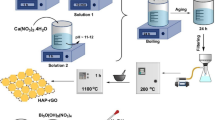
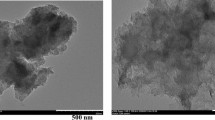
Abstract
Spent carbon cathode (SCC) is a hazardous waste from the aluminum electrolysis industry. It is commonly used as a carbon source in the current disposal and recovery strategies, such as combustion, or as a reductant for smelting. The novelty of this study is to propose a strategy for recycling SCC as a graphite resource and to investigate the unique structural characteristics and adsorption properties of graphene oxide produced from this low temperature graphitized carbon. The adsorption kinetics and isotherms of SCC-GO on methylene blue (MB) were studied and compared with the GO prepared from natural flake graphite (NFG) and artificial graphite (AG). The results show that SCC-GO exhibits the highest adsorption rate and adsorption capacity (647.83 mg/g) for MB, which is much higher than NFG-GO (451.22 mg/g) and AG-GO (533.12 mg/g). The analysis of the spectroscopy and morphology confirmed that SCC-GO has a high degree of crystal defects, oxidation, and surface wrinkle. Overall, this study reveals the unique structure of SCC-GO and highlights its significant scientific and application potential as an ultra-low temperature graphitized carbon. This research is also significant for recycling aluminum electrolytic cathode solid waste in the form of a graphite source.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are incorporated into the article and its online supplementary material.
References
Agarwal V, Zetterlund PB (2021) Strategies for reduction of graphene oxide—a comprehensive review. Chem Eng J 405:127018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127018
Ahmadijokani F, Ahmadipouya S, Molavi H et al (2020) Impact of scale, activation solvents, and aged conditions on gas adsorption properties of UiO-66. J Environ Manage 274:111155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111155
Al-Gaashani R, Najjar A, Zakaria Y et al (2019) XPS and structural studies of high quality graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide prepared by different chemical oxidation methods. Ceram Int 45:14439–14448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.04.165
Archana S, Jayanna BK, Ananda A et al (2021) Synthesis of nickel oxide grafted graphene oxide nanocomposites—a systematic research on chemisorption of heavy metal ions and its antibacterial activity. Environ Nanotechnology, Monit Manag 16:100486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2021.100486
Badenhorst H (2014) Microstructure of natural graphite flakes revealed by oxidation: limitations of XRD and Raman techniques for crystallinity estimates. Carbon N Y 66:674–690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2013.09.065
Bai KK, Zhou Y, Zheng H et al (2014) Creating one-dimensional nanoscale periodic ripples in a continuous mosaic graphene monolayer. Phys Rev Lett 113:86102. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.086102
Botas C, Pérez-Mas AM, Álvarez P et al (2013) Optimization of the size and yield of graphene oxide sheets in the exfoliation step. Carbon N Y 63:576–578
Brial V, Tran H, Sorelli L et al (2021) Evaluation of the reactivity of treated spent pot lining from primary aluminum production as cementitious materials. Resour Conserv Recycl 170:105584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105584
Casallas Caicedo FM, Vera López E, Agarwal A et al (2020) Synthesis of graphene oxide from graphite by ball milling. Diam Relat Mater 109:108064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2020.108064
Chang L, Cao Y, Peng W et al (2021) Highly efficient and selective recovery of Cu(II) from wastewater via ion flotation with amidoxime functionalized graphene oxide as nano collector. Sep Purif Technol 279:119674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119674
Chen R, Chen Y, Liang X et al (2022a) Oxidative exfoliation of spent cathode carbon: a two-in-one strategy for its decontamination and high-valued application. Chinese J Chem Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2022.10.020
Chen W, Salvatierra RV, Li JT et al (2023a) Flash recycling of graphite anodes. Adv Mater 35:2207303. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202207303
Chen Y, Li P, Bu X et al (2022b) Resource utilization strategies for spent pot lining: a review of the current state. Sep Purif Technol 300:121816
Chen Y, Li P, Bu X et al (2022c) In-depth purification of spent pot-lining by oxidation-expansion acid leaching—a comparative study. Sep Purif Technol 303:122313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.122313
Chen Y, Li S, Lin S et al (2023b) Promising energy-storage applications by flotation of graphite ores: a review. Chem Eng J 454:139994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.139994
Chen Z, Liu J, Chen L et al (2021) Emission-to-ash detoxification mechanisms of co-combustion of spent pot lining and pulverized coal. J Hazard Mater 418:126380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126380
Cheng P, Tang H, Dong Y et al (2021) Knowledge mapping of research on land use change and food security: a visual analysis using citespace and vosviewer. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18:102372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413065
Dell MB (2013) Reaction between carbon lining and hall bath. Essent Readings Light Met Electrode Technol Alum Prod 4:946–952. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118647745.ch125
Foo KY, Hameed BH (2010) Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem Eng J 156:2–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.09.013
Ho YS, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(98)00112-5
Jawi MA, Chow CM, Pujari S et al (2020) Environmental benefits of using spent pot lining (SPL) in cement production. In: Minerals, metals and materials series. Springer, pp 1251–1260
Ko S, Kwon YJ, Lee JU, Jeon YP (2020) Preparation of synthetic graphite from waste PET plastic. J Ind Eng Chem 83:449–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2019.12.018
Li S, Zheng Z, Liu S et al (2022) Ultrahigh thermal and electric conductive graphite films prepared by g-C3N4 catalyzed graphitization of polyimide films. Chem Eng J 430:132530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.132530
Liang C, Chen Y, Wu M et al (2021) Green synthesis of graphite from CO2 without graphitization process of amorphous carbon. Nat Commun 12:119. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-20380-0
Liao K, Li X, Xiao X, Jiang Y et al (2020) Local corrosion characteristics of a graphene-oxide-modified inner coating. J Cent South Univ 27:3213–3226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4541-5
Liu JB, Gong HS, Ye GL, Fei HL (2022) Graphene oxide-derived single-atom catalysts for electrochemical energy conversion. Rare Met 41:1703–1726. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-021-01904-z
