Abstract
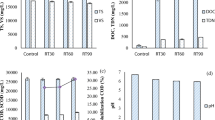
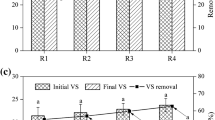
The hydrothermal pretreatment (HTP) characteristics and the fate of phosphorus (P) and anaerobic digestion (AD) performance of dewatered sewage sludge (DSS) were investigated at different hydrothermal conditions. The maximum methane yield reached 241 mL CH4/g COD when the hydrothermal conditions were 200 °C-2 h-10% (A4), and the yield was 78.28% higher than that without pretreatment (A0) and 29.62% higher than that of the initial hydrothermal conditions (A1, 140 °C-1 h-5%). Proteins, polysaccharides, and volatile fatty acids (VFAs) were the main hydrothermal products of DSS. 3D-EEM analysis revealed that tyrosine, tryptophan proteins, and fulvic acids decreased after HTP, but the content of humic acid-like substances increased, and this phenomenon was more noticeable after AD. Solid-organic P was converted into liquid-P during the hydrothermal process, and nonapatite inorganic P was converted into organic P during AD. All samples achieved positive energy balance, and the energy balance of A4 was 10.50 kJ/g VS. Microbial analysis showed that the composition of the anaerobic microbial degradation community changed as the sludge organic composition was altered. Results showed that the HTP improved the anaerobic digestion of DSS.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Amodeo C, Hattou S, Buffiere P, Benbelkacem H (2021) Temperature phased anaerobic digestion (TPAD) of organic fraction of municipal solid waste (OFMSW) and digested sludge (DS): effect of different hydrolysis conditions. Waste Manag 126:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2021.02.049
Aragón-Briceño C, Ross AB, Camargo-Valero MA (2017) Evaluation and comparison of product yields and bio-methane potential in sewage digestate following hydrothermal treatment. Appl Energy 208:1357–1369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.09.019
Aragón-Briceño CI, Grasham O, Ross AB, Dupont V, Camargo-Valero MA (2020) Hydrothermal carbonization of sewage digestate at wastewater treatment works: influence of solid loading on characteristics of hydrochar, process water and plant energetics. Renew Energy 157:959–973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.05.021
Arelli V, Mamindlapelli NK, Begum S, Juntupally S, Anupoju GR (2021) Solid state anaerobic digestion of food waste and sewage sludge: impact of mixing ratios and temperature on microbial diversity, reactor stability and methane yield. Sci Total Environ 793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148586.
Bardi MJ, Aminirad H (2020) Synergistic effects of co-trace elements on anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and sewage sludge at high organic load. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:18129–18144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08252-y
Becker G, Wüst D, Köhler H, Lautenbach A, Kruse A (2019) Novel approach of phosphate-reclamation as struvite from sewage sludge by utilising hydrothermal carbonization. J Environ Manag 238:119–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.02.121
Belete YZ, Mau V, Yahav Spitzer R, Posmanik R, Jassby D, Iddya A, Kassem N, Tester JW, Gross A (2021) Hydrothermal carbonization of anaerobic digestate and manure from a dairy farm on energy recovery and the fate of nutrients. Bioresour Technol 333:125164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125164
Campuzano R, González-Martínez S (2016) Characteristics of the organic fraction of municipal solid waste and methane production: a review. Waste Manag 54:3–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.05.016
Cao Z, Jung D, Olszewski MP, Arauzo PJ, Kruse A (2019) Hydrothermal carbonization of biogas digestate: effect of digestate origin and process conditions. Waste Manag 100:138–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2019.09.009
Chen H, Rao Y, Cao L, Shi Y, Hao S, Luo G, Zhang S (2019) Hydrothermal conversion of sewage sludge: focusing on the characterization of liquid products and their methane yields. Chem Eng J 357:367–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.09.180
Danso-Boateng E, Shama G, Wheatley AD, Martin SJ, Holdich RG (2015) Hydrothermal carbonisation of sewage sludge: effect of process conditions on product characteristics and methane production. Bioresour Technol 177:318–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.11.096
