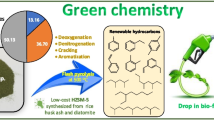
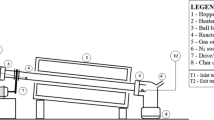
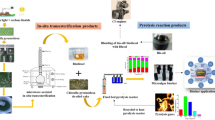
Abstract
Recovering renewable chemicals from de-fatted microalgal residue derived from lipid extraction within the algal-derived biofuel sector is crucial, given the rising significance of microalgal-derived biodiesel as a potential substitute for petroleum-based liquid fuels. As a circular economy strategy, effective valorization of de-fatted biomass significantly improves the energetic and economic facets of establishing a sustainable algal-derived biofuel industry. In this scenario, this study investigates flash catalytic pyrolysis as a sustainable pathway for valorizing Scenedesmus sp. post-extraction residue (SPR), potentially yielding a bio-oil enriched with upgraded characteristics, especially renewable aromatic hydrocarbons. In the scope of this study, volatile products from catalytic and non-catalytic flash pyrolysis were characterized using a micro-furnace type temperature programmable pyrolyzer coupled with gas chromatographic separation and mass spectrometry detection (Py–GC/MS). Flash pyrolysis of SPR resulted in volatile products with elevated oxygen and nitrogen compounds with concentrations of 46.4% and 26.4%, respectively. In contrast, flash pyrolysis of lyophilized microalgal biomass resulted in lower concentrations of these compounds, with 40.9% oxygen and 17.3% nitrogen. Upgrading volatile pyrolysis products from SPR led to volatile products comprised of only hydrocarbons, while completely removing oxygen and nitrogen-containing compounds. This was achieved by utilizing a low-cost HZSM-5 catalyst within a catalytic bed at 500 °C. Catalytic experiments also indicate the potential conversion of SPR into a bio-oil rich in monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, primarily BETX, with toluene comprising over one-third of its composition, thus presenting a sustainable pathway for producing an aromatic hydrocarbon-rich bio-oil derived from SPR. Another significant finding was that 97.8% of the hydrocarbon fraction fell within the gasoline range (C5–C12), and 35.5% fell within the jet fuel range (C8–C16). Thus, flash catalytic pyrolysis of SPR exhibits significant promise for application in drop-in biofuel production, including green gasoline and bio-jet fuel, aligning with the principles of the circular economy, green chemistry, and bio-refinery.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets utilized and/or analyzed in the current study can be made available by the corresponding author upon a reasonable request.
References
Almahri A, Morad M, Aljohani MM et al (2023) Atrazine reclamation from an aqueous environment using a ruthenium-based metal-organic framework. Process Saf Environ Prot 177:52–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2023.06.091
Almeida HN, Calixto GQ, Chagas BME et al (2017) Characterization and pyrolysis of Chlorella vulgaris and Arthrospira platensis: potential of bio-oil and chemical production by Py-GC/MS analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:14142–14150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9009-2
Al-Wasidi AS, AlZahrani IIS, Naglah AM et al (2021) Effective removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution using metal-organic framework; modelling analysis, statistical physics treatment and DFT calculations. ChemistrySelect 6:11431–11447. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.202102330
Anand V, Sunjeev V, Vinu R (2016) Catalytic fast pyrolysis of Arthrospira platensis (spirulina) algae using zeolites. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 118:298–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2016.02.013
Andrade LA, Barrozo MAS, Vieira LGM (2016) Thermo-chemical behavior and product formation during pyrolysis of mango seed shell. Ind Crops Prod 85:174–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.03.004
Andrade LA, Barrozo MAS, Vieira LGM (2018a) Catalytic solar pyrolysis of microalgae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Sol Energy 173:928–938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2018.08.035
Andrade LA, Batista FRX, Lira TS et al (2018b) Characterization and product formation during the catalytic and non-catalytic pyrolysis of the green microalgae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Renew Energy 119:731–740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.12.056
Azizi K, Keshavarz Moraveji M, Arregi A et al (2020) On the pyrolysis of different microalgae species in a conical spouted bed reactor: bio-fuel yields and characterization. Bioresour Technol 311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123561
Azizi S, Mowla D (2016) CFD modeling of algae flash pyrolysis in the batch fluidized bed reactor including heat carrier particles. Int J Chem React Eng 14:463–480. https://doi.org/10.1515/ijcre-2014-0185
Barbosa AS, Siqueira LAM, Medeiros RLBA et al (2019) Renewable aromatics through catalytic flash pyrolysis of pineapple crown leaves using HZSM-5 synthesized with RHA and diatomite. Waste Manag 88:347–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2019.03.052
Campanella A, Muncrief R, Harold MP et al (2012) Thermolysis of microalgae and duckweed in a CO 2-swept fixed-bed reactor: bio-oil yield and compositional effects. Bioresour Technol 109:154–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.12.115