Maruyama S, Fukutsuka T, Miyazaki K et al (2018) Lithium-ion intercalation and deintercalation behaviors of graphitized carbon nanospheres. J Mater Chem A 6:1128–1137. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ta07902h
Ming X, Wei A, Liu Y et al (2022) 2D-topology-seeded graphitization for highly thermally conductive carbon fibers. Adv Mater 34:2201867. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202201867
Muzyka R, Drewniak S, Pustelny T et al (2021) Characterization of graphite oxide and reduced graphene oxide obtained from different graphite precursors and oxidized by different methods using raman spectroscopy statistical analysis. Materials (Basel) 14:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040769
Padhi DK, Parida KM, Singh SK (2016) Mechanistic aspects of enhanced congo red adsorption over graphene oxide in presence of methylene blue. J Environ Chem Eng 4:3498–3511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.07.011
Reynosa-Martínez AC, Tovar GN, Gallegos WR et al (2020) Effect of the degree of oxidation of graphene oxide on As(III) adsorption. J Hazard Mater 384:121440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121440
Robshaw TJ, Atkinson D, Howse JR et al (2022) Recycling graphite from waste aluminium smelter Spent Pot Lining into lithium-ion battery electrode feedstock. Clean Prod Lett 2:100004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clpl.2022.100004
Surekha G, Krishnaiah KV, Ravi N, Padma Suvarna R (2020) FTIR, Raman and XRD analysis of graphene oxide films prepared by modified Hummers method. In: Journal of Physics: Conference Series. IOP Publishing, p 12012
Tang H, Zhao Y, Shan S et al (2018) Wrinkle- and edge-adsorption of aromatic compounds on graphene oxide as revealed by atomic force microscopy, molecular dynamics simulation, and density functional theory. Environ Sci Technol 52:7689–7697. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b00585
Thambiliyagodage CJ, Ulrich S, Araujo PT, Bakker MG (2018) Catalytic graphitization in nanocast carbon monoliths by iron, cobalt and nickel nanoparticles. Carbon N Y 134:452–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2018.04.002
Xia S, Yang H, Lu W et al (2022) Fe–Co based synergistic catalytic graphitization of biomass: influence of the catalyst type and the pyrolytic temperature. Energy 239:122262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.122262
Yadav KK, Singh H, Rana S et al (2020) Utilization of waste coir fibre architecture to synthesize porous graphene oxide and their derivatives: an efficient energy storage material. J Clean Prod 276:124240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124240
Yan H, Tao X, Yang Z et al (2014) Effects of the oxidation degree of graphene oxide on the adsorption of methylene blue. J Hazard Mater 268:191–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.01.015
Yang K, Zhao Z, Xin X et al (2019) Graphitic carbon materials extracted from spent carbon cathode of aluminium reduction cell as anodes for lithium ion batteries: converting the hazardous wastes into value-added materials. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 104:201–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2019.09.012
Yu D, Chattopadhyay K (2018) Enhancement of the nickel converter slag-cleaning operation with the addition of spent potlining. Int J Miner Metall Mater 25:881–891. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-018-1637-0
Yu D, Paktunc D (2019) Carbothermic reduction of chromite fluxed with aluminum spent potlining. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China (English Ed) 29:200–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64929-5
Zeng X, Bin ZB, Qiu W et al (2022) A review of the preparation and applications of wrinkled graphene oxide. Xinxing Tan Cailiao/New Carbon Mater 37:290–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-5805(22)60594-8
Zhan P, Xu J, Wang J et al (2022) A review of recycled aggregate concrete modified by nanosilica and graphene oxide: materials, performances and mechanism. J Clean Prod 375:134116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134116
Zhang S, Liu Q, Zhang H et al (2020) Structural order evaluation and structural evolution of coal derived natural graphite during graphitization. Carbon N Y 157:714–723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.10.104
Zhao L, Ding B, Qin XY et al (2022) Revisiting the roles of natural graphite in ongoing lithium-ion batteries. Adv Mater 34:2106704. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202106704
Zhao Q, Wang Y, Dong H et al (2021) Preparation of anode materials for lithium-ion batteries by spent carbon anode from electrolytic aluminum. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105932
Zhao S, Wen Y, Du C et al (2020) Introduction of vacancy capture mechanism into defective alumina microspheres for enhanced adsorption of organic dyes. Chem Eng J 402:126180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126180
Zhou Q, Wen B, Zhang J et al (2023) Influence of graphite Gibbs surface free energy on the initial viscosity and stability of traditional anode slurry in lithium-ion batteries. J Cent South Univ 30:665–676. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-023-5250-7
Funding
The fellowship of the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2022M722872) supported this work. This paper was also funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Henan (No. 232300421320), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52204296), and the Henan Province Science and Technology Research Project (China) (No. 222102320398).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PL: methodology, resources, writing—original draft. YC: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, resources, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. HZ: software, writing—review and editing. XB: writing—review and editing. LW: writing—review and editing. XL: conceptualization, supervision, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
No human or superior animals have been used in this work.
Consent to participate
All authors agreed with the content, and all gave explicit consent to submit.
Consent for publication
All authors agreed with the publication of the manuscript in Environmental Science and Pollution Research.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: George Z. Kyzas
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, ., Chen, Y., Zeng, H. et al. Structure characteristics and adsorption performance of graphene oxide prepared by spent carbon cathode—an ultra-low temperature graphitized carbon material. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 120515–120527 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30884-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30884-z