De la Rubia MA, Villamil JA, Rodriguez JJ, Mohedano AF (2018) Effect of inoculum source and initial concentration on the anaerobic digestion of the liquid fraction from hydrothermal carbonisation of sewage sludge. Renew Energy 127:697–704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.05.002
Ekpo U, Ross AB, Camargo-Valero MA, Williams PT (2016) A comparison of product yields and inorganic content in process streams following thermal hydrolysis and hydrothermal processing of microalgae, manure and digestate. Bioresour Technol 200:951–960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.11.018
Frølund B, Griebe T, Nielsen PH (1995) Enzymatic activity in the activated-sludge floc matrix. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 43:755–761. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00164784
García M, Urrea JL, Collado S, Oulego P, Díaz M (2017) Protein recovery from solubilized sludge by hydrothermal treatments. Waste Manag 67:278–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.05.051
Guo L, Lu M, Li Q, Zhang J, Zong Y, She Z (2014) Three-dimensional fluorescence excitation–emission matrix (EEM) spectroscopy with regional integration analysis for assessing waste sludge hydrolysis treated with multi-enzyme and thermophilic bacteria. Bioresour Technol 171:22–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.08.025
Hamalainen A, Kokko M, Kinnunen V, Hilli T, Rintala J (2021) Hydrothermal carbonisation of mechanically dewatered digested sewage sludge-energy and nutrient recovery in centralised biogas plant. Water Res 201:117284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2021.117284
He Z-W, Liu W-Z, Wang L, Tang C-C, Guo Z-C, Yang C-X, Wang A-J (2016) Clarification of phosphorus fractions and phosphorus release enhancement mechanism related to pH during waste activated sludge treatment. Bioresour Technol 222:217–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.10.010
He Z-W, Tang C-C, Wang L, Guo Z-C, Zhou A-J, Sun D, Liu W-Z, Wang A-J (2017) Transformation and release of phosphorus from waste activated sludge upon combined acid/alkaline treatment. RSC Adv 7:35340–35345. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra03696e
Hu P, Liu J, Bao H, Wu L, Jiang L, Zou L, Wu Y, Qian G, Li Y-Y (2018) Enhancing phosphorus release from waste activated sludge by combining high-voltage pulsed discharge pretreatment with anaerobic fermentation. J Clean Prod 196:1044–1051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.06.153
Huang R, Fang C, Lu X, Jiang R, Tang Y (2017) Transformation of phosphorus during (hydro)thermal treatments of solid biowastes: reaction mechanisms and implications for P reclamation and recycling. Environ Sci Technol 51:10284–10298. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b02011
Jeong SY, Lee EJ, Ban SE, Lee JW (2021) Structural characterization of the lignin-carbohydrate complex in biomass pretreated with Fenton oxidation and hydrothermal treatment and consequences on enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency. Carbohydr Polym 270:118375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118375
Jiang H, Qin Y, Gadow SI, Li Y-Y (2017) The performance and kinetic characterization of the three metabolic reactions in the thermophilic hydrogen and acidic fermentation of cassava residue. Int J Hydrogen Energy 42:2868–2877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.01.061
Khanh Nguyen V, Kumar Chaudhary D, Hari Dahal R, Hoang Trinh N, Kim J, Chang SW, Hong Y, Duc La D, Nguyen XC, Hao Ngo H, Chung WJ, Nguyen DD (2021) Review on pretreatment techniques to improve anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. Fuel 285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119105.
Kim D, Lee K, Park KY (2015) Enhancement of biogas production from anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge by hydrothermal pre-treatment. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 101:42–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2015.03.025
Latif MA, Mehta CM, Batstone DJ (2015) Low pH anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge for enhanced phosphorous release. Water Res 81:288–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.05.062
Li S, Zeng W, Jia Z, Wu G, Xu H, Peng Y (2020) Phosphorus species transformation and recovery without apatite in FeCl3-assisted sewage sludge hydrothermal treatment. Chem Eng J 399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125735.
