Abstract
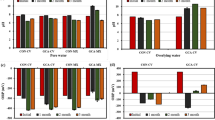
Ecological concrete (eco-concrete) is a kind of environment-friendly material with porous characteristics. In this study, the eco-concrete was used to remove the total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), and total organic carbon (TOC) in marine coastal sediment. The bacterial communities in sediment and on eco-concrete surface were also investigated by using high-throughput sequencing and quantitative PCR of 16S rRNA gene. We found that the mean removal efficiencies of TN, TP, and TOC in treatment group were 8.3%, 8.4%, and 12.3% after 28 days. The bacterial community composition in the treatment group was significantly different from that in the control group on day 28. In addition, the bacterial community composition on eco-concrete surface was slightly different from that in sediment, and the copy numbers of 16S rRNA gene were higher on eco-concrete surface than in sediment. The types of eco-concrete aggregates (gravel, pebble, and zeolite) also had effects on the bacterial community composition and 16S rRNA gene copy numbers. Furthermore, we found the abundant genus Sulfurovum increased significantly on eco-concrete surface in the treatment group after 28 days. Bacteria belonging to this genus were found having denitrification ability and were commonly detected in bioreactors for nitrate removal. Overall, our study expands the application scopes of eco-concrete and suggests that the bacterial communities in eco-concrete can potentially enhance the removal efficiency of nutrients in coastal sediment.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw sequence data in this study have been deposited in the Genome Sequence Archive (National Genomics Data Center, China National Center forBioinformation / Beijing Institute of Genomics, Chinese Academy of Sciences) (https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/gsa/) with the accession number CRA010233.
References
Bao T, Yu ZM, Damtie MM, Wu K, Jin J, Zhang Y, Wei XL, Frost RL (2020) Use of autoclaved aerated concrete particles for simultaneous removal of nitrogen and phosphorus as filter media from domestic wastewater. Environ Technol 41:3032–3042
Barcellos D, Queiroz HM, Nóbrega GN, de Oliveira Filho RL, Santaella ST, Otero XL, Ferreira TO (2019) Phosphorus enriched effluents increase eutrophication risks for mangrove systems in northeastern Brazil. Mar Pollut Bull 142:58–63
Callahan BJ, McMurdie PJ, Rosen MJ, Han AW, Johnson AJA, Holmes SP (2016) DADA2: high-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods 13:581
Casado Coy N, Sanchez Jerez P, Holmer M, Sanz Lazaro C (2020) Bioturbation may not always enhance the metabolic capacity of organic polluted sediments. Mar Environ Res 155:104882
Chang CY, Chen SY, Klipkhayai P, Chiemchaisri C (2019) Bioleaching of heavy metals from harbor sediment using sulfur-oxidizing microflora acclimated from native sediment and exogenous soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:6818–6828
Chase JM (2010) Stochastic community assembly causes higher biodiversity in more productive environments. Science 328:1388–1391
Chen C, Ren N, Wang A, Yu Z, Lee DJ (2008) Microbial community of granules in expanded granular sludge bed reactor for simultaneous biological removal of sulfate, nitrate and lactate. Appl Microbiol Biot 79:1071
Chen D, Yu C, Bao T, Zhu C, Qing C, Chen T (2016) Simultaneous removal of nitrogen and phosphorus using autoclaved aerated concrete particles in biological aerated filters. Desalin Water Treat 57:19402–19410
Clarke KR, Gorley RN (2015) PRIMER v7: user manual/tutorial. PRIMER-E Ltd: Plymouth, UK
Deegan LA, Johnson DS, Warren RS, Peterson BJ, Fleeger JW, Fagherazzi S, Wollheim WM (2012) Coastal eutrophication as a driver of salt marsh loss. Nature 490:388
Espinosa RM (2020) Microorganisms and their metabolic capabilities in the context of the biogeochemical nitrogen cycle at extreme environments. Int J Mol Sci 21:4228
Fodelianakis S, Moustakas A, Papageorgiou N, Manoli O, Tsikopoulou I, Michoud G, Daffonchio D, Karakassis I, Ladoukakis ED (2017) Modified niche optima and breadths explain the historical contingency of bacterial community responses to eutrophication in coastal sediments. Mol Ecol 26:2006–2018
