Abstract
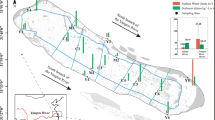
Following the alarming reports of microplastic pollution in the marine environment, increased attention has been given to microplastics in other environmental media. Despite the attention, there is limited research available on the depth-distribution of microplastics in freshwater. Specifically, in the case of water sources used for drinking or tap, the height of intake facilities varies, and it is highly likely that there is a correlation between the vertical distribution of microplastics and these water intake structures. Further, because the size of microplastics varies widely in the environment, the commonly used sampling devices are not suitable for selectively extracting microplastics without causing cross-contamination. Thus, we developed a suitable device for microplastics of size 5–20 µm and studied microplastic distribution in freshwater at various depths by considering various types of microplastics and aqueous systems. Lake and river, two major water sources, were selected for the study of microplastics distribution in water system. The microplastic distribution characteristics in both water systems showed that polypropylene and polyethylene were the most abundant across all depths because of their production volume. Plastic types with higher density were found only at the lower layers, and polystyrene was found in the upper layers because of the environmental effects on its buoyancy caused pore diameter and surface area. The lake and river had higher microplastic distribution in the lower layer and upper layer, respectively. This was because the flow rate in river was higher than that of lake. The higher flow rate reduced the settling velocity in river. Thus, hydrodynamic stability influences the vertical distribution and concentrations of microplastics in the water systems. These results are expected to be used for understanding the behavioral characteristics of microplastics in water systems and to manage water sources.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Aigars J, Barone M, Suhareva N, Putna-Nimane I, Dimante-Deimantovica I (2021) Occurrence and spatial distribution of microplastics in the surface waters of the Baltic Sea and the Gulf of Riga. Mar Pollut Bull 172:112860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112860
Alimi OS, Budarz JF, Hernandez LM, Tufenkji N (2018) Microplastics and nanoplastics in aquatic environments: aggregation, deposition, and enhanced contaminant transport. Environ Sci Technol 52(4):1704–1724. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b05559
Amrutha K, Warrier AK (2020) The first report on the source-to-sink characterization of microplastic pollution from a riverine environment in tropical India. Sci Total Environ 739:140377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140377
Andrady AL (2011) Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar Pollut Bull 62(8):1596–1605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.05.030
Bikker J, Lawson J, Wilson S, Rochman CM (2020) Microplastics and other anthropogenic particles in the surface waters of the Chesapeake Bay. Mar Pollut Bull 156:111257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111257
Chen HL, Selvam SB, Ting KN, Gibbins CN (2021) Microplastic pollution in freshwater systems in Southeast Asia: contamination levels, sources, and ecological impacts. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:54222–54237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15826-x
Coppock RL, Cole M, Lindeque PK, Queirós AM, Galloway TS (2017) A small-scale, portable method for extracting microplastics from marine sediments. Environ Pollut 230:829–837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.07.017
Corcoran PL, Belontz SL, Ryan K, Walzak MJ (2019) Factors controlling the distribution of microplastic particles in benthic sediment of the Thames River, Canada. Environ Sci Technol 54(2):818–825. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b04896
Dai Z, Zhang H, Zhou Q, Tian Y, Chen T, Tu C, Fu C, Luo Y (2018) Occurrence of microplastics in the water column and sediment in an inland sea affected by intensive anthropogenic activities. Environ Pollut 242:1557–1565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.07.131
Di M, Wang J (2018) Microplastics in surface waters and sediments of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci Total Environ 616:1620–1627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.150
Fu L, Li J, Wang G, Luan Y, Dai W (2021) Adsorption behavior of organic pollutants on microplastics. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 217:112207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112207
Geyer R, Jambeck JR, Law KL (2017) Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci Adv 3:e1700782. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1700782
Hernandez E, Nowack B, Mitrano DM (2017a) Polyester textiles as a source of microplastics from households: a mechanistic study to understand microfiber release during washing. Environ Sci Technol 51(12):7036–7046. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b01750
Hernandez LM, Yousefi N, Tufenkji N (2017b) Are there nanoplastics in your personal care products? Environ Sci Technol Lett 4(7):280–285. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.7b00187
Hidalgo-Ruz V, Gutow L, Thompson RC, Thiel M (2012) Microplastics in the marine environment: a review of the methods used for identification and quantification. Environ Sci Technol 46(6):3060–3075. https://doi.org/10.1021/es2031505
Holmes LA, Turner A, Thompson RC (2014) Interactions between trace metals and plastic production pellets under estuarine conditions. Mar Chem 167:25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2014.06.001