Liu C, Li H, Zhang Y, Si D, Chen Q (2016) Evolution of microbial community along with increasing solid concentration during high-solids anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. Bioresour Technol 216:87–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.05.048
Liu J, Deng S, Qiu B, Shang Y, Tian J, Bashir A, Cheng X (2019) Comparison of pretreatment methods for phosphorus release from waste activated sludge. Chem Eng J 368:754–763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.205
Liu Z, Zhou S, Dai L, Dai X (2020) The transformation of phosphorus fractions in high-solid sludge by anaerobic digestion combined with the high temperature thermal hydrolysis process. Bioresour Technol 309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123314.
Mao L, Tsui TH, Zhang J, Dai Y, Tong YW (2021) System integration of hydrothermal liquefaction and anaerobic digestion for wet biomass valorization: biodegradability and microbial syntrophy. J Environ Manag 293:112981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112981
Marin-Batista JD, Mohedano AF, Rodriguez JJ, de la Rubia MA (2020) Energy and phosphorous recovery through hydrothermal carbonization of digested sewage sludge. Waste Manag 105:566–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2020.03.004
Mau V, Quance J, Posmanik R, Gross A (2016) Phases’ characteristics of poultry litter hydrothermal carbonization under a range of process parameters. Bioresour Technol 219:632–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.08.027
Mecozzi M, Pietroletti M, Gallo V, Conti ME (2009) Formation of incubated marine mucilages investigated by FTIR and UV–VIS spectroscopy and supported by two-dimensional correlation analysis. Mar Chem 116:18–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2009.09.004
Mottet A, François E, Latrille E, Steyer JP, Déléris S, Vedrenne F, Carrère H (2010) Estimating anaerobic biodegradability indicators for waste activated sludge. Chem Eng J 160:488–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.03.059
Nielfa A, Cano R, Fdz-Polanco M (2015) Theoretical methane production generated by the co-digestion of organic fraction municipal solid waste and biological sludge. Biotechnol Rep (amst) 5:14–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2014.10.005
Park M, Kim N, Jung S, Jeong TY, Park D (2021) Optimization and comparison of methane production and residual characteristics in mesophilic anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge by hydrothermal treatment. Chemosphere 264:128516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128516
Passos F, Ferrer I (2015) Influence of hydrothermal pretreatment on microalgal biomass anaerobic digestion and bioenergy production. Water Res 68:364–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.10.015
Pilli S, More T, Yan S, Tyagi RD, Surampalli RY (2015) Anaerobic digestion of thermal pre-treated sludge at different solids concentrations–computation of mass-energy balance and greenhouse gas emissions. J Environ Manag 157:250–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.04.023
Posmanik R, Darzi R, Glicksberg R, Shabtay A, Cohen-Zinder M (2020) Hydrothermal conversion of beef cattle manure can enhance energy recovery in confined feedlots. Environ Sci Water Res Technol 6:1125–1138. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ew00856j
Ruban V, López-Sánchez J, Pardo P, Rauret G, Muntau H, Quevauviller P (1999) Selection and evaluation of sequential extraction procedures for the determination of phosphorus forms in lake sediment. J Environ Monit 1:51–56. https://doi.org/10.1039/A807778I
Ruban V, López-Sánchez J, Pardo P, Rauret G, Muntau H, Quevauviller P (2001) Harmonized protocol and certified reference material for the determination of extractable contents of phosphorus in freshwater sediments–a synthesis of recent works. Fresenius’ J Anal Chem 370:224–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002160100753
Saerens B, Geerts S, Weemaes M (2021) Phosphorus recovery as struvite from digested sludge - experience from the full scale. J Environ Manage 280:111743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111743
Shi Y, Chen Z, Cao Y, Fan J, Clark JH, Luo G, Zhang S (2021) Migration and transformation mechanism of phosphorus in waste activated sludge during anaerobic fermentation and hydrothermal conversion. J Hazard Mater 403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123649.
