Abstract
Air pollution is a danger to economies throughout the European Union. Industry, population expansion, a building boom owing to housing and infrastructure development, increasing vehicle traffic, crowded streets, a lack of availability of clean fuel, and ineffective control programs are the primary causes. Toxic air is a double-edged sword for a country’s health since it affects just a tiny fraction of Europe’s population. The financial burden and healthcare expenses for people rise when health expenditures rise. The present research looks at how dangerous air levels, healthcare costs, and the expansion of the European Union’s economy are all connected. The findings are based on data collected over 29 years and account for the abovementioned variables. The results of the unit root test have the significant probability values of all variables: health expenditures (HE), gross domestic product (GDP), nitrous oxides (NOX), and carbon dioxides (CO2) emissions at both level and first difference. We used the Johansen, Kao, and Pedroni cointegration tests to test the null hypothesis of no cointegration to see that sample variables had a long-term association. The PMG-ARDL test was used to get these findings. The results confirmed the significant probability values of dependent variables in long- and short-run results that GDP has a positive and significant effect on health expenditure, while NOX and CO2 emissions have a negative and significant impact on (HE), in the European Union. To verify the results, we applied the robustness test, fully modified OLS (FMOLD), and dynamic OLS (DOLS); the robustness test results validated the PMG-ARDL test results. Environmental pollution (CO2, NOX) has a significant and negative impact on healthcare expenditures and a significant effect on GDP (HE) in the EU region. The findings of this research have implications for a wide range of parties, including those who would examine the link between factors in a study meant to improve air quality, distribute health resources, or develop strategies for economic development.
Graphical Abstract


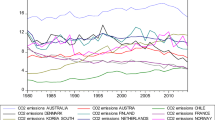
Source: The author’s compilation of the data derived from World Data Indicators, derived from World Data Indicators, is used in this research

Source: The author’s compilation of the data, derived from World Data Indicators, is used in this research

Source: The author’s compilation of the data, derived from World Data Indicators, is used in this research

Source: The author’s compilation of the data, derived from World Data Indicators, is used in this research

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be provided upon request.
References
Acemoglu D, Finkelstein A, Notowidigdo MJ (2013) Income and health spending: evidence from oil price shocks MIT Press. https://dspace.mit.edu/handle/1721.1/83903
Ahmad M, Jiang P, Majeed A, Umar M, Khan Z, Muhammad S (2020) The dynamic impact of natural resources, technological innovations and economic growth on ecological footprint: an advanced panel data estimation. Resour Policy 69:101817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2020.101817
Akadiri SS, Adebayo TS (2022) Asymmetric nexus among financial globalization, non-renewable energy, renewable energy use, economic growth, and carbon emissions: Impact on environmental sustainability targets in India. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(11):16311–16323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16849-0
Alola AA, Bekun FV, Sarkodie SA (2019) Dynamic impact of trade policy, economic growth, fertility rate, renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on ecological footprint in Europe. Sci Total Environ 685:702–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.139
Anderson ML (2020) As the wind blows: the effects of long-term exposure to air pollution on mortality. J Eur Econ Assoc 18(4):1886–1927. https://doi.org/10.1093/jeea/jvz051
Anyanwu JC, Erhijakpor AEO (2009) Health expenditures and health outcomes in Africa*. Afr Dev Rev 21(2):400–433. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8268.2009.00215.x
Apergis N, Ben Jebli M, Ben Youssef S (2018) Does renewable energy consumption and health expenditures decrease carbon dioxide emissions? Evidence for sub-Saharan Africa countries. Renew Energy 127:1011–1016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.05.043
Badida P, Krishnamurthy A, Jayaprakash J (2023) Meta analysis of health effects of ambient air pollution exposure in low- and middle-income countries. Environ Res 216:114604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.114604
Baltagi BH, Moscone F (2010) Health care expenditure and income in the OECD reconsidered: evidence from panel data. Econ Model 27(4):804–811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2009.12.001
Barkat K, Sbia R, Maouchi Y (2019) Empirical evidence on the long and short run determinants of health expenditure in the Arab world. Q Rev Econ Finance 73:78–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.qref.2018.11.009
Bayat R, Ashrafi K, Shafiepour Motlagh M, Hassanvand MS, Daroudi R, Fink G, Künzli N (2019) Health impact and related cost of ambient air pollution in Tehran. Environ Res 176:108547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.108547
