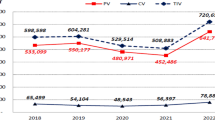
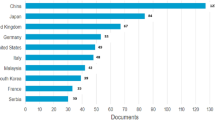
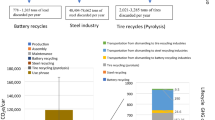
Abstract
Effective end-of-life vehicle (ELV) management is crucial for minimizing the environmental and health impacts of Indonesia’s growing automotive industry. However, proper ELV management has received limited attention. To bridge this gap, we conducted a qualitative study to identify barriers to effective ELV management in Indonesia’s automotive sector. Through in-depth interviews with key stakeholders and a strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats analysis, we identified internal and external factors influencing ELV management. Our findings reveal major barriers, including inadequate government regulation and enforcement, insufficient infrastructure and technology, low education and awareness, and a lack of financial incentives. We also identified internal factors such as limited infrastructure, inadequate strategic planning, and challenges in waste management and cost collection methods. Based on these findings, we recommend a comprehensive and integrated approach to ELV management involving enhanced coordination among government, industry, and stakeholders. The government should enforce regulations and provide financial incentives to encourage proper ELV management practices. Industry players should invest in technology and infrastructure to support effective ELV treatment. By addressing these barriers and implementing our recommendations, policymakers can develop sustainable ELV management policies and decisions in Indonesia’s fast-paced automotive sector. Our study contributes valuable insights to guide the development of effective strategies for ELV management and sustainability in Indonesia.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aderoju OM, Dias GA, Alberto GJ (2018) A spaced-based concept in municipal solid waste management and monitoring in developing countries. Int J Environ Impact: Manag Mitig Rec 1(4):482–490. https://doi.org/10.2495/EI-V1-N4-482-490
Akinyode BF, Khan TH (2018) Step by step approach for qualitative data analysis. Int J Built Environ Sustain 5(3):163–174. https://doi.org/10.11113/ijbes.v5.n3.267
Andersson M, Ljunggren Söderman M, Sandén BA (2019) Challenges of recycling multiple scarce metals: the case of Swedish ELV and WEEE recycling. Res Policy 63:101403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2019.101403
Ayçin E, Kayapinar Kaya S (2021) Towards the circular economy: analysis of barriers to implementation of Turkey’s zero waste management using the fuzzy DEMATEL method. Waste Manag Res 39(8):1078–1089. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X20988781
Azevedo BD, Scavarda LF, Caiado RGG, Fuss M (2021) Improving urban household solid waste management in developing countries based on the German experience. Waste Manag 120:772–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2020.11.001
Bekele D, Silshi Merid A (2020) Determinants of poverty in rural Ethiopia: evidence from Tenta woreda, Amhara Region. J Sustain Rural Dev 3(1):3–14. https://doi.org/10.32598/JSRD.02.02.40
Beloborodko A, Romagnoli F, Rosa M, Disanto C, Salimbeni R et al (2015) SWOT analysis approach for advancement of waste-to-energy cluster in Latvia. Energy Procedia 72:163–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2015.06.023
Bening CR, Kahlert S, Asiedu E (2022) The true cost of solving the plastic waste challenge in developing countries: the case of Ghana. J Clean Prod 330:129649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129649
Bui TD, Tsai FM, Tseng ML, Ali MDH (2020) Identifying sustainable solid waste management barriers in practice using the fuzzy Delphi method. Resour Conserv Recycl 154:104625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104625
Chauhan A, Singh A, Jharkharia S (2018) An interpretive structural modeling (ISM) and decision-making trail and evaluation laboratory (DEMATEL) method approach for the analysis of barriers of waste recycling in India. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 68(2):100–110. https://doi.org/10.1080/10962247.2016.1249441
Chen D, Faibil D, Agyemang M (2020) Evaluating critical barriers and pathways to implementation of e-waste formalization management systems in Ghana: a hybrid BWM and fuzzy TOPSIS approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(35):44561–44584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10360-8
Dabic-Miletic S, Simic V, Karagoz S (2021) End-of-life tire management: a critical review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:68053–68070. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16263-6
Dzwigo H, Trushkina N, Kwilinski A (2021) The organizational and economic mechanism of implementing the concept of green logistics. Virt Econ 4(2):41–75. https://doi.org/10.34021/ve.2021.04.02(3)
Galvin R (2015) How many interviews are enough? Do qualitative interviews in building energy consumption research produce reliable knowledge? J Build Eng 1:2–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2014.12.001
Guo W, Xi B, Huang C, Li J, Tang Z et al (2021) Solid waste management in China: policy and driving factors in 2004–2019. Resour Conserv Recycl 173:105727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105727
Hamid N, Setyowati DL, Juhadi Priyanto AS, Suswanti Royyani MA, Aroyandini EN (2021) Sustainable development of the coastal environment through participatory mapping of abrasion-prone areas. J Environ Manag Tour 12(7):1997–2010. https://doi.org/10.14505/jemt.v12.7(55).24
Hoang AQ, Takahashi S, Tue NM, Tuyen LH, Tran TM et al (2023) Occurrence, emission sources, and risk assessment of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and current-use brominated flame retardants in settled dust from end-of-life vehicle processing, urban, and rural areas, northern Vietnam. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(1):2061–2074. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22396-z
Ismail R, Sitinjak C, Tahir Z, Che Rose RA, Mat Yazid MR et al (2023) A model analysis on the knowledge, attitude, and readiness of ELVs policy among Malaysians: a cross-sectional study. Front Built Environ 8:270. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbuil.2022.1038563
Karagoz S, Aydin N, Simic V (2020a) End-of-life vehicle management: a comprehensive review. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 22(2):416–442. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-019-00945-y
