Abstract
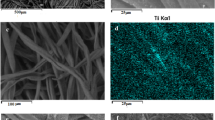
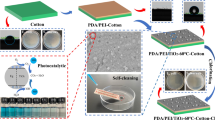
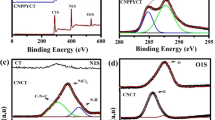
CaCu3Ti4O12 (CCTO) nanoparticles (NPs) were screen printed on pristine cotton fabric. The CCTO-coated fabric was characterized using attenuated total reflectance-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR), Raman, X-ray diffraction (XRD), x-ray photoelectron spectrometer (XPS), and field emission-scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM). The modified fabric photocatalytic antibacterial and dye-degradation abilities were assessed. After 2 h of bacterial contact, unwashed CCTO-embedded cotton reduced E. coli and S. aureus by 95.1% and 94.3%, respectively. After 20 washing cycles, the modified fabric was able to eliminate S. aureus and E. coli by more than 85%. The cloth coated with CCTO-NPs degraded the methylene blue (MB) dye by 82% in 4 h, as opposed to the pure cotton’s 11% degradation rate. The embedding of CCTO-NPs onto the cotton surface had minimal effect on fabric intrinsic properties like tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and water–vapor permeability.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Ahmadi A, Hajilou M, Zavari S, Yaghmaei S (2022) A comparative review on adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of classified dyes with metal/non-metal-based modification of graphitic carbon nitride nanocomposites: synthesis, mechanism, and affecting parameters. J Clean Prod 134967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134967
Ahmadipour M, Ain MF, Ahmad ZA (2016) A short review on copper calcium titanate (CCTO) electroceramic: synthesis, dielectric properties, film deposition, and sensing application. Nano-Micro Lett 8:291–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-016-0089-1
Ahmadipour M, Arjmand M, Ahmad ZA, Pung S-Y (2020) Photocatalytic degradation of organic dye by sol–gel-synthesized CaCu3Ti4O12 powder. J Mater Eng Perform 29:2006–2014. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-04712-1
Almeida AFL, Fechine PBA, Graça MPF et al (2009) Structural and electrical study of CaCu3Ti4O12 (CCTO) obtained in a new ceramic procedure. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 20:163–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-008-9675-4
Bag SS, Sinha S, Banerjee A, Golder A (2022) Simultaneous sensing and photocatalytic degradation to free water from toxic dye pollutants for possible agricultural and household applications: role of generated holes and hydroxyl radicals. J Environ Chem Eng 10:108919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.108919
Barman J, Tirkey A, Batra S et al (2022) The role of nanotechnology based wearable electronic textiles in biomedical and healthcare applications. Mater Today Commun 32:104055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.104055
Cai Y, Cheng W, Ji C et al (2021) Perylenediimide/silver nanohybrids with visible-light photocatalysis enhanced antibacterial effect. Dye Pigment 195:109698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2021.109698
Chilivery R, Zhang R, Chen G et al (2023) Facile in situ construction of novel hybrid 3D-BiOCl@PDA heterostructures with vacancy induced charge transfer for efficient visible light driven photocatalysis and antibacterial activity. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 656:130415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.130415
Clark JH, Dyer MS, Palgrave RG et al (2011) Visible light photo-oxidation of model pollutants using CaCu 3 Ti 4 O 12: an experimental and theoretical study of optical properties, electronic structure, and selectivity. J Am Chem Soc 133:1016–1032. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja1090832
Dong Y, Hou L, Wu P (2020) Exploring the diffusion behavior of urea aqueous solution in the viscose film by ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Cellulose 27:2403–2415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-02997-y
Duan H, Li J, Gu J et al (2022) One-pot preparation of cotton fibers with simultaneous enhanced durable flame-retardant and antibacterial properties by grafting copolymerized with vinyl monomers. React Funct Polym 181:105438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2022.105438
Fan Y, Liu Y, Cui H et al (2020) Photocatalytic overall water splitting by SrTiO3 with surface oxygen vacancies. Nanomaterials 10:2572. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122572
Fernandes D, Raubach CW, Jardim PLG et al (2021) Synthesis of NaNbO3 nanowires and their photocatalytic activity. Ceram Int 47:10185–10188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.12.070
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