Horton AA, Walton A, Spurgeon DJ, Lahive E, Svendsen C (2017) Microplastics in freshwater and terrestrial environments: evaluating the current understanding to identify the knowledge gaps and future research priorities. Sci Total Environ 586:127–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.01.190
Hüffer T, Weniger A-K, Hofmann T (2018) Sorption of organic compounds by aged polystyrene microplastic particles. Environ Pollut 236:218–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.01.022
Imhof HK, Schmid J, Niessner R, Ivleva NP, Laforsch C (2012) A novel, highly efficient method for the separation and quantification of plastic particles in sediments of aquatic environments. Limnol Oceanogr Methods 10(7):524–537. https://doi.org/10.4319/lom.2012.10.524
Jódar-Reyes AB, Martín-Rodríguez A, Ortega-Vinuesa JL (2006) Effect of the ionic surfactant concentration on the stabilization/destabilization of polystyrene colloidal particles. J Colloid Interface Sci 298(1):248–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2005.12.035
Ju S, Yi J, Lee J, Kim J, Lim C, Lee J, Kim K, Yoon Y (2023) High-efficiency microplastic sampling device improved using CFD analysis. Sustainability 15(5):3907. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15053907
Karlsson TM, Kärrman A, Rotander A, Hassellöv M (2020) Comparison between manta trawl and in situ pump filtration methods, and guidance for visual identification of microplastics in surface waters. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(5):5559–5571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07274-5
Kumar R, Sharma P, Verma A, Jha PK, Singh P, Gupta PK, Chandra R, Prasad PVV (2021) Effect of physical characteristics and hydrodynamic conditions on transport and deposition of microplastics in riverine ecosystem. Water 13(19):2710. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192710
Law KL, Thompson RC (2014) Microplastics in the seas. Science 345(6193):144–145. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1254065
Li C, Busquets R, Campos LC (2020) Assessment of microplastics in freshwater systems: a review. Sci Total Environ 707:135578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135578
Liro M, Emmerik TV, Wyżga B, Liro J, Mikuś P (2020) Macroplastic storage and remobilization in rivers. Water 12(7):2055. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12072055
Liu F, Olesen KB, Borregaard AR, Vollertsen J (2019a) Microplastics in urban and highway stormwater retention ponds. Sci Total Environ 671:992–1000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.416
Liu G, Zhu Z, Yang Y, Sun Y, Yu F, Ma J (2019b) Sorption behavior and mechanism of hydrophilic organic chemicals to virgin and aged microplastics in freshwater and seawater. Environ Pollut 246:26–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.11.100
Liu Y, Zhang J, Cai C, He Y, Chen L, Xiong X, ... Liu W (2020) Occurrence and characteristics of microplastics in the Haihe River: an investigation of a seagoing river flowing through a megacity in northern China. Environ Pollut 262:114261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114261
Mani T, Burkhardt-Holm P (2020) Seasonal microplastics variation in nival and pluvial stretches of the Rhine River–from the Swiss catchment towards the North Sea. Sci Total Environ 707:135579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135579
McDevitt JP, Criddle CS, Morse M, Hale RC, Bott CB, Rochman CM (2017) Addressing the issue of microplastics in the wake of the Microbead-Free Waters Act—a new standard can facilitate improved policy. Environ Sci Technol 51(12):6611–6617. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b05812
Miao L, Gao Y, Adyel TM, Huo Z, Liu Z, Wu J, Hou J (2021) Effects of biofilm colonization on the sinking of microplastics in three freshwater environments. J Hazard Mater 413:125370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125370
Montoto-Martínez T, Meléndez-Díez C, Melián-Ramírez A, Hernández-Brito JJ, Gelado-Caballero MD (2022) Comparison between the traditional Manta net and an innovative device for microplastic sampling in surface marine waters. Mar Pollut Bull 185:114237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.114237
Mu J, Qu L, Jin F, Zhang S, Fang C, Ma X, Zhang W, Huo C, Cong Y, Wang J (2019a) Abundance and distribution of microplastics in the surface sediments from the northern Bering and Chukchi Seas. Environ Pollut 245:122–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.10.097
Mu J, Zhang S, Qu L, Jin F, Fang C, Ma X, Zhang W, Wang J (2019b) Microplastics abundance and characteristics in surface waters from the Northwest Pacific, the Bering Sea, and the Chukchi Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 143:58–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.04.023
Müller A, Becker R, Dorgerloh U, Simon F-G, Braun U (2018) The effect of polymer aging on the uptake of fuel aromatics and ethers by microplastics. Environ Pollut 240:639–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.04.127
Nizzetto L, Bussi G, Futter MN, Butterfield D, Whitehead PG (2016) A theoretical assessment of microplastic transport in river catchments and their retention by soils and river sediments. Environ Sci Process Impacts 18(8):1050–1059. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6em00206d
Nuelle M-T, Dekiff JH, Remy D, Fries E (2014) A new analytical approach for monitoring microplastics in marine sediments. Environ Pollut 184:161–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.07.027
Osman AI, Hosny M, Eltaweil AS, Omar S, Elgarahy AM, Farghali M, Yap P-S, Wu YS, Nagandran S, Batumalaie K, Gopinath SCB, John OD, Sekar M, Saikia T, Karunanithi P, Hatta M, Akinyede KA (2023) Microplastic sources, formation, toxicity and remediation: a review. Environ Chem Lett. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-023-01593-3