Karagoz S, Deveci M, Simic V, Aydin N, Bolukbas U (2020b) A novel intuitionistic fuzzy MCDM-based CODAS approach for locating an authorized dismantling center: a case study of Istanbul. Waste Manag Res 38(6):660–672. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X19899729
Karagoz S, Aydin N, Simic V (2022) A novel stochastic optimization model for reverse logistics network design of end-of-life vehicles: a case study of Istanbul. Environ Model Assess 27(4):599–619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-022-09834-5
Korica P, Cirman A, Žgajnar Gotvajn A (2022) Comparison of end-of-life vehicles management in 31 European countries: a LMDI analysis. Waste Manag Res 40(8):1156–1166. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242x221074118
Li J, Yu K, Gao P (2014) Recycling and pollution control of the end of life vehicles in China. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 16(1):31–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-013-0226-6
Lokahita B, Samudro G, Huboyo HS, Aziz M, Takahashi F (2019) Energy recovery potential from excavating municipal solid waste dumpsite in Indonesia. Energy Procedia 158:243–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2019.01.083
Ludlow J, Jalil-Vega F, Schmidt Rivera X, Garrido RA, Hawkes A et al (2021) Organic waste to energy: resource potential and barriers to uptake in Chile. Sustain Prod Consum 28:1522–1537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2021.08.017
Mairizal AQ, Sembada AY, Tse KM, Rhamdhani MA (2021) Electronic waste generation, economic values, distribution map, and possible recycling system in Indonesia. J Clean Prod 293:126096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126096
Maizel H (2021) School counselors in Israel as case managers in critical events: a qualitative study. Int J Adv Couns 43(3):243–264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10447-021-09440-2
Mekonnen GB, Tokai A (2020) A historical perspective of municipal solid waste management and recycling system in Japan: learning for developing countries. J Sustain Dev 13(3):85–101. https://doi.org/10.5539/jsd.v13n3p85
Nguyen DQ, Nguyen TT, Vu TC, Nguyen TD, Pham HH et al (2020) End-of-life vehicles management and initial estimation of the material flow from ELV in Viet Nam. Vietnam J Sci Technol 58(5A):138–149. https://doi.org/10.15625/2525-2518/58/5a/15223
Oduro-Appiah K, Scheinberg A, Afful A, de Vries N (2021) The contribution of participatory engagement strategies to reliable data gathering and inclusive policies in developing countries: municipal solid waste management data in the Greater Accra Metropolitan Area of Ghana. Afr J Sci Technol Innov Dev 13(6):735–746. https://doi.org/10.1080/20421338.2020.1797267
Olay-Romero E, Turcott-Cervantes DE, del Consuelo Hernández-Berriel M, de Cortázar AL, Cuartas-Hernández M et al (2020) Technical indicators to improve municipal solid waste management in developing countries: a case in Mexico. Waste Manag 107:201–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2020.03.039
Onwuegbuzie AJ, Leech NL, Collins KMT (2012) Qualitative analysis techniques for the review of the literature. Qual Rep 17(28):56. https://doi.org/10.46743/2160-3715/2012.1754
Parthan SR, Milke MW, Wilson DC, Cocks JH (2012) Cost function analysis for solid waste management: a developing country experience. Waste Manag Res 30(5):485–491. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X11425565
Shaohua L, Hanif I, Chaudhary MG (2023) Association between energy consumption preferences and macroeconomic stability: an empirical analysis from developing Asia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(7):18777–18784. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23352-7
Sharma NK, Sharma S (2020) Municipal solid waste management in developing countries: future challenges and possible opportunities. J Green Eng 10(10):8788–8797
Simic V (2019) Interval-parameter conditional value-at-risk two-stage stochastic programming model for management of end-of-life vehicles. Environ Model Assess 24(5):547–567. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-018-9648-9
Sitinjak C, Ismail R, Bantu E, Fajar R, Simanullang WF (2022a) Study of public perception toward end-of-life vehicles (ELV) management in Indonesia. Int J Sustain Dev Plan 17(4):1341–1347
Sitinjak C, Ismail R, Tahir Z, Fajar R, Simanullang WF et al (2022b) Acceptance of ELV management: the role of social influence, knowledge, attitude, institutional trust, and health issues. Sustain 14(6):10201. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141610201
Sodhi HS, Singh D, Singh BJ (2020) SWOT analysis of waste management techniques quantitatively. Int J Adv Oper Manag 12(2):103–121. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJAOM.2020.108260
Spoann V, Fujiwara T, Seng B, Lay C, Yim M (2019) Assessment of public-private partnership in municipal solid waste management in Phnom Penh, Cambodia. Sustain 11(5):1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11051228
Uddin I, Ullah A, Saqib N, Kousar R, Usman M (2023) Heterogeneous role of energy utilization, financial development, and economic development in ecological footprint: How far away are developing economies from developed ones. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:58378–58398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26584-3
Wang F, Cheng Z, Reisner A, Liu Y (2018) Compliance with household solid waste management in rural villages in developing countries. J Clean Prod 202:293–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.135
Wong YC, Mahyuddin N, Aminuddin AMR (2020) Development of thermal insulation sandwich panels containing end-of-life vehicle (ELV) headlamp and seat waste. Waste Manag 118:402–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2020.08.036
Availability of data and materials
All authors consent when it is published.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Material preparation and data collection were performed by Charli Sitinjak. The study conception and design were performed by Charli Sitinjak, Vladimir Simic, and Rozmi Ismail. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Charli Sitinjak and Vladimir Simic. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
All authors consent.
Consent for publication
All authors consent when it is published.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sitinjak, C., Simic, V., Ismail, R. et al. Barriers to effective implementation of end-of-life vehicle management in Indonesia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 87286–87299 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28554-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28554-1