Gaspar D, Fernandes SN, de Oliveira AG et al (2014) Nanocrystalline cellulose applied simultaneously as the gate dielectric and the substrate in flexible field effect transistors. Nanotechnology 25:094008. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/25/9/094008
Huang W, Tao F, Li F et al (2020) Antibacterial nanomaterials for environmental and consumer product applications. NanoImpact 20:100268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.impact.2020.100268
Jenifer A, Sriram S (2023) Enhanced photocatalytic organic dye degradation activities of pristine and Zn-doped V2O5 nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 611:155629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.155629
Jesurani S, Kanagesan S, Velmurugan R, Kalaivani T (2012) Phase formation and high dielectric constant of calcium copper titanate using sol–gel route. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 23:668–674. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-011-0468-9
Jiang M, Cheng Z, Zhao D et al (2022) Preparation and characterization of Mg-doped CaCu3Ti4O12 thin films. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 32:1589–1597. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(22)65895-3
Jin X, Li W, Wang S et al (2023) Developing flame-retardant, antibacterial cotton fabric by incorporating a linear polysiloxane-based coating. Ind Crops Prod 191:115934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.115934
Kaur S, Singh DP (2020) On the structural, dielectric and energy storage behaviour of PVDF- CaCu3Ti4O12 nanocomposite films. Mater Chem Phys 239:122301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.122301
Kaur S, Kumar A, Sharma AL, Singh DP (2019) Dielectric and energy storage behavior of CaCu3Ti4O12 nanoparticles for capacitor application. Ceram Int 45:7743–7747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.01.077
Kawrani S, Boulos M, Cornu D, Bechelany M (2019) From synthesis to applications: copper calcium titanate (CCTO) and its magnetic and photocatalytic properties. ChemistryOpen 8:922–950. https://doi.org/10.1002/open.201900133
Kumar S, Sharma M, Powar S et al (2019) Impact of remnant surface polarization on photocatalytic and antibacterial performance of BaTiO3. J Eur Ceram Soc 39:2915–2922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2019.03.029
Kumar A, Sharma M, Vaish R (2022) Screen printed calcium fluoride nanoparticles embedded antibacterial cotton fabric. Mater Chem Phys 288:126449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2022.126449
Kumar A, Sharma M, Vaish R (2022a) Durable thermoregulating, antibacterial, and UV protective smart cotton embedded with polyethylene glycol and BaTiO 3. ACS Appl Eng.https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaenm.2c00039
Kumar A, Sharma M, Vaish R (2022c) Durable antibacterial cotton fabric via spray-coating of photocatalytic MoS2. Mater Chem Phys 126658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2022.126658
Kumar A, Sharma M, Vaish R (2022d) BaTiO 3 Nanoparticles embedded antibacterial cotton fabric with UV protection characteristics. J Nat Fibers 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/15440478.2022.2139325
Kumar A, Sharma M, Vaish R, ben Ahmed S (2022e) Poling effect on piezocatalytic antibacterial and dye degradation activities of BaTiO3 nanoparticles embedded cotton fabric. J Alloys Compd 168530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.168530
Kushwaha HS, Madhar NA, Ilahi B et al (2016) Efficient solar energy conversion using CaCu3Ti4O12 photoanode for photocatalysis and photoelectrocatalysis. Sci Rep 6:18557. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep18557
Mamba G, Mafa PJ, Muthuraj V et al (2022) Heterogeneous advanced oxidation processes over stoichiometric ABO3 perovskite nanostructures. Mater Today Nano 18:100184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtnano.2022.100184
Masar M, Ali H, Guler AC et al (2023) Multifunctional bandgap-reduced ZnO nanocrystals for photocatalysis, self-cleaning, and antibacterial glass surfaces. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 656:130447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.130447
Moradi Z, Jahromi SZ, Ghaedi M (2021) Design of active photocatalysts and visible light photocatalysis. Interface Science and Tech 32: 557–623. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-818806-4.00012-7
Otitoju TA, Jiang D, Ouyang Y et al (2020) Photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B using CaCu3Ti4O12 embedded polyethersulfone hollow fiber membrane. J Ind Eng Chem 83:145–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2019.11.022
