Abstract
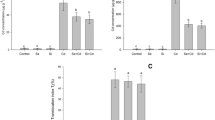
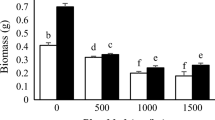
Different techniques have been used to alleviate metal toxicity in medicinal plants; accordingly, nanoparticles (NPs) have a noticeable interest in modulating oxidative stresses. Therefore, this work aimed to compare the impacts of silicon (Si), selenium (Se), and zinc (Zn) NPs on the growth, physiological status, and essential oil (EO) of sage (Salvia officinalis L.) treated with foliar application of Si, Se, and Zn NPs upon lead (Pb) and cadmium (Cd) stresses. The results showed that Se, Si, and Zn NPs decreased Pb accumulation by 35, 43, and 40%, and Cd concentration by 29, 39, and 36% in sage leaves. Shoot plant weight showed a noticeable reduction upon Cd (41%) and Pb (35%) stress; however, NPs, particularly Si and Zn improved plant weight under metal toxicity. Metal toxicity diminished relative water content (RWC) and chlorophyll, whereas NPs significantly enhanced these variables. The noticeable raises in malondialdehyde (MDA) and electrolyte leakage (EL) were observed in plants exposed to metal toxicity; however, they were alleviated with foliar application of NPs. The EO content and EO yield of sage plants decreased by the heavy metals but increased by the NPs. Accordingly, Se, Si, and Zn NPS elevated EO yield by 36, 37, and 43%, respectively, compared with non-NPs. The primary EO constituents were 1,8-cineole (9.42–13.41%), α-thujone (27.40–38.73%), β-thujone (10.11–12.94%), and camphor (11.31–16.45%). This study suggests that NPs, particularly Si and Zn, boosted plant growth by modulating Pb and Cd toxicity, which could be advantageous for cultivating this plant in areas with heavy metal–polluted soils.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data are available on request.
References
Adams RP (2007) Identification of essential oil components by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Carol Stream: Allured publishing corporation 456:544–545
Adrees M, Khan ZS, Hafeez M, Rizwan M, Hussain K, Asrar M, Ali S (2021) Foliar exposure of zinc oxide nanoparticles improved the growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and decreased cadmium concentration in grains under simultaneous Cd and water deficient stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 208:111627
Afshari M, Pazok A, Sadeghipour O (2021) Foliar-applied silicon and its nanoparticles stimulate physio-chemical changes to improve growth, yield and active constituents of coriander (Coriandrum Sativum L.) essential oil under different irrigation regimes. Silicon 13:4177–4188
Ali S, Rizwan M, Hussain A, ur Rehman MZ, Ali B, Yousaf B, Ahmad P (2019) Silicon nanoparticles enhanced the growth and reduced the cadmium accumulation in grains of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Physiol Biochem 140:1–8
Aram S, Weisany W, Daliri MS, Mirkalaie SAAM (2021) Phenology, physiology, and fatty acid profile of canola (Brassica napus L.) under agronomic management practices (Direct Seeding and Transplanting) and zinc foliar application. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 21(2):1735–1744
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24:1–8
Babashpour-Asl M, Farajzadeh-Memari-Tabrizi E, Yousefpour-Dokhanieh A (2022) Foliar-applied selenium nanoparticles alleviate cadmium stress through changes in physio-biochemical status and essential oil profile of coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.) leaves. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(53):80021–80031
Baig MA, Qamar S, Ali AA, Ahmad J, Qureshi MI (2020) Heavy metal toxicity and tolerance in crop plants. In: Contaminants in agriculture. Springer, Cham, pp 201–216
Bashir A, ur Rehman MZ, Hussaini KM, Adrees M, Qayyum MF, Sayal AU, Alyemeni MN (2021) Combined use of zinc nanoparticles and co-composted biochar enhanced wheat growth and decreased Cd concentration in grains under Cd and drought stress: a field study. Environ Technol Innov 23:101518
Beduk F, Aydin S, Aydin ME, Bahadir M (2022) Consequences of heavy metals in water and wastewater for the environment and human health. In: Water and Wastewater Management. Springer, Cham, pp 221–228
Cai ZM, Peng JQ, Chen Y, Tao L, Zhang YY, Fu LY, Shen XC (2021) 1, 8-Cineole: a review of source, biological activities, and application. J Asian Nat Prod Res 23:938–954. https://doi.org/10.1080/10286020.2020.1839432
Cui J, Liu T, Li F, Yi J, Liu C, Yu H (2017) Silica nanoparticles alleviate cadmium toxicity in rice cells: mechanisms and size effects. Environ Pollut 228:363–369