Bedir S (2016) Healthcare expenditure and economic growth in developing countries. Adv Econ Business 4(2):76–86. https://doi.org/10.13189/aeb.2016.040202
Behera DK, Dash U (2019) Prioritization of government expenditure on health in India: a fiscal space perspective. Socioecon Plann Sci 68:100667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seps.2018.11.004
Beniston M (2003) Climatic change in mountain regions: a review of possible impacts. Clim Change 59(1):5–31. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024458411589
Bildirici ME, Kayıkçı F (2013) Effects of oil production on economic growth in Eurasian countries: panel ARDL approach. Energy 49:156–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2012.10.047
Blázquez-Fernández C, Cantarero-Prieto D, Pascual-Sáez M (2019) On the nexus of air pollution and health expenditures: new empirical evidence. Gac Sanit 33(4):389–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaceta.2018.01.006
Bosah CP, Li S, Ampofo GKM, Liu K (2021) Dynamic nexus between energy consumption, economic growth, and urbanization with carbon emission: evidence from panel PMG-ARDL estimation. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28(43):61201–61212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14943-x
Cesur R, Tekin E, Ulker A (2018) Can natural gas save lives? Evidence from the deployment of a fuel delivery system in a developing country. J Health Econ 59:91–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhealeco.2018.03.001
Chaabouni S, Saidi K (2017) The dynamic links between carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, health spending and GDP growth: a case study for 51 countries. Environ Res 158:137–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2017.05.041
Chandio AA, Jiang Y, Amin A, Akram W, Ozturk I, Sinha A, Ahmad F (2022) Modeling the impact of climatic and non-climatic factors on cereal production: evidence from Indian agricultural sector. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(10):14634–14653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16751-9
Delhi Air Quality Index (AQI) and India air pollution | IQAir. (2023, November 26). https://www.iqair.com/india/delhi
Deryugina T, Heutel G, Miller NH, Molitor D, Reif J (2019) The mortality and medical costs of air pollution: evidence from changes in wind direction. Am Econ Rev 109(12):4178–4219. https://doi.org/10.1257/aer.20180279
Djellouli N, Abdelli L, Elheddad M, Ahmed R, Mahmood H (2022) The effects of non-renewable energy, renewable energy, economic growth, and foreign direct investment on the sustainability of African countries. Renew Energy 183:676–686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.10.066
Dogan B, Madaleno M, Tiwari AK, Hammoudeh S (2020) Impacts of export quality on environmental degradation: does income matter? Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(12):13735–13772. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07371-5
Ebenstein A (2012) The Consequences of industrialization: evidence from water pollution and digestive cancers in China. Rev Econ Stat 94(1):186–201. https://doi.org/10.1162/REST_a_00150
Fan VY, Savedoff WD (2014) The health financing transition: a conceptual framework and empirical evidence. Soc Sci Med 105:112–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2014.01.014
Faramarzi A, Javan-Noughabi J, Sadeghi A, Rezapour A (2019) Impact of the economic crisis on healthcare resources: a panel data analysis in Eastern Mediterranean countries during 2005 to 2013. Clin Epidemiol Global Health 7(1):98–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cegh.2018.02.004
Foty, R. G. (n.d.). Measuring the short-term effect of ambient air pollution on acute health service use in ontarians living with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Fuller R, Landrigan PJ, Balakrishnan K, Bathan G, Bose-O’Reilly S, Brauer M, Caravanos J, Chiles T, Cohen A, Corra L, Cropper M, Ferraro G, Hanna J, Hanrahan D, Hu H, Hunter D, Janata G, Kupka R, Lanphear B, Yan C (2022) Pollution and health: a progress update. Lancet Planet Health 6(6):e535–e547. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2542-5196(22)00090-0
Gerdtham U-G, Søgaard J, Andersson F, Jönsson B (1992) An econometric analysis of health care expenditure: a cross-section study of the OECD countries. J Health Econ 11(1):63–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-6296(92)90025-V
Giammanco MD, Gitto L (2019) Health expenditure and FDI in Europe. Econ Anal Policy 62:255–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eap.2019.04.001
Gómez González L, Linares C, Díaz J, Egea A, Calle-Martínez A, Luna MY, Navas MA, Ascaso-Sánchez MS, Ruiz-Páez R, Asensio C, Padrón-Monedero A, López-Bueno JA (2023) Short-term impact of noise, other air pollutants and meteorological factors on emergency hospital mental health admissions in the Madrid region. Environ Res 224:115505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.115505
Graff Zivin J, Neidell M, Sanders NJ, Singer G (2023) When externalities collide: influenza and pollution. Am Econ J Appl Econ 15(2):320–351. https://doi.org/10.1257/app.20210500
