas M, Rahi AA, Brtnicky M, Holátko J, Tarar ZH, Nasir M (2020) Alleviation of cadmium adverse effects by improving nutrients uptake in bitter gourd through cadmium tolerant rhizobacteria. Environments 7(8):54
Zhang L, Hu Y, Chen Y, Qi D, Cai B, Zhao Y, Li Z, Wang Y, Nie Z, Xie J (2023) Cadmium-tolerant Bacillus cereus 2–7 alleviates the phytotoxicity of cadmium exposure in banana plantlets. Sci Total Environ 903:166645
Zhao K, Yang Y, Peng H, Zhang L, Zhou Y, Zhang J, Du C, Liu J, Lin X, Wang N (2022) Silicon fertilizers, humic acid and their impact on physicochemical properties, availability and distribution of heavy metals in soil and soil aggregates. Total Environ 822:153483
Zheng X, Yang S, Chen L, Kimotho RN, Chen M, Chen J, Zhang J, Li XJP, Soil (2021) A newly-isolated Cd-loving Purpureocillium sp. strain YZ1 substantially alleviates Cd toxicity to wheat. 464:289–302
Zhou D, Huang X-F, Chaparro JM, Badri DV, Manter DK, Vivanco JM, Guo J (2015) Root and bacterial secretions regulate the interaction between plants and PGPR leading to distinct plant growth promotion effects. Plant Soil 401:259–272
Zhou Z, Ming Q, An Y, Ruan D, Chen G, Wei H, Wang M, Wu ZJ (2021) Performance and microbial community analysis of anaerobic sludge digestion enhanced by in-situ microaeration. J Water Process 42:102171
Zhu Z, Huang Y, Wu X, Liu Z, Zou J, Chen Y, Su N, Cui JJE, Safety E (2019) Increased antioxidative capacity and decreased cadmium uptake contribute to hemin-induced alleviation of cadmium toxicity in Chinese cabbage seedlings. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 177:47-57
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the support provided by ShiFang Anda Chemicals CO., LTD.
Funding
Author Qing Chen has received research support from the China Agriculture Research System of Ministry of Finance (MOF) and Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs (MARA) (CARS-23-B15) and the Chinese Universities Scientific Fund (Grant No. 2021TC117).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Qing Chen, Yutao Peng, Longcheng Li, and Chensi Wang. Data curation: Longcheng Li, Chensi Wang, and Wenhao Wang. Formal analysis: Longcheng Li, Chensi Wang, Wenhao Wang, Lin Zhou, and Donghan Zhang. Funding acquisition: Qing Chen. Investigation: Hongjie Liao, Zihao Wang, and Bingcheng Li. Supervision: Qing Chen and Yangping Xu. Writing including review and editing: Longcheng Li and Chensi Wang. Writing of the original draft: Longcheng Li, Chensi Wang, and Yutao Peng.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Highlights
Inoculant K2 B. subtilis increased the abundance of dominant microbial communities.
Reduced the Cd accumulation in the edible parts of cabbage.
Corn steep liquor-based K2 B. subtilis inhibited Cd translocation.
K2 B. subtilis reversed Cd peroxidation damage by triggering antioxidant defense.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Wang, C., Wang, W. et al. Uncovering the mechanisms of how corn steep liquor and microbial communities minimize cadmium translocation in Chinese cabbage. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 22576–22587 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32579-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32579-5