Panko JM, Chu J, Kreider ML, Unice KM (2013) Measurement of airborne concentrations of tire and road wear particles in urban and rural areas of France, Japan, and the United States. Atmos Environ 72:192–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.01.040
Prata JC, da Costa JP, Duarte AC, Rocha-Santos T (2019) Methods for sampling and detection of microplastics in water and sediment: a critical review. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem 110:150–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.10.029
Quinn B, Murphy F, Ewins C (2017) Validation of density separation for the rapid recovery of microplastics from sediment. Anal Methods 9(9):1491–1498. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ay02542k
Ramsperger AFRM, Narayana VKB, Gross W, Mohanraj J, Thelakkat M, Greiner A, Schmalz H, Kress H, Laforsch C (2020) Environmental exposure enhances the internalization of microplastic particles into cells. Sci Adva 6(50):eabd1211. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abd1211
Rochman CM, Kross SM, Armstrong JB, Bogan MT, Darling ES, Green SJ, Smyth AR, Veríssimo D (2015) Scientific evidence supports a ban on microbeads. Environ Sci Technol 49(18):10759–10761. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b03909
Sarkar DJ, Sarkar SD, Mukherjee S, Das BK (2021) Impact and fate of microplastics in the riverine ecosystem. In: Contaminants in drinking and wastewater sources, pp. 95–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-4599-3_4
Shim WJ, Song YK, Hong SH, Jang M (2016) Identification and quantification of microplastics using Nile red staining. Mar Pollut Bull 113(1–2):469–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.10.049
Song Z, Yang X, Chen F, Zhao F, Zhao Y, Ruan L, ... Yang Y (2019) Fate and transport of nanoplastics in complex natural aquifer media: effect of particle size and surface functionalization. Sci Total Environ 669:120–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.102
Sun Y, Yuan J, Zhou T, Zhao Y, Yu F, Ma J (2020) Laboratory simulation of microplastics weathering and its adsorption behaviors in an aqueous environment: a systematic review. Environ Pollut 265:114864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114864
Thompson RC, Olsen Y, Mitchell RP, Davis A, Rowland SJ, John AWG, McGonigle D, Russell AE (2004) Lost at sea: where is all the plastic? Science 304:838–838. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1094559
Tien C-J, Wang Z-X, Chen CS (2020) Microplastics in water, sediment and fish from the Fengshan River system: relationship to aquatic factors and accumulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by fish. Environ Pollut 265:114962. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114962
Waldschläger K, Schüttrumpf H (2019) Effects of particle properties on the settling and rise velocities of microplastics in freshwater under laboratory conditions. Environ Sci Technol 53(4):1958–1966. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b06794
Watkins L, McGrattan S, Sullivan PJ, Walter MT (2019) The effect of dams on river transport of microplastic pollution. Sci Total Environ 664:834–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.028
Wu F, Pennings SC, Tong C, Xu Y (2020a) Variation in microplastics composition at small spatial and temporal scales in a tidal flat of the Yangtze Estuary, China. Sci Total Environ 699:134252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134252
Wu M, Yang C, Du C, Liu H (2020b) Microplastics in waters and soils: occurrence, analytical methods and ecotoxicological effects. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 202:110910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110910
Yan M, Wang L, Dai Y, Sun H, Liu C (2021) Behavior of microplastics in inland waters: aggregation, settlement, and transport. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 107(4):700–709. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-03087-2
Zhang L, Liu J, Xie Y, Zhong S, Yang B, Lu D, Zhong Q (2020) Distribution of microplastics in surface water and sediments of Qin River in Beibu Gulf, China. Sci Total Environ 708:135176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135176
Zhao S, Danley M, Ward JE, Li D, Mincer TJ (2017) An approach for extraction, characterization and quantitation of microplastic in natural marine snow using Raman microscopy. Anal Methods 9(9):1470–1478. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ay02302a
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Korea Testing & Research Institute (KTR) for providing synthesized polymers and the Ministry of Environment (MOE) of Republic of Korea for providing temperature, suspended solid concentration, flow rate, and precipitation of the sampling site.
Funding
This research was supported by Korea Environment Industry and Technology Institute (KEITI) through Measurement and Risk assessment Program for Management of Microplastics Project, funded by Korea Ministry of Environment (MOE) (Grant numbers 2020003110005) and National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. 2020R1A2C2101347).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation and data collection were performed by Junho Lee, Seonghyun Ju, Chaehwi Lim, Homin Kye, Jiyoon Kim, and Jihoon Lee. Analysis was performed by Kyung Tae Kim, Hye-Won Yu, Ingyu Lee, Hyunook Kim, and Yeojoon Yoon. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Junho Lee, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Thomas D. Bucheli
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J., Ju, S., Lim, C. et al. Evaluation of vertical distribution characteristics of microplastics under 20 μm in lake and river waters in South Korea. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 99875–99884 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29409-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29409-5