Grant WB, Strange RC, Garland CF (2003) Sunshine is good medicine. The health benefits of ultraviolet-B induced vitamin D production. J Cosmet Dermatol 2(2):86–98. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1473-2130.2004.00041.x
Grossman M (1972) On the concept of health capital and the demand for health. J Polit Econ 80(2):223–255
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1991) Environmental Impacts of a North American Free Trade Agreement (Working Paper 3914). National Bureau of Economic Research. https://doi.org/10.3386/w3914
Hair JF, Hult GTM, Ringle CM, Sarstedt M (2017) A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München. https://epub.ub.uni-muenchen.de/96122/
Halken S (2003) Early sensitisation and development of allergic airway disease—risk factors and predictors. Paediatr Respir Rev 4(2):128–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1526-0542(03)00026-5
Hanif I, Faraz Raza SM, Gago-de-Santos P, Abbas Q (2019) Fossil fuels, foreign direct investment, and economic growth have triggered CO2 emissions in emerging Asian economies: some empirical evidence. Energy 171:493–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.01.011
Hansel NN, McCormack MC, Belli AJ, Matsui EC, Peng RD, Aloe C, Paulin L, Williams DL, Diette GB, Breysse PN (2013) In-home air pollution is linked to respiratory morbidity in former smokers with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 187(10):1085–1090. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201211-1987OC
Hao Y, Liu S, Lu Z-N, Huang J, Zhao M (2018) The impact of environmental pollution on public health expenditure: dynamic panel analysis based on Chinese provincial data. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25(19):18853–18865. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2095-y
Hao X, Li Y, Ren S, Wu H, Hao Y (2023) The role of digitalization on green economic growth: does industrial structure optimization and green innovation matter? J Environ Manage 325:116504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116504
Hille E, Shahbaz M, Moosa I (2019) The impact of FDI on regional air pollution in the Republic of Korea: a way ahead to achieve the green growth strategy? Energy Econ 81:308–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2019.04.004
Ji Q, Zhang D (2019) How much does financial development contribute to renewable energy growth and upgrading of energy structure in China? Energy Policy 128:114–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2018.12.047
Johansen S, Juselius K (1990) Maximum likelihood estimation and inference on cointegration—with applications to the demand for money. Oxford Bull Econ Stat 52(2):169–210. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-0084.1990.mp52002003.x
Jütting JP (2004) Do community-based health insurance schemes improve poor people’s access to health care? Evidence from Rural Senegal. World Dev 32(2):273–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2003.10.001
Kao C (1999) Spurious regression and residual-based tests for cointegration in panel data. J Econom 90(1):1–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4076(98)00023-2
Khoshnevis Yazdi S, Dariani AG (2019) CO2 emissions, urbanisation and economic growth: evidence from Asian countries. Econ Res Ekon Istraž 32(1):510–530. https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677X.2018.1556107
Kim D, Chen Z, Zhou L-F, Huang S-X (2018) Air pollutants and early origins of respiratory diseases. Chronic Dis Transl Med 4(2):75–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cdtm.2018.03.003
Kim H-J, Kim H-S, Kim S, Hwang J, Lee H, Park B, Kim B (2023) Effects of vitamin D on associations between air pollution and mental health outcomes in Korean adults: results from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). J Affect Disord 320:390–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2022.09.144
Kollerup A, Kjellberg J, Ibsen R (2022) Ageing and health care expenditures: the importance of age per se, steepening of the individual-level expenditure curve, and the role of morbidity. Eur J Health Econ 23(7):1121–1149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-021-01413-x
Kyriopoulos I, Nikoloski Z, Mossialos E (2019) The impact of the Greek economic adjustment programme on household health expenditure. Soc Sci Med 222:274–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2019.01.021
Le T-H, Nguyen CP, Park D (2020) Financing renewable energy development: insights from 55 countries. Energy Res Soc Sci 68:101537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.erss.2020.101537
Levin A, Lin C-F, James Chu C-S (2002) Unit root tests in panel data: asymptotic and finite-sample properties. J Econom 108(1):1–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4076(01)00098-7
Li R, Shan Y, Bi J, Liu M, Ma Z, Wang J, Hubacek K (2021) Balance between poverty alleviation and air pollutant reduction in China. Environ Res Lett 16(9):094019. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ac19db