Dhopte AM, Manuel LM (2002) Principles and techniques for plant scientists, 1st edn. Updesh Purohit for Agrobios (India), Odhpur
El Moukhtari A, Lamsaadi N, Oubenali A, Mouradi M, Savoure A, Farissi M (2021) Exogenous silicon application promotes tolerance of legumes and their N2 fixing symbiosis to salt stress. Silicon 14:6517–6534
El-Saadony MT, Desoky ESM, Saad AM, Eid RS, Selem E, Elrys AS (2021) Biological silicon nanoparticles improve Phaseolus vulgaris L. yield and minimize its contaminant contents on a heavy metals-contaminated saline soil. J Environ Sci 106:1–14
Esmaielpour B, Shiekhalipour M, TORABI GM (2020) Effects of zinc nanoparticles on growth, some physiological characteristics, and essential oil yield of Dracocephalum moldavica L. under salinity stress conditions. Iranian J Med Arom Plant Res 36:867–884
Fatemi H, Esmaiel Pour B, Rizwan M (2021) Foliar application of silicon nanoparticles affected the growth, vitamin C, flavonoid, and antioxidant enzyme activities of coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.) plants grown in lead (Pb)-spiked soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:1417–1425
Ghorbani A, Esmaeilizadeh M (2017) Pharmacological properties of Salvia officinalis and its components. J Trad Complem Med 7:433–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcme.2016.12.014
Gutsch A, Zouaghi S, Renaut J, Cuypers A, Hausman JF, Sergeant K (2018) Changes in the proteome of Medicago sativa leaves in response to long-term cadmium exposure using a cell-wall targeted approach. Int J Molecul Sci 19:2498
Haider FU, Liqun C, Coulter JA, Cheema SA, Wu J, Zhang R, Farooq M (2021) Cadmium toxicity in plants: impacts and remediation strategies. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 211:111887
Handa N, Kohli SK, Kaur R, Sharma A, Kumar V, Thukral AK, Bhardwaj R (2018) Role of compatible solutes in enhancing antioxidative defense in plants exposed to metal toxicity. Plants under metal and metalloid stress: responses, tolerance and remediation, pp 207–228
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts: I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198
Huang B, Chen YE, Zhao YQ, Ding CB, Liao JQ, Hu C, Yuan M (2019) Exogenous melatonin alleviates oxidative damages and protects photosystem II in maize seedlings under drought stress. Front Plant Sci 10:677
Hussain A, Ali S, Rizwan M, ur Rehman MZ, Javed MR, Imran M, Nazir R (2018) Zinc oxide nanoparticles alter the wheat physiological response and reduce the cadmium uptake by plants. Environment Pollut 242:1518–1526
Hussain B, Lin Q, Hamid Y, Sanaullah M, Di L, Khan MB, Yan X (2020) Foliage application of selenium and silicon nanoparticles alleviates Cd and Pb toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Sci Total Environ 712:136497
Hussain F, Hadi F, Rongliang Q (2021) Effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles on antioxidants, chlorophyll contents, and proline in Persicaria hydropiper L. and its potential for Pb phytoremediation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:34697–34713
Ikram M, Javed B, Raja NI (2021) Biomedical potential of plant-based selenium nanoparticles: a comprehensive review on therapeutic and mechanistic aspects. Int J Nanomed 16:249
Ismael MA, Elyamine AM, Moussa MG, Cai M, Zhao X, Hu C (2019) Cadmium in plants: uptake, toxicity, and its interactions with selenium fertilizers. Metallomics 11:255–277
Jakovljević M, Jokić S, Molnar M, Jašić M, Babić J, Jukić H, Banjari I (2019) Bioactive profile of various Salvia officinalis L. preparations. Plants 8:55
Khosropour E, Attarod P, Shirvany A, Pypker TG, Bayramzadeh V, Hakimi L, Moeinaddini M (2019) Response of Platanus orientalis leaves to urban pollution by heavy metals. J For Res 30:1437–1445
Khosropour E, Weisany W, Tahir NAR, Hakimi L (2022) Vermicompost and biochar can alleviate cadmium stress through minimizing its uptake and optimizing biochemical properties in Berberis integerrima bunge. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:17476–17486
Kicińska A, Pomykała R, Izquierdo-Diaz M (2022) Changes in soil pH and mobility of heavy metals in contaminated soils. Europ J Soil Sci 73:e13203
Kulak M, Gul F, Sekeroglu N (2020) Changes in growth parameter and essential oil composition of sage (Salvia officinalis L.) leaves in response to various salt stresses. Ind Crop Prod 145:112078
Liu N, Huang X, Sun L, Li S, Chen Y, Cao X, Rinnan R (2020) Screