Abstract
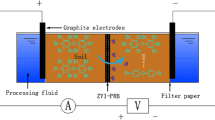
2,4-Dichlorophenol (2,4-DCP) is difficult to degrade rapidly in the environment due to its stable chemical properties, so it was easy to lead to serious chlorophenol pollution in soil. Consequently, a remediation method which is efficient, safe, and economical is required. In this study, electrokinetic (EK) remediation was used to transfer sodium persulfate (Na2S2O8) into soil to degrade 2,4-DCP, and the effect of several factors (including the addition location of Na2S2O8, applied voltage, and running time) on the remediation efficiency was explored. The concentration of Na2S2O8, residual efficiency of 2,4-DCP and distribution characteristics of pH, and electrical conductivity were analyzed. The results showed that the cathode was the optimal position to add Na2S2O8. Under this condition, Na2S2O8 was uniformly distributed in the whole soil column through electromigration. The optimal removal efficiency of 2,4-DCP in soil by adding Na2S2O8 was approximately 26% when the voltage gradient was 1.0 V/cm and the operating time was 9 days, which was mainly due to the degradation of S2O82−.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Chen H, Zhang ZL, Yang ZL, Yang Q, Li B, Bai ZY (2015) Heterogeneous fenton-like catalytic degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in water with FeS. Chem Eng J 273:481–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.03.079
Chen DS, Zhang Y, Lang JL, Zhou Y, Li Y, Guo XR, Wang WL, Liu B (2019) Evaluation of different control measures in 2014 to mitigate the impact of ship emissions on air quality in the Pearl River Delta China. Atmospheric Environ 216:116911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2019.116911
Chen YX, Zhi D, Zhou YY, Huang AQ, Wu SK, Yao B, Tang YF, Sun CR (2021) Electrokinetic techniques, their enhancement techniques and composite techniques with other processes for persistent organic pollutants remediation in soil: a review. J Ind Eng Chem 97:163–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2021.03.009
Chowdhury AIA, Gerhard JI, Reynolds D, Sleep BE, O’Carroll DM (2017) Electrokinetic-enhanced permanganate delivery and remediation of contaminated low permeability porous media. Water Res 113:215–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.02.005
Dong HY, Qiang ZM, Hu J, Sans C (2017) Accelerated degradation of iopamidol in iron activated persulfate systems: roles of complexing agents. Chem Eng J 316:288–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.01.099
Fan GP, Cang L, Fang GD, Qin WX, Ge LQ, Zhou DM (2014) Electrokinetic delivery of persulfate to remediate PCBs polluted soils: effect of injection spot. Chemosphere 117:410–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.08.006
Gan L, Li BB, Guo MY, Weng XL, Wang T, Chen ZL (2018) Mechanism for removing 2,4-dichlorophenol via adsorption and Fenton-like oxidation using iron-based nanoparticles. Chemosphere 206:168–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.04.162
Hoekstra EJ, De Weerd H, De Leer EWB, Brinkman UAT (1999) Natural formation of chlorinated phenols, dibenzo-p-dioxins, and dibenzofurans in soil of a Douglas fir forest. Environ Sci Technol 33:2543–2549. https://doi.org/10.1021/es9900104
Isosaari P, Piskonen R, Ojala P, Voipio S, Eilola K, Lehmus E, Itavaara M (2007) Integration of electrokinetics and chemical oxidation for the remediation of creosote-contaminated clay. J Hazard Mater 144:538–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.10.068
Li J, Fu Q, Liao Q, Zhu X, Ye DD, Tian X (2009) Persulfate: a self-activated cathodic electron acceptor for microbial fuel cells. J Power Sources 194:269–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2009.04.055
Li JH, Zhang BG, Sun YY, Guo HY (2011) Simultaneous and repetitious removal of 2,4-dichlorophenol and copper from soils using an aqueous solution of ethyl-lactate-amended EDDS. Soil & Sediment Contam 20:605–616. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320383.2011.587851
Li RC, Gao Y, Jin XY, Chen ZL, Megharaj M, Naidu R (2015) Fenton-like oxidation of 2,4-DCP in aqueous solution using iron-based nanoparticles as the heterogeneous catalyst. J Colloid Interface Sci 438:87–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2014.09.082
Li X, Zhou MH, Pan YW, Xu LT (2017) Pre-magnetized Fe-0/persulfate for notably enhanced degradation and dechlorination of 2,4-dichlorophenol. Chem Eng J 307:1092–1104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.140
Liang CJ, Huang CF, Mohanty N, Kurakalva RM (2008) A rapid spectrophotometric determination of persulfate anion in ISCO. Chemosphere 73:1540–1543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.08.043
Liu L, Lin S, Zhang W, Farooq U, Shen GX, Hu SQ (2018) Kinetic and mechanistic investigations of the degradation of sulfachloropyridazine in heat-activated persulfate oxidation process. Chem Eng J 346:515–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.04.068
Liu ZB, Ren X, Duan XY, Sarmah AK, Zhao XS (2023) Remediation of environmentally persistent organic pollutants (POPs) by persulfates oxidation system (PS): A review. Sci Total Environ 863:160818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160818
Manokararajah K, Ranjan RS (2005) Electrokinetic denitrification of nitrates in a nitrate contaminated silty loam soil. Appl Eng Agric 21:541–549. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.18438
Michalowicz J, Posmyk M, Duda W (2009) Chlorophenols induce lipid peroxidation and change antioxidant parameters in the leaves of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Plant Physiol 166:559–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2008.09.011
Miklos DB, Remy C, Jekel M, Linden KG, Drewes JE, Hubner U (2018) Evaluation of advanced oxidation processes for water and wastewater treatment—a critical review. Water Res 139:118–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.03.042
Paixao IC, Lopez-Vizcaino R, Solano AMS, Martinez-Huitle CA, Navarro V, Rodrigo MA, dos Santos EV (2020) Electrokinetic-Fenton for the remediation low hydraulic conductivity soil contaminated with petroleum. Chemosphere 248:126029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126029
Reynolds DA, Jones EH, Gillen M, Yusoff I, Thomas DG (2008) Electrokinetic migration of permanganate through low-permeability media. Ground Water 46:629–637. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.2008.00415.x
Rodriguez-Hernandez MC, De la-Cruz RFG, Leyva E, Navarro-Tovar G (2017) Typha latifolia as potential phytoremediator of 2,4-dichlorophenol: analysis of tolerance, uptake and possible transformation processes. Chemosphere 173:190–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.12.043
Roulier M, Kemper M, Al-Abed S, Murdoch L, Cluxton P, Chen JL, Davis-Hoover W (2000) Feasibility of electrokinetic soil remediation in horizontal Lasagna (TM) cells. J Hazard Mater 77:161–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3894(00)00241-7
Shan YP, Qin JY, Harms H, Wick LY (2020) Electrokinetic effects on the interaction of phenanthrene with geo-sorbents. Chemosphere 242:125161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125161
Shi Y, Chen Y (2017) Research status and development direction of contaminated soil bioremediation technology in China. World Sci-Tech R&D 39: 24–32. http://dx.chinadoi.cn/https://doi.org/10.16507/j.issn.1006-6055.2017.02.002
Song Y, Cang L, Fang GD, Ata-Ul-Karim ST, Xu HT, Zhou DM (2018) Electrokinetic delivery of anodic in situ generated active chlorine to remediate diesel-contaminated sand. Chem Eng J 337:499–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.12.122
Song W, Li J, Wang ZY, Zhang XL (2019) A mini review of activated methods to persulfate-based advanced oxidation process. Water Sci Technol 79:573–579. https://doi.org/10.2166/wcc.2018.168
Suanon F, Tang L, Sheng HJ, Fu YH, Xiang LL, Wang ZQ, Shao XW, Mama D, Jiang X, Wang F (2020) Organochlorine pesticides contaminated soil decontamination using TritonX-100-enhanced advanced oxidation under electrokinetic remediation. J Hazard Mater 393:122388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122388
Tsitonaki A, Petri B, Crimi M, Mosbaek H, Siegrist RL, Bjerg PL (2010) In situ chemical oxidation of contaminated soil and groundwater using persulfate: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 40:55–91. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643380802039303
Usman M, Tascone O, Faure P, Hanna K (2014) Chemical oxidation of hexachlorocyclohexanes (HCHs) in contaminated soils. Sci Total Environ 476:434–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.01.027
Wang Q, Lu XH, Cao Y, Ma J, Jiang J, Bai XF, Hu T (2017) Degradation of Bisphenol S by heat activated persulfate: kinetics study, transformation pathways and influences of co-existing chemicals. Chem Eng J 328:236–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.07.041
Wu MZ, Reynolds DA, Fourie A, Prommer H, Thomas DG (2012) Electrokinetic in situ oxidation remediation: assessment of parameter sensitivities and the influence of aquifer heterogeneity on remediation efficiency. J Contam Hydrol 136:72–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2012.04.005
Xie S, Zhang J, Shen H, He L, Chen J, Zhang X, Liu F (2017) Research progress on the properties, harmfulness, and the determination methods of chlorophenols. Chin J Anal Lab 36:1351–1355. http://dx.chinadoi.cn/https://doi.org/10.13595/j.cnki.issn1000-0720.2017.0290
Yang GCC, Yeh CF (2011) Enhanced nano-Fe3O4/S2O82- oxidation of trichloroethylene in a clayey soil by electrokinetics. Sep Purif Technol 79:264–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2011.03.003
You SJ, Zhao QL, Zhang JN, Jiang JQ, Zhao SQ (2006) A microbial fuel cell using permanganate as the cathodic electron acceptor. J Power Sources 162:1409–1415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.07.063
Zhi D, Lin YH, Jiang L, Zhou YY, Huang AQ, Yang J, Luo L (2020) Remediation of persistent organic pollutants in aqueous systems by electrochemical activation of persulfates: a review. J Environ Manag 260:110125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110125
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22278263).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s design. Yunfeng Xu provided conceptualization and funding acquisition. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Qinqin Lu and Jianfang Fu. Xiaoxun Huang contributed to the draft of the manuscript and analysis. Yangwei Qu and Xueping Chen commented on the manuscript. Weiguo Gao contributed to writing review and editing of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
We confirm that the manuscript has been read and approved by all named authors.
Consent for publication
We confirm that the manuscript has been read and approved by all named authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Kitae Baek
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Huang, X., Qu, Y. et al. Remediation of 2,4-dichlorophenol-contaminated soil by electrokinetic delivery of persulfate technology. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 3926–3937 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30450-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30450-7