Abstract
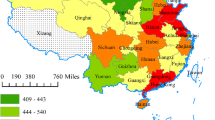
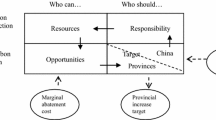
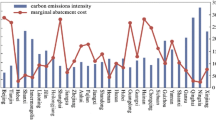
The allocation of provincial carbon emission quotas under total amount control is an effective way for China to achieve its carbon peak and neutrality targets. Firstly, in order to study the factors influencing China’s carbon emissions, the expanded STIRPAT model was constructed; and combined with the scenario analysis method, the total of national carbon emission quota under the peak scenario was predicted. Then, the index system of regional carbon quota allocation is constructed based on the principles of equity, efficiency, feasibility, and sustainability; and the allocation weight is determined by the grey correlation analysis method. Finally, the total carbon emission quota under the peak scenario is distributed in 30 provinces of China, and the future carbon emission space is also analyzed. The results show that: (1) only under the low-carbon development scenario, can China reach the peak target by 2030, with a peak carbon of about 14,080.31 million tons; (2) under the comprehensive allocation principle, China’s provincial carbon quota allocation is characterized by high levels in the west and low in the east. Among them, Shanghai and Jiangsu receive fewer quotas, while Yunnan, Guangxi, and Guizhou receive more; and (3) the future carbon emission space for the entire country is modestly surplus, with regional variations. Whereas Hainan, Yunnan, and Guangxi have surpluses, Shandong, Inner Mongolia, and Liaoning have significant deficits.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bai CE, Zhang Q (2017) China’s growth potential to 2050: a supply-side forecast based on cross-country productivity convergence and its featured labor force. Chin J Econ 4(04):1–27. https://doi.org/10.16513/j.cnki.cje.2017.04.001
Bian Y, Liu Y (2021) Establish total carbon emission control system. Chin Open J 000(005):14–20. https://doi.org/10.19625/j.cnki.cn44-1338/f.2021.0056
Chen B, Zhang H, Li W et al (2022) Research on provincial carbon quota allocation under the background of carbon neutralization. Energy Rep 8:903–915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2022.02.023
Chen F, Zhao T, Xia H et al (2021) Allocation of carbon emission quotas in Chinese provinces based on Super-SBM model and ZSG-DEA model. Clean Technol Environ Policy 23(8):2285–2301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-021-02137-5
Cheng TJ, Da YJ, Zheng XQ (2023) Research on the allocation of carbon emission rights in China’s provinces based on grouped centralized DEA. Soft Science 1–11 [2023–02–20]
Cheng XJ, Sun SQ, Zhu GJ et al (2021) Research on regional decomposition of total carbon emissions in hunan province under intensity emission reduction target. J Changsha Univ 35(5):72–76
Du J, Pan M, Chen Y et al (2020) An efficiency-based allocation of carbon emissions allowance: a case study in China. J Clean Prod 251:119346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119346
Duan FM et al (2018) Estimation of marginal abatement costs of CO2 in Chinese provinces under 2020 carbon emission rights allocation: 2005–2020. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25(24):24445–24468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2497-x
Ehrlich PR, Holdren JP (1971) Impact of population growth. Science 171(3977):1212–1217. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.171.3977.1212
Fang K et al (2019a) How can China achieve its intended nationally determined contributions by 2030? A multi-criteria allocation of China’s carbon emission allowance. Appl Energy 241:380–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.03.055
Fang K, Li S, Ye R et al (2020) New progress in Global Climate Governance—a review of regional carbon emission rights allocation. J Ecol 40(01):10–23. https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb201811122444
Fang K, Tang Y, Zhang Q et al (2019b) Will China peak its energy-related carbon emissions by 2030? Lessons from 30 Chinese provinces. Appl Energy 255:113852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.113852
Fang K, Zhang QF, Ye RK et al (2018) Allocating China’s carbon emission allowance to the provincial quotas in the context of the Paris Agreement. Acta Sci Circumst 38(3):1224–1234. https://doi.org/10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2017.0402
Feng Q, Wu ZB, Xu JP (2022) Research on inter-provincial carbon emission allowance allocation based on input-output scale. Chin J Manag Sci 1–10[2022–04–18]. https://doi.org/10.16381/j.cnki.issn1003-207x.2021.0040
Feng ZY, Tang WH, Niu ZW et al (2018) Bi-level allocation of carbon emission permits based on clustering analysis and weighted voting: a case study in China. Appl Energy 228:1122–1135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.07.005