Liang L-L, Mirelman AJ (2014) Why do some countries spend more for health? An assessment of sociopolitical determinants and international aid for government health expenditures. Soc Sci Med 114:161–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2014.05.044
Mardani A, Streimikiene D, Cavallaro F, Loganathan N, Khoshnoudi M (2019) Carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions and economic growth: a systematic review of two decades of research from 1995 to 2017. Sci Total Environ 649:31–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.229
Marupuru S, Axon DR (2021) Association of multimorbidity on healthcare expenditures among older United States adults with pain. J Aging Health 33(9):741–750. https://doi.org/10.1177/08982643211011841
Mladenović I, Milovančević M, Sokolov Mladenović S, Marjanović V, Petković B (2016) Analyzing and management of health care expenditure and gross domestic product (GDP) growth rate by adaptive neuro-fuzzy technique. Comput Hum Behav 64:524–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2016.07.052
Murray CJL, Aravkin AY, Zheng P, Abbafati C, Abbas KM, Abbasi-Kangevari M, Abd-Allah F, Abdelalim A, Abdollahi M, Abdollahpour I, Abegaz KH, Abolhassani H, Aboyans V, Abreu LG, Abrigo MRM, Abualhasan A, Abu-Raddad LJ, Abushouk AI, Adabi M, Lim SS (2020) Global burden of 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. The Lancet 396(10258):1223–1249. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30752-2
Murthy VNR, Ketenci N (2017) Is technology still a major driver of health expenditure in the United States? Evidence from cointegration analysis with multiple structural breaks. Int J Health Econ Manag 17(1):29–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10754-016-9196-2
Neidell MJ (2004) Air pollution, health, and socio-economic status: the effect of outdoor air quality on childhood asthma. J Health Econ 23(6):1209–1236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhealeco.2004.05.002
Newhouse JP (1977) Medical-care expenditure: a cross-national survey. J Hum Resour 12(1):115–125. https://doi.org/10.2307/145602
Nixon J, Ulmann P (2006) The relationship between health care expenditure and health outcomes evidence and caveats for a causal link. Eur J Health Econ 7(1):7–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-005-0336-8
Olayungbo DO, Quadri A (2019) Remittances, financial development and economic growth in sub-Saharan African countries: evidence from a PMG-ARDL approach. Financial Innov 5(1):9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40854-019-0122-8
Pammolli F, Riccaboni M, Magazzini L (2012) The sustainability of European health care systems: beyond income and aging. Eur J Health Econ 13(5):623–634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-011-0337-8
Pedroni P (1999) Critical values for cointegration tests in heterogeneous panels with multiple regressors
Pesaran MH, Smith RP (1998) Structural analysis of cointegrating VARs. J Econ Surveys 12(5):471–505. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-6419.00065
Pesaran MH, Shin Y, Smith RP (1999) Pooled mean group estimation of dynamic heterogeneous panels. J Am Stat Assoc 94(446):621–634. https://doi.org/10.2307/2670182
Pokhrel AK, Bates MN, Verma SC, Joshi HS, Sreeramareddy CT, Smith KR (2010) Tuberculosis and indoor biomass and kerosene use in Nepal: a case-control study. Environ Health Perspect 118(4):558–565
Raghutla C, Padmagirisan P, Sakthivel P, Chittedi KR, Mishra S (2022) The effect of renewable energy consumption on ecological footprint in N-11 countries: evidence from Panel Quantile Regression Approach. Renew Energy 197:125–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2022.07.100
Rahman MdH, Majumder SC (2022) Empirical analysis of the feasible solution to mitigate the CO2 emission: evidence from Next-11 countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(48):73191–73209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20908-5
Raza SA, Shah N, Sharif A (2019) Time frequency relationship between energy consumption, economic growth and environmental degradation in the United States: evidence from transportation sector. Energy 173:706–720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.01.077
Saleem H, Khan MB, Shabbir MS (2020) The role of financial development, energy demand, and technological change in environmental sustainability agenda: evidence from selected Asian countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(5):5266–5280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07039-0
Sarkodie SA, Strezov V (2018) Empirical study of the Environmental Kuznets curve and Environmental Sustainability curve hypothesis for Australia, China, Ghana and USA. J Clean Prod 201:98–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.039
Shah SAR, Zhang Q, Abbas J, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Pilař L (2023) Technology, urbanization and natural gas supply matter for carbon neutrality: a new evidence of environmental sustainability under the prism of COP26. Resour Policy 82:103465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2023.103465
Tai M-Y, Chao C-C, Hu S-W (2015) Pollution, health and economic growth. North Am J Econ Finance 32:155–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.najef.2015.02.004
