Abstract
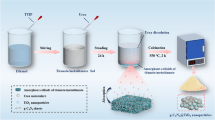
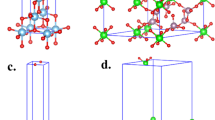
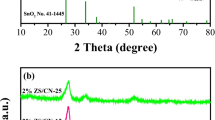
Constructing superior Z-type photocatalytic heterojunction is beneficial to effectively enlarge interface contact, improve the photo-generated carrier separation rate, and retain the high redox ability. In this work, we designed a hierarchical core–shell g-C3N4/TiO2 structure to build Z-type heterojunction via combining simple template method and pyrolysis process. A close-knit Z-type heterojunction was constructed using TiO2 as a thick core and g-C3N4 as an ultra-thin shell. The effects of lamp source, wavelength, tetracycline (TC) concentration, and photocatalyst dose on the degradation performance on TC of g-C3N4/TiO2 were inspected. 0.1TiO2/g-C3N4 photocatalyst had the best degradation rate and highest removal rate within 30 min, and its degradation rate was about 49, 23, and 5 times than pure g-C3N4, TiO2, and commercial TiO2/g-C3N4 in respect. Moreover, compared with degradation ability under Xenon lamp, LED irradiation for g-C3N4/TiO2 composites showed a remarkable selective degradation. The fast and efficient Z-type transfer pathway of 0.1 g-C3N4/TiO2 was realized by forming an optimized interface and abundant surface active sites ascribed to the combined action of thick TiO2 core and ultra-thin g-C3N4 shell. In addition, the degradation intermediates were analyzed by LC–MS and suggested pathways of degradation. The work could provide novel design concept to obtain reliable Z-type photocatalysts with hierarchical core–shell structure applied in degradation of antibiotic wastewater.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study available from the corresponding author on request.
References
Bai X, Wang Y, Li Y, Wang X (2019) Adsorption–photocatalytical remediation for series of tetracycline contaminants with BiOCl–CdS composite under simulated sunlight. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 104:94–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2019.08.016
Chen C, Zhang J, Xiong X, Lin J, Yang S, Xi J, Kong Z (2022) A novel Z-type multidimensional FeSe2/CuSe heterojunction photocatalyst with high photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical performance. Int J Hydrog Energy 47(67):28879–28893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.06.219
Dewil R, Mantzavinos D, Poulios I, Rodrigo MA (2017) New perspectives for advanced oxidation processes. J Environ Manage 195:93–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.04.010
Dong G, Huang L, Wu X, Wang C, Liu Y, Liu G, Wang L, Liu X, Xia H (2018) Effect and mechanism analysis of MnO2 on permeable reactive barrier (PRB) system for the removal of tetracycline. Chemosphere 193:702–710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.085
Fan D, Guo C, Ma H, Zhao D, Li Y, Wu D, Wei Q (2016) Facile fabrication of an aptasensor for thrombin based on graphitic carbon nitride/TiO2 with high visible-light photoelectrochemical activity. Biosens Bioelectron 75:116–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.08.029
Gan W, Fu X, Guo J, Zhang M, Li D, Ding C, Lu Y, Wang P, Sun Z (2022) Ag nanoparticles decorated 2D/2D TiO2/g-C3N4 heterojunction for efficient removal of tetracycline hydrochloride: synthesis, degradation pathways, and mechanism. Appl Surf Sci 606:154837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.154837
Guo J, Jiang L, Liang J, Xu W, Yu H, Zhang J, Ye S, Xing W, Yuan X (2021) Photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline antibiotics using delafossite silver ferrite-based Z-scheme photocatalyst: pathways and mechanism insight. Chemosphere 270:128651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128651
Hao J, Zhang S, Ren F, Wang Z, Lei J, Wang X, Cheng T, Li L (2017) Synthesis of TiO2@g-C3N4 core-shell nanorod arrays with Z-scheme enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible light. J Colloid Interface Sci 508:419–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.08.065
Hao H, Wang Z, Shi J, Li X, Lang X (2018) Improving the visible light photocatalytic aerobic oxidation of sulfides into sulfoxides on dye-sensitized TiO2. ChemCatChem 10(20):4545–4554. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201801304
Hunge YM, Yadav AA, Kang SW, Kim H (2021) Photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline antibiotics using hydrothermally synthesized two-dimensional molybdenum disulfide/titanium dioxide composites. J Colloid Interface Sci 606:454–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.07.151