Smolders GJ, van der Meij J, van Loosdrecht MC, Heijnen JJ (1994) Model of the anaerobic metabolism of the biological phosphorus removal process: stoichiometry and pH influence. Biotechnol Bioeng 43:461–470. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.260430605
Tchobanoglus G, Burton F, Stensel HD (2003) Wastewater engineering: treatment and reuse. J Am Water Works Assn 95:201. https://doi.org/10.2136/awwa2003.3478
Turner BL, Mahieu N, Condron LM (2003) Phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectral assignments of phosphorus compounds in soil NaOH–EDTA extracts. Soil Sci Soc Am J 67:497–510. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2003.4970
Wang L, Li A (2015) Hydrothermal treatment coupled with mechanical expression at increased temperature for excess sludge dewatering: the dewatering performance and the characteristics of products. Water Res 68:291–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.10.016
Wang T, Zhai Y, Zhu Y, Peng C, Wang T, Xu B, Li C, Zeng G (2017) Feedwater pH affects phosphorus transformation during hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge. Bioresour Technol 245:182–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.114
Wang Q, Xu Q, Du Z, Zhang W, Wang D, Peng Y (2021) Mechanistic insights into the effects of biopolymer conversion on macroscopic physical properties of waste activated sludge during hydrothermal treatment: importance of the Maillard reaction. Sci Total Environ 769:144798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144798
Wilson CA, Novak JT (2009) Hydrolysis of macromolecular components of primary and secondary wastewater sludge by thermal hydrolytic pretreatment. Water Res 43:4489–4498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.07.022
Xiao B, Qin Y, Wu J, Chen H, Yu P, Liu J, Li Y-Y (2018) Comparison of single-stage and two-stage thermophilic anaerobic digestion of food waste: performance, energy balance and reaction process. Energy Convers Manag 156:215–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2017.10.092
Xie C, Zhao J, Tang J, Xu J, Lin X, Xu X (2011) The phosphorus fractions and alkaline phosphatase activities in sludge. Bioresour Technol 102:2455–2461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.11.011
Yang G, Zhang P, Zhang G, Wang Y, Yang A (2015) Degradation properties of protein and carbohydrate during sludge anaerobic digestion. Bioresour Technol 192:126–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.05.076
Zhang Q, Wang M, Ma X, Gao Q, Wang T, Shi X, Zhou J, Zuo J, Yang Y (2019) High variations of methanogenic microorganisms drive full-scale anaerobic digestion process. Environ Int 126:543–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.03.005
Zhang D, Feng Y, Huang H, Khunjar W, Wang Z-W (2020) Recalcitrant dissolved organic nitrogen formation in thermal hydrolysis pretreatment of municipal sludge. Environ Int 138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105629.
Zhao X, Becker G, Faweya N, Correa CR, Yang S, Xie X, Kruse A (2018) Fertilizer and activated carbon production by hydrothermal carbonization of digestate. Biomass Convers Bior 8:423–436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-017-0291-5
Zheng T, Zhang K, Chen X, Ma Y, Xiao B, Liu J (2021) Effects of low- and high-temperature thermal-alkaline pretreatments on anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Bioresour Technol 337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125400.
Zhou J, You X, Niu B, Yang X, Gong L, Zhou Y, Wang J, Zhang H (2020) Enhancement of methanogenic activity in anaerobic digestion of high solids sludge by nano zero-valent iron. Sci Total Environ 703:135532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135532
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Luyu Wang, Jun Zhou, and Lei Gong designed the study. Qinwei Jia, Xiaofan Ma, and Yuhang Zhao participated in material preparation, data collection, and analysis. Haonan Zhang provided many valuable suggestions on the interpretation of data. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Luyu Wang, and the manuscript was revised by Luyu Wang and Jun Zhou. All the authors commented on the previous versions of the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ta Yeong Wu
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Zhou, J., Jia, Q. et al. Anaerobic digestion of hydrothermally pretreated dewatered sewage sludge: effects of process conditions on methane production and the fate of phosphorus. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 66767–66780 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26990-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26990-7