Feng ZX, Wang AJ (2016) Comparative study of China regional carbon peak—based on National Data and Shaanxi Province. J Xi’an Jiaotong Univ (Soc Sci) 36(04):96–104. https://doi.org/10.15896/j.xjtuskxb.201604014
Guo W, Liu XF, Wu XL (2017) Efficiency allocation of provincial carbon reduction target in China’s Thirteenth Five Year Plan period. China Population. Resour Environ 27(5):72–83. https://doi.org/10.12062/cpre.20170306
Han L (2009) Research on legal issues of international greenhouse gas emission trading. China Legal Publishing House, Beijing
Han R et al (2016) Integrated weighting approach to carbon emission quotas: an application case of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. J Clean Prod 131:448–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.05.001
Han R, Yu BY, Tang BJ et al (2017) Carbon emissions quotas in the Chinese road transport sector: a carbon trading perspective. Energy Policy 106:298–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2017.03.071
Hubacek, Klaus, Baiocchi et al (2017) Global carbon inequality. Energy Ecol Environ 2(6):361–369.https://doi.org/10.1007/s40974-017-0072-9
Kong YC, Zhao T, Yuan R et al (2019) Allocation of carbon emission quotas in Chinese provinces based on equality and efficiency principles. J Clean Prod 211:222–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.11.178
Li JF, Gu AL, Zhang CL et al (2019) Economic development, energy demand, and carbon emission prospects of China’s provinces during the 14th Five-Year Plan period: application of CMRCGE model. Adv Clim Chang Res 15(06):649–659. https://doi.org/10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2019.060
Li P, Lou F, Wang HW (2017) Analysis and forecast of China’s total economy and its structure from 2016–2035. Strategic Study of CAE 19(01):13–20. https://doi.org/10.15302/J-SSCAE-2017.01.003
Li W, Ma H, Lu C (2023) Research on the economic abatement pathway of carbon peaking in China based on marginal abatement costs and abatement tasks allocation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(3):7956–7972. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22641-5
Li Y et al (2020) Regional and provincial CO2 emission reduction task decomposition of China’s 2030 carbon emission peak based on the efficiency, equity and synthesizing principles. Struct Chang Econ Dyn 53:237–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strueco.2020.02.007
Ou YH, Li Z, Li PL (2021) Trend and policy implication of urbanization rate in China during the 14th Five Year Plan period. Urban Dev Stud 28(06):1–9
Qin Q et al (2017) A multi-criteria decision analysis model for carbon emission quota allocation in China’s east coastal areas: efficiency and equity. J Clean Prod 168:410–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.08.220
Quan C, Cheng X, Yu S et al (2020) Analysis on the influencing factors of carbon emission in China’s logistics industry based on LMDI method. Sci Total Environ 734:138473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138473
Renaud Gignac, Damon Matthews H (2015) Allocating a 2 °C cumulative carbon budget to countries. Environ Res Lett 10(7):075004. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/10/7/075004
Song DY, Liu XP (2013) Spatial distribution of provincial carbon emissions. China Popul Resour Environ 23(05):7–13. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2013.05.002
Song J, Chen R, Ma X (2022) Provincial allocation of energy consumption, air pollutant and CO2 emission quotas in China: based on a weighted environment ZSG-DEA model. Sustainability 14(4):2243. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14042243
Song JK, Zhang KX, Cao ZJ (2017) Provincial allocation of carbon emission quotas — under the fusion of fairness and efficiency. J Arid Land Resour Environ 31(05):7–13. https://doi.org/10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2017.136
Tan Q, Zheng J, Ding Y et al (2020) Provincial carbon emission quota allocation study in China from the perspective of abatement cost and regional cooperation. Sustainability 12(20):8457. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208457
Tan XC, Niu MM, Gu BH et al (2023) Evaluation of China’s provincial carbon quota allocation scheme from the perspective of high-quality development. Clim Chang Res 19(1):74–83. https://doi.org/10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2022.136
Tian M, Hu YJ, Wang H et al (2022) Regional allowance allocation in China based on equity and efficiency towards achieving the carbon neutrality target: a composite indicator approach. J Clean Prod 342:130914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130914
Tian Y, Lin ZJ (2021) Provincial distribution of China’s carbon emission rights and assessment of its emission reduction potential under the Paris Agreement. J Nat Resour 36(04):921–933. 104. https://doi.org/10.31497/zrzyxb.20210409