Jiang D, Xiao P, Shao L, Li D, Chen M (2017) RGO-promoted all-solid-state g-C3N4/BiVO4 Z-scheme heterostructure with enhanced photocatalytic activity toward the degradation of antibiotics. Ind Eng Chem Res 56(31):8823–8832. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.7b01840
Jiang G, Geng K, Wu Y, Han Y, Shen X (2018a) High photocatalytic performance of ruthenium complexes sensitizing g-C3 N4 /TiO2 hybrid in visible light irradiation. Appl Catal B 227:366–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.01.034
Jiang X, Xing Q, Luo X, Li F, Zou J, Liu S, Li X, Wang X (2018b) Simultaneous photoreduction of Uranium(VI) and photooxidation of arsenic (III) in aqueous solution over g-C3 N4 /TiO2 heterostructured catalysts under simulated sunlight irradiation. Appl Catal B 228:29–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.01.062
Jo WK, Natarajan TS (2015) Influence of TiO2 morphology on the photocatalytic efficiency of direct Z-scheme g-C3N4/TiO2 photocatalysts for isoniazid degradation. Chem Eng J 281:549–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.06.120
Kayal A, Mandal S (2022) Microbial degradation of antibiotic: future possibility of mitigating antibiotic pollution. Environ Monit Assess 194(9):639. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10314-2
Kong L, Zhang X, Wang C, Xu J, Du X, Li L (2018) Ti3+ defect mediated g-C3N4/TiO2 Z-scheme system for enhanced photocatalytic redox performance. Appl Surf Sci 448:188–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.04.011
Li J, Zhang M, Li X, Li Q, Yang J (2017) Effect of the calcination temperature on the visible light photocatalytic activity of direct contact Z-scheme g-C3N4-TiO2 heterojunction. Appl Catal B 212:106–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.04.061
Li Y, Chang H, Wang Z, Shen Q, Liu X, Xue J, Jia H (2022) A 3D C@TiO2 multishell nanoframe for simultaneous photothermal catalytic hydrogen generation and organic pollutant degradation. J Colloid Interface Sci 609:536–546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.11.052
Liu F, Nguyen TP, Wang Q, Massuyeau F, Dan Y, Jiang L (2019) Construction of Z-scheme g-C3N4/Ag/P3HT heterojunction for enhanced visible-light photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline (TC) and methyl orange (MO). Appl Surf Sci 496:143653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.143653
Liu B, Sun Y, Zheng T, He X, Wang P, Wang J (2020) Wang Regeneration of carbon nanotube saturated with tetracycline by microwave-ultraviolet system: performance and degradation pathway. Chem Eng J 394:124752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124752
Maziarz W (2019) TiO2/SnO2 and TiO2/CuO thin film nano-heterostructures as gas sensors. Appl Surf Sci 480:361–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.02.139
Meng A, Zhang L, Cheng B, Yu J (2019) Dual cocatalysts in TiO2 photocatalysis. Adv Mater 31(30):1807660. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201807660
Milh H, Yu X, Cabooter D, Dewil R (2021) Degradation of ciprofloxacin using UV-based advanced removal processes: comparison of persulfate-based advanced oxidation and sulfite-based advanced reduction processes. Sci Total Environ 764:144510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144510
Monga D, Basu S (2019) Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of industrial dye by g-C3N4/TiO2 nanocomposite: role of shape of TiO2. Adv Powder Technol 30(5):1089–1098. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2019.03.004
Pan J, Zhang Y, Guan Y, Yan Y, Tang H, Liu X, Wang M, Wei X (2022) Multifunctional Ni nanoparticles decorated SiC nanofibers/g-C3N4 nanosheets heterojunctions for drastically increased LED-light-driven hydrogen generation. Appl Surf Sci 579:152171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.152171
Pan J, Guan Y, Zhang Y, Xu Z, Han S, Tang H, Yan X, Liu H, Lu Q (2023) Near-infrared-induced photothermal enhanced photocatalytic H2 production for 3D/2D heterojunctions of snowflake-like CuS/g-C3N4 nanosheets. Inorg Chem 62(1):624–635. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.2c04000
Perumal K, Shanavas S, Ahamad T, Karthigeyan A, Murugakoothan P (2023) Construction of Ag2CO3/BiOBr/CdS ternary composite photocatalyst with improved visible-light photocatalytic activity on tetracycline molecule degradation. J Environ Sci-China 125:47–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2021.10.021