Garnova ES, Zhilina TN, Tourova TP, Lysenko AM (2003) Anoxynatronum sibiricum gen.nov., sp.nov. alkaliphilic saccharolytic anaerobe from cellulolytic community of Nizhnee Beloe (Transbaikal region). Extremophiles 7:213–220
Herlemann DPR, Labrenz M, Jürgens K, Bertilsson S, Waniek JJ, Andersson AF (2011) Transitions in bacterial communities along the 2000 km salinity gradient of the Baltic Sea. ISME J 5:1571–1579
Inagaki F, Takai K, Nealson KH, Horikoshi K (2004) Sulfurovum lithotrophicum gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel sulfur-oxidizing chemolithoautotroph within the ε-Proteobacteria isolated from Okinawa Trough hydrothermal sediments. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:1477–1482
Kim HH, Park CG (2016) Plant growth and water purification of porous vegetation concrete formed of blast furnace slag, natural jute fiber and styrene butadiene latex. Sustainability 8:386
Li L, Zhang H, Zhou X, Chen M, Lu L, Cheng X (2019) Effects of super absorbent polymer on scouring resistance and water retention performance of soil for growing plants in ecological concrete. Ecol Eng 138:237–247
Ling X, Lu G, Xue C (2022) Environmental and anthropogenic factors affect bacterial community and nitrogen removal in the Yarlung Zangbo River. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 29:84590–84599
Liu C, Zhao C, Wang A, Guo Y, Lee DJ (2015a) Denitrifying sulfide removal process on high-salinity wastewaters. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:6463–6469
Liu L, Yang J, Yu Z, Wilkinson DM (2015b) The biogeography of abundant and rare bacterioplankton in the lakes and reservoirs of China. ISME J 9:2068–2077
Liu L, Ji J, Guo Y, Chen J (2021) Use of ecological concrete for nutrient removal in coastal sediment and its effects on sediment microbial communities. Mar Pollut Bull 162:111911
Lopez Gutierrez JC, Henry S, Hallet S, Martin Laurent F, Catroux G, Philippot L (2004) Quantification of a novel group of nitrate-reducing bacteria in the environment by real-time PCR. J Microbiol Methods 57:399–407
Lv G, Shi Y (2018) Effect of ecological concrete applied to water pollution control of urban river. Desalin Water Treat 121:6–13
Manirakiza B, Zhang S, Addo FG, Isabwe A, Nsabimana A (2022) Exploring microbial diversity and ecological function of epiphytic and surface sediment biofilm communities in a shallow tropical lake. Sci Total Environ 808:151821
McCrackin ML, Jones HP, Jones PC, Moreno-Mateos D (2017) Recovery of lakes and coastal marine ecosystems from eutrophication: a global meta-analysis. Limnol Oceanogr 62:507–518
Mori K, Yamaguchi K, Hanada S (2018) Sulfurovum denitrificans sp. nov., an obligately chemolithoautotrophic sulfur-oxidizing epsilonproteobacterium isolated from a hydrothermal field. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68:2183–2187
Moulana A, Anderson RE, Fortunato CS, Huber JA (2020) Selection is a significant driver of gene gain and loss in the pangenome of the bacterial genus Sulfurovum in geographically distinct deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Ecol Evol 5:e00673-e719
Park SB, Tia M (2004) An experimental study on the water-purification properties of porous concrete. Cement Concrete Res 34:177–184
Qian J, Zhang M, Jing R, Bai L, Zhou B, Zhao M, Pei X, Wei L, Chen GH (2019) Thiosulfate as the electron acceptor in sulfur bioconversion-associated process (SBAP) for sewage treatment. Water Res 163:114850
Renner LD, Weibel DB (2011) Physicochemical regulation of biofilm formation. MRS Bull 36:347–355
Ryzhmanova Y, Oshurkova V, Troshina O, Abashina T, Ariskina E, Avtukh A, Shcherbakova V (2017) Anoxynatronum buryatiense sp. nov., an anaerobic alkaliphilic bacterium from a low mineralization soda lake in Buryatia, Russia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:4704–4709
Shen H, Thrush SF, Wan X, Li H, Qiao Y, Jiang G, Sun R, Wang L, He P (2016) Optimization of hard clams, polychaetes, physical disturbance and denitrifying bacteria of removing nutrients in marine sediment. Mar Pollut Bull 110:86–92
Stegen JC, Lin X, Fredrickson JK, Chen X, Kennedy DW, Murray CJ, Rockhold ML, Konopka A (2013) Quantifying community assembly processes and identifying features that impose them. ISME J 7:2069–2079
Tang VT, Pakshirajan K (2018) Novel advanced porous concrete in constructed wetlands: preparation, characterization and application in urban storm runoff treatment. Water Sci Technol 78:2374–2382