Chagas BME, Dorado C, Serapiglia MJ et al (2016) Catalytic pyrolysis-GC/MS of Spirulina: evaluation of a highly proteinaceous biomass source for production of fuels and chemicals. Fuel 179:124–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.03.076
Costa JEB, Barbosa AS, Melo MAF et al (2022) Renewable aromatics through catalytic pyrolysis of coconut fiber (Cocos nucífera Linn.) using low cost HZSM-5. Renew Energy 191:439–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2022.03.111
de Paiva EM, Mattos ALA, da Silva JCG et al (2023) Pyrolysis of cashew nutshell residues for bioenergy and renewable chemicals: kinetics, thermodynamics, and volatile products. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 177:106303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2023.106303
Delmiro TM, Wilson RRYOV, Melo DMA et al (2021) Catalytic flash pyrolysis of Monoraphidium sp. before and after lipid extraction. Algal Res 54:102199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2021.102199
Du Z, Hu B, Ma X et al (2013) Catalytic pyrolysis of microalgae and their three major components: carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Bioresour Technol 130:777–782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.12.115
El-Desouky MG, El-Bindary MA, El-Bindary AA (2021) Effective adsorptive removal of anionic dyes from aqueous solution. Vietnam J Chem 59:341–361. https://doi.org/10.1002/vjch.202000184
El-Desouky MG, Khalil MA, El-Bindary AA, El-Bindary MA (2022) Biological, biochemical and thermochemical techniques for biofuel production: an updated review. Biointerface Res Appl Chem 12:3034–3054. https://doi.org/10.33263/BRIAC123.30343054
El-Gammal OA, El-Bindary AA, Sh Mohamed F et al (2022) Synthesis, characterization, design, molecular docking, anti COVID-19 activity, DFT calculations of novel Schiff base with some transition metal complexes. J Mol Liq 346:117850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117850
El-Metwaly NM, Katouah HA, El-Desouky MG et al (2022) Fabricating of Fe 3 O 4 @Ag-MOF nanocomposite and evaluating its adsorption activity for removal of doxorubicin. J Environ Sci Heal Part A 57:1099–1115. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2022.2156230
Fong MJB, Loy ACM, Chin BLF et al (2019) Catalytic pyrolysis of Chlorella vulgaris: kinetic and thermodynamic analysis. Bioresour Technol 289:121689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121689
Francavilla M, Kamaterou P, Intini S et al (2015) Cascading microalgae biorefinery: fast pyrolysis of Dunaliella tertiolecta lipid extracted-residue. Algal Res 11:184–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2015.06.017
Gaurh P, Pramanik H (2018) Production of benzene/toluene/ethyl benzene/xylene (BTEX) via multiphase catalytic pyrolysis of hazardous waste polyethylene using low cost fly ash synthesized natural catalyst. Waste Manag 77:114–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.05.013
Gong X, Zhang B, Zhang Y et al (2014) Investigation on pyrolysis of low lipid microalgae Chlorella vulgaris and Dunaliella salina. Energy Fuels 28:95–103. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef401500z
Harman-Ware AE, Morgan T, Wilson M et al (2013) Microalgae as a renewable fuel source: fast pyrolysis of Scenedesmus sp. Renew Energy 60:625–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2013.06.016
Huang Z, Zhang J, Pan M et al (2022) Valorisation of microalgae residues after lipid extraction: pyrolysis characteristics for biofuel production. Biochem Eng J 179:108330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2021.108330
Ji X, Liu B, Chen G, Ma W (2015) The pyrolysis of lipid-extracted residue of Tribonema minus in a fixed-bed reactor. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 116:231–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2015.09.006
Kim S-S, Ly HV, Kim J et al (2015) Pyrolysis of microalgae residual biomass derived from Dunaliella tertiolecta after lipid extraction and carbohydrate saccharification. Chem Eng J 263:194–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.11.045
Li F, Srivatsa SC, Batchelor W, Bhattacharya S (2017) A study on growth and pyrolysis characteristics of microalgae using thermogravimetric analysis-infrared spectroscopy and synchrotron Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Bioresour Technol 229:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.01.005
Li F, Srivatsa SC, Bhattacharya S (2019) A review on catalytic pyrolysis of microalgae to high-quality bio-oil with low oxygeneous and nitrogenous compounds. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 108:481–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.03.026
Mata TM, Martins AA, Caetano NS (2010) Microalgae for biodiesel production and other applications: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 14:217–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2009.07.020
Mehmood MA, Ahmad MS, Liu Q et al (2019) Helianthus tuberosus as a promising feedstock for bioenergy and chemicals appraised through pyrolysis, kinetics, and TG-FTIR-MS based study. Energy Convers Manag 194:37–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2019.04.076