Qiu J, Feng Y, Zhang X, Zhang X, Jia M, Yao J (2018) Facile stir-dried preparation of g-C3N4/TiO2 homogeneous composites with enhanced photocatalytic activity. RSC Adv 7(18):10668–10674. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra00050b
Rehman ZU, Bilal M, Hou J, Butt FK, Ahmad J, Ali S, Hussain A (2022) Photocatalytic CO2 reduction using TiO2-based photocatalysts and TiO2 Z-scheme heterojunction composites: a review. Molecules 27(7):2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072069
Tang R, Gong D, Deng Y, Xiong S, Zheng F, Li L, Zhou Z, Su L, Zhao J (2021) π-π stacking derived from graphene-like biochar/g-C3 N4 with tunable band structure for photocatalytic antibiotics degradation via peroxymonosulfate activation. J Hazard Mater 423:126944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126944
Xu W, Lai S, Pillai SC, Chu W, Hu Y, Jiang X, Fu M, Wu X, Li F, Wang H (2020) Visible light photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline with porous Ag/graphite carbon nitride plasmonic composite: degradation pathways and mechanism. J Colloid Interface Sci 574:110–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.04.038
Yu J, Wang S, Low J, Xiao W (2013) Enhanced photocatalytic performance of direct Z-scheme g-C3N4-TiO2 photocatalysts for the decomposition of formaldehyde in air. Phys Chem Chem Phys 15(39):16883–16890. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cp53131g
Yu H, Wang D, Zhao B, Lu Y, Wang X, Zhu S, Qin W, Huo M (2020) Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline under visible light by using a ternary photocatalyst of Ag3PO4/AgBr/g-C3N4 with dual Z-scheme heterojunction. Sep Purif Technol 237:116365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.116365
Zhang B, He X, Yu C, Liu G, Ma D, Cui C, Yan Q, Zhang Y, Zhang G, Ma J, Xin Y (2022) Degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride by ultrafine TiO2 nanoparticles modified g-C3N4 heterojunction photocatalyst: influencing factors, products and mechanism insight. Chin Chem Lett 33(3):1337–1342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2021.08.008
Zhu Q, Sun Y, Xu S, Li Y, Lin X, Qin Y (2019) Rational design of 3D/2D In2O3 nanocube/ZnIn2S4 nanosheet heterojunction photocatalyst with large-area “high-speed channels” for photocatalytic oxidation of 2,4-dichlorophenol under visible light. J Hazard Mater 382:121098. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121098
Zong H, Zhao T, Zhou G, Qian R, Feng T, Pan J (2019) Revisiting structural and photocatalytic properties of g-C3N4/TiO2: is surface modification of TiO2 by calcination with urea an effective route to “solar” photocatalyst? Catal Today 335:252–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2018.12.015
Zuo G, Wang Y, Teo W, Xian Q, Zhao Y (2021) Direct Z-scheme TiO2–ZnIn2S4 nanoflowers for cocatalyst-free photocatalytic water splitting. Appl Catal B 291:120126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120126
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51502116), the Special Funding of China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2016T90425), and the Innovative Practice Postdoctoral Project Foundation of Jiangmen City in China (No. JMBSH2021A03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jianmei Pan: conceptualization, methodology, software, resources, project administration, writing — review and editing, supervision. Hu Liu: methodology, data curation, writing — original draft, software, writing — review and editing. Keyu E: visualization, investigation, software. Yi Guan: supervision. Wenbo Gou: software, validation. Peng Wang: investigation, validation. Ze Du: formal analysis. Chenfei Ma: software.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
The authors affirm that human research participants provided informed consent for publication of the images in Fig. 1 a, b, and c.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: George Z. Kyzas
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Pan, J., E, K. et al. Selective efficient photocatalytic degradation of antibiotics and direct Z-type migration pathway for hierarchical core–shell TiO2/g-C3N4 composites. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 4582–4594 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31358-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31358-y