Tang CC, Tian Y, Liang H, Zuo W, Wang ZW, Zhang J, He ZW (2018a) Enhanced nitrogen and phosphorus removal from domestic wastewater via algae-assisted sequencing batch biofilm reactor. Bioresource Technol 250:185–190
Tang J, Zhu N, Zhu Y, Zamir SM, Wu Y (2018b) Sustainable pollutant removal by periphytic biofilm via microbial composition shifts induced by uneven distribution of CeO2 nanoparticles. Bioresource Technol 248:75–81
Terry LG, Summers RS (2018) Biodegradable organic matter and rapid-rate biofilter performance: a review. Water Res 128:234–245
Vaughn CC, Hoellein TJ (2018) Bivalve impacts in freshwater and marine ecosystems. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 49:183–208
Wang J, Ersan YC, Boon N, De Belie N (2016) Application of microorganisms in concrete: a promising sustainable strategy to improve concrete durability. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:2993–3007
Wang H, Lyu W, Hu X, Chen L, He Q, Zhang W, Song J, Wu J (2019) Effects of current intensities on the performances and microbial communities in a combined bio-electrochemical and sulfur autotrophic denitrification (CBSAD) system. Sci Total Environ 694:133775
Wang X, Yang X, Ren J, Han N, Xing F (2021) A novel treatment method for recycled aggregate and the mechanical properties of recycled aggregate concrete. J Market Res 10:1389–1401
Wang H, Liu X, Wang Y, Zhang S, Zhang G, Han Y, Li M, Liu L (2023) Spatial and temporal dynamics of microbial community composition and factors influencing the surface water and sediments of urban rivers. J Environ Sci 124:187–197
Xiao K, Zhou L, He B, Qian L, Wan S, Qu L (2016) Nitrogen and phosphorus removal using fluidized-carriers in a full-scale A2O biofilm system. Biochem Eng J 115:47–55
Xiao X, Agusti S, Lin F, Li K, Pan Y, Yu Y, Zheng Y, Wu J, Duarte CM (2017) Nutrient removal from Chinese coastal waters by large-scale seaweed aquaculture. Sci Rep 7:46613
Yang YD, Hu YG, Wang ZM, Zeng ZH (2018) Variations of the nirS-, nirK-, and nosZ-denitrifying bacterial communities in a northern Chinese soil as affected by different long-term irrigation regimes. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:14057–14067
Yu Y, Lee C, Kim J, Hwang S (2005) Group-specific primer and probe sets to detect methanogenic communities using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Biotechnol Bioeng 89:670–679
Yuan D, Cui L, An Y, Chen B, Guo X, Li Y, Zhao R, Cui S, Wang S, Kou Y (2019) Investigating the pollutant-removal performance and DOM characteristics of rainfall surface runoff during different ecological concrete revetments treatment. Ecol Indic 105:655–662
Zhang L, Zhang C, Hu C, Liu H, Bai Y, Qu J (2015) Sulfur-based mixotrophic denitrification corresponding to different electron donors and microbial profiling in anoxic fluidized-bed membrane bioreactors. Water Res 85:422–431
Zhang Z, Deng Y, Feng K, Cai W, Li S, Yin H, Xu M, Ning D, Qu Y (2019) Deterministic assembly and diversity gradient altered the biofilm community performances of bioreactors. Environ Sci Technol 53:1315–1324
Zhu Y, Tu X, Chai X-S, Wei Q, Guo L (2018) Biological activities and nitrogen and phosphorus removal during the anabaena flos-aquae biofilm growth using different nutrient form. Bioresource Technol 251:7–12
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31971469), the Qishan Scholar Program of Fuzhou University (GXRC-20061), the Science and Technology Program of Quanzhou, China (2022N042), and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2019YFE0124700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Liu L and Chen J conceived the idea and designed the experiments; Zhang M and Liu L wrote the paper; Ji J and Guo Y performed the experiments. Liu LM, Zhang M, and Ji J analyzed the data. All the authors revised the manuscript and approved the final edition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
All authors approved the version to be published and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Robert Duran
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Ji, J., Liu, L. et al. Response of microbial communities to nutrient removal in coastal sediment by using ecological concrete. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 70817–70826 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27386-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27386-3