Morrill JC, Sawyer JE, Smith SB et al (2017) Post-extraction algal residue in beef steer finishing diets: II. Beef flavor, fatty acid composition, and tenderness. Algal Res 25:578–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2017.07.007
Mustapha SI, Rawat I, Bux F, Isa YM (2021) Catalytic pyrolysis of nutrient-stressed Scenedesmus obliquus microalgae for high-quality bio-oil production. Renew Energy 179:2036–2047. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.08.043
Niu Q, Ghysels S, Wu N et al (2022) Effects of demineralization on the composition of microalgae pyrolysis volatiles in py-GC–MS. Energy Convers Manag 251:114979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2021.114979
Rahman NAA, Fermoso J, Sanna A (2018) Effect of Li-LSX-zeolite on the in-situ catalytic deoxygenation and denitrogenation of Isochrysis sp. microalgae pyrolysis vapours. Fuel Process Technol 173:253–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2018.01.020
Scaldaferri CA, Pasa VMD (2019) Hydrogen-free process to convert lipids into bio-jet fuel and green diesel over niobium phosphate catalyst in one-step. Chem Eng J 370:98–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.063
Shahid A, Ishfaq M, Ahmad MS et al (2019) Bioenergy potential of the residual microalgal biomass produced in city wastewater assessed through pyrolysis, kinetics and thermodynamics study to design algal biorefinery. Bioresour Technol 289:121701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121701
Sharifzadeh M, Sadeqzadeh M, Guo M et al (2019) The multi-scale challenges of biomass fast pyrolysis and bio-oil upgrading: review of the state of art and future research directions. Prog Energy Combust Sci 71:1–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecs.2018.10.006
Thangalazhy-Gopakumar S, Adhikari S, Chattanathan SA, Gupta RB (2012) Catalytic pyrolysis of green algae for hydrocarbon production using H+ZSM-5 catalyst. Bioresour Technol 118:150–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.05.080
Wang K, Brown RC (2013) Catalytic pyrolysis of microalgae for production of aromatics and ammonia. Green Chem 15:675–681. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3gc00031a
Wang K, Brown RC, Homsy S et al (2013) Fast pyrolysis of microalgae remnants in a fluidized bed reactor for bio-oil and biochar production. Bioresour Technol 127:494–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.08.016
Wang S, Cao B, Liu X et al (2018) A comparative study on the quality of bio-oil derived from green macroalga Enteromorpha clathrata over metal modified ZSM-5 catalysts. Bioresour Technol 256:446–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.01.134
Wang S, Li Z, Bai X et al (2019) Catalytic pyrolysis of lignin in a cascade dual-catalyst system of modified red mud and HZSM-5 for aromatic hydrocarbon production. Bioresour Technol 278:66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.01.037
Xiu S, Shahbazi A (2012) Bio-oil production and upgrading research: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 16:4406–4414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2012.04.028
Yaman S (2004) Pyrolysis of biomass to produce fuels and chemical feedstocks. Energy Convers Manag 45:651–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0196-8904(03)00177-8
Yang C, Li R, Zhang B et al (2019) Pyrolysis of microalgae: a critical review. Fuel Process Technol 186:53–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2018.12.012
Zainan NH, Srivatsa SC, Bhattacharya S (2015) Catalytic pyrolysis of microalgae Tetraselmis suecica and characterization study using in situ synchrotron-based infrared microscopy. Fuel 161:345–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2015.08.030
Zhang Y, Liu C, Nian P et al (2024) Facile preparation of high-performance hydrochar/TiO2 heterojunction visible light photocatalyst for treating Cr(VI)-polluted water. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 681:132775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2023.132775
Funding
The authors express their gratitude to LabTam − UFRN and LNA − EAJ − UFRN for the infrastructure made available to support the development of this study. The authors also acknowledge financial support from PETROBRAS and Brazil’s National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq/Brazil Process 307433/2020–0).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Julio de Andrade Oliveira Marques: conceptualization, investigation, methodology, visualization, data curation, formal analysis, and writing—original draft. José Luiz Francisco Alves: formal analysis, investigation, visualization, and writing—original draft. Gislane Pinho de Oliveira: formal analysis and investigation. Dulce Maria de Araújo Melo: resources. Graco Aurelio Camara de Melo Viana: funding acquisition. Renata Martins Braga: conceptualization, visualization, supervision, investigation, resources, writing—review and editing, and project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: George Z. Kyzas
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Marques, J.d., Alves, J.L.F., de Oliveira, G.P. et al. Catalytic flash pyrolysis of Scenedesmus sp. post-extraction residue using low-cost HZSM-5 catalyst with the perspective to produce renewable aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 18785–18796 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32336-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32336-8