Wang F, Ge X (2022) Inter-provincial responsibility allocation of carbon emission in China to coordinate regional development. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(5):7025–7041. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-421632/v1
Wang Q, Gao CY (2016) Analysis of allocation principles for China’s provincial carbon emission allowance under the equity and efficiency dimension. China Popul Resour Environ 26(07):53–61. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2016.07.007
Wang WJ, Chen ZL (2019) Research on initial carbon quota allocation scheme of provincial regions in China -from the perspective of responsibility and goal, fairness and efficiency. J Manag World (35):81–98. https://doi.org/10.19744/j.cnki.11-1235/f.2019.0036
Wang WJ, Kong XX (2022) Analysis on China’s provincial carbon quota allocation based on the 2030 carbon peak goal. J Quant Technol Econ 39(07):113–132. https://doi.org/10.13653/j.cnki.jqte.2022.07.002
Wang WJ, Zhuang GY (2012) Carbon emission rights allocation and climate equity demands in international climate negotiations. Foreign Aff Rev (1):72–84. https://doi.org/10.13569/j.cnki.far.2012.01.001
Wang Y, Cheng Y, Yang GC et al (2018) Provincial decomposition of China’s carbon emission rights under the constraints of 2020 and 2030 carbon intensity targets. Chin Environ Sci 38(08):3180–3188. https://doi.org/10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.2018.0339
Wang Y, Jia W, Bi Y (2017) Provincial decomposition of China’s 2030 carbon dioxide emission peak target from the perspective of efficiency: Research on the zero sum gains DEA model. Acta Sci Circumst 37(11):4399–4408. https://doi.org/10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2017.0348
Wei C, Ni J, Du L (2012) Regional allocation of carbon dioxide abatement in China. China Econ Rev 23(3):552–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chieco.2011.06.002
Yang BC, Li XT, Su YP et al (2020) Carbon quota allocation at the provincial level in China under principles of equity and efficiency. Carbon Manag 11(1):11–23. https://doi.org/10.1080/17583004.2019.1682755
Yang C, Wu LJ, Li JF et al (2019) Research on the distribution of carbon emission rights in China from the perspective of equity. Resour Sci 41(10):1801–1813. https://doi.org/10.18402/resci.2019.10.04
Yi WJ et al (2011) How can China reach its CO2 intensity reduction targets by 2020? A regional allocation based on equity and development. Energy Policy 39(5):2407–2415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2011.01.063
Zhan D (2022) Allocation of carbon emission quotas among provinces in China: efficiency, fairness and balanced allocation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17309-5
Zhang YG (2015) Total amount or intensity: the debate on carbon emission reduction targets. Acad Res (09):76–80+122
Zhang YJ, Hao JF (2017) Carbon emission quota allocation among China’s industrial sectors based on the equity and efficiency principles. Ann Oper Res 255(1–2):117–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-016-2232-2
Zhou D, Wang WJ, Chen ZJ (2020) Redistribution of China’s carbon emission quota from the perspective of the importance of quota indicators. Chin Environ Sci 40(12):5551–5560. https://doi.org/10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.2020.0614
Zhu QT, Wu J, Hong HD et al (2015) Simulation on carbon permits allocation in the post-Kyoto era. Acta Sci Circumst 35(1):329–336. https://doi.org/10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2014.0812
Zhu WW, Miao ZY, Gan GS (2020) Carbon emission reduction allocation strategy based on the context-dependent DEA method. Resour Sci 42(11):2170–2183. https://doi.org/10.18402/resci.2020.11.10
Funding
This work is supported by Hunan Provincial Philosophy & Society Science Foundation of China (17YBA241,21YBA214), Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (2022JJ30203), Changsha Municipal Natural Science Foundation (kq2202304), Project of Hunan Provincial Social Science Achievement Review Committee (XSP22YBC573, XSP2023ZDI005), and Excellent Youth Funding of Hunan Provincial Education Department (20B155).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Conceptualization: Chunguang Quan. Formal analysis: Guiju Zhu. Writing—original draft: Shiqi Ouyang. Writing—review and editing: Xiaojuan Cheng. Supervision: Chunguang Quan.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ilhan Ozturk
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, X., Ouyang, S., Quan, C. et al. Regional allocation of carbon emission quotas in China under the total control target. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 66683–66695 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26874-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26874-w