Pandiyarasan V, Archana J, Pavithra A, et al (2017) Hydrothermal growth of reduced graphene oxide on cotton fabric for enhanced ultraviolet protection applications. Mater Lett 188:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2016.11.047
Praxedes FM, Moreno H, Simões AZ et al (2022) Interface matters: design of an efficient CaCu3Ti4O12-rGO photocatalyst. Powder Technol 404:117478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2022.117478
Rafiq A, Ikram M, Ali S et al (2021) Photocatalytic degradation of dyes using semiconductor photocatalysts to clean industrial water pollution. J Ind Eng Chem 97:111–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2021.02.017
Rhouma S, Saîd S, Autret C et al (2017) Comparative studies of pure, Sr-doped, Ni-doped and co-doped CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics: enhancement of dielectric properties. J Alloys Compd 717:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.05.053
Shen L, Jiang J, Liu J et al (2022) Cotton fabrics with antibacterial and antiviral properties produced by a simple pad-dry-cure process using diphenolic acid. Appl Surf Sci 600:154152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.154152
Tang X, Gu Q, Gao P, Wen W (2021) Ultra-sensitive wide-range small capacitive pressure sensor based on porous CCTO-PDMS membrane. Sensors Actuators Rep 3:100027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snr.2021.100027
Verma S, Sharma M, Vaish R (2022) Photo-piezocatalysis in electrospun PVDF + WS 2 membrane. Environ Sci Nano.https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00699E
Wang M, Liu J, Xu C, Feng L (2022) Sonocatalysis and sono-photocatalysis in CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics. Ceram Int 48:11338–11345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.12.357
Xing H, Cheng J, Tan X et al (2020) Ag nanoparticles-coated cotton fabric for durable antibacterial activity: derived from phytic acid–Ag complex. J Text Inst 111:855–861. https://doi.org/10.1080/00405000.2019.1668137
Xu D, Yue X, Song J et al (2019a) Improved dielectric and non-ohmic properties of (Zn + Zr) codoped CaCu3Ti4O12 thin films. Ceram Int 45:11421–11427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.03.008
Xu D, Yue X, Zhang Y et al (2019b) Enhanced dielectric properties and electrical responses of cobalt-doped CaCu3Ti4O12 thin films. J Alloys Compd 773:853–859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.09.340
Xu Q, Wang X, Wang P et al (2022) Durable antibacterial cotton fabric fabricated using a “self-created” mist polymerization device. Int J Biol Macromol 216:148–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.06.184
Yang C, Song H, Liu D (2013) Effect of coupling agents on the dielectric properties of CaCu3Ti4O12/PVDF composites. Compos Part B Eng 50:180–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.02.006
Yontar AK, Avcioğlu S, Çevik S (2022) Nature-based nanocomposites for adsorption and visible light photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye. J Clean Prod 380:135070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135070
Zhang W, Zeng Q-M, Tang R-C (2022) Gallic acid functionalized polylysine for endowing cotton fiber with antibacterial, antioxidant, and drug delivery properties. Int J Biol Macromol 216:65–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.06.186
Zhu N, Zhou S, Gong J, et al (2022) In situ synthesis of cuprous oxide on cotton fiber for developing functional textile with broad-spectrum antibacterial activity. Ind Crops Prod 187:115442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.115442
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Amit Kumar: writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, conceptualization, methodology, experimental, characterization, investigation, and validation.
Moolchand Sharma: data curation, characterization, investigation, and validation.
Rahul Vaish: supervision, resources, writing—review and editing, formal analysis, conceptualization, methodology, and investigation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This research did not contain any studies involving animal or human participants, nor did it take place in any private or protected areas.
Consent to participate
All authors of this manuscript consent to participate.
Consent to publish
All authors of this manuscript have consented to its publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Sami Rtimi
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A., Sharma, M. & Vaish, R. CaCu3Ti4O12 nanoparticle-loaded cotton fabric for dual photocatalytic antibacterial and dye degradation applications. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 117011–117021 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26835-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26835-3