Toplicianu S. (n.d.). Associate Professor PHD Valahia University of Targoviste
, (2020, February 5). EPA year in review 2019 [Collections and Lists]. https://www.epa.gov/newsroom/epa-year-review-2019
Usman A, Ozturk I, Ullah S, Hassan A (2021) Does ICT have symmetric or asymmetric effects on CO2 emissions? Evidence from selected Asian economies. Technol Soc 67:101692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2021.101692
Vyas N, Wimberly CE, Beaman MM, Kaplan SJ, Rasmussen LJH, Wertz J, Gifford EJ, Walsh KM (2023a) Systematic review and meta-analysis of the effect of adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) on brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels. Psychoneuroendocrinology 151:106071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2023.106071
Vyas V, Mehta K, Sharma R (2023) The nexus between toxic-air pollution, health expenditure, and economic growth: an empirical study using ARDL. Int Rev Econ Finance 84(C) 154–166
Wang K-M (2011) Health care expenditure and economic growth: quantile panel-type analysis. Econ Model 28(4):1536–1549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2011.02.008
Wang H, Abbas KM, Abbasifard M, Abbasi-Kangevari M, Abbastabar H, Abd-Allah F, Abdelalim A, Abolhassani H, Abreu LG, Abrigo MRM, Abushouk AI, Adabi M, Adair T, Adebayo OM, Adedeji IA, Adekanmbi V, Adeoye AM, Adetokunboh OO, Advani SM, Murray CJL (2020) Global age-sex-specific fertility, mortality, healthy life expectancy (HALE), and population estimates in 204 countries and territories, 1950–2019: a comprehensive demographic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. The Lancet 396(10258):1160–1203. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30977-6
Wang L, Huang Y, Ghafoor A, Hafeez M, Salahodjaev R (2023) Asymmetric macroeconomic determinants of renewable energy consumption: do financial institutions and ICT trade matter? Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(4):9841–9851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22816-0
World Bank Open Data (n.d.) World Bank Open Data. Retrieved May 20, 2023, from https://data.worldbank.org
Yang J, Sun Y, Sun H, Lau CKM, Apergis N, Zhang K (2022) Role of financial development, green technology innovation, and macroeconomic dynamics toward carbon emissions in China: analysis based on bootstrap ARDL approach Front Environ Science 10 https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fenvs.2022.886851
Yorulmaz Ö (2016) Can healthcare ever be less than a necessity in MENA countries? A semiparametric estimation of the relationship between healthcare expenditure and GDP. Qual Quant 50(3):1233–1244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-015-0201-5
Zaidi S, Saidi K (2018) Environmental pollution, health expenditure and economic growth in the Sub-Saharan Africa countries: panel ARDL approach. Sustain Cities Soc 41:833–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2018.04.034
Zaman K, Abd-el Moemen M (2017) The influence of electricity production, permanent cropland, high technology exports, and health expenditures on air pollution in Latin America and the Caribbean Countries. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 76:1004–1010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.03.103
Zaman uz Q, Wang Z, Zaman S, Rasool SF (2021) Investigating the nexus between education expenditure, female employers, renewable energy consumption and CO2 emission: evidence from China. J Clean Prod 312:127824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127824
Zhang Z, Bashir T, Song J, Aziz S, Yahya G, Bashir S, Zamir A (2022) The effects of Environmental Kuznets Curve toward environmental pollution, energy consumption on sustainable economic growth through moderate role of technological innovation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(1):405–416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16956-y
Zheng J, Wang X (2021) Can mobile information communication technologies (ICTs) promote the development of renewables?-evidence from seven countries. Energy Policy 149:112041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2020.112041
Funding
This research is funded by the following:
1. Innovative Team of Philosophy and Social Sciences in Jiangsu. Higher Learning No. 2017ZSTD002
2. Jiangsu Provincial Social Science Foundation. No. 21EYB010/14SHC005
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Liqun Zhang conducted the analysis and wrote the paper. Meanwhile, Changzheng ZHANG conceptualized, collected the data, and did the final proofreading of the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Ethical approval is not required.
Consent to participate
All authors participated in this research.
Consent for publication
Consent for publication is not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Eyup Dogan
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Zhang, L. The relationship between toxic air pollution, health expenditure, and economic growth in the European Union: fresh evidence from the PMG-ARDL model. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 21107–21123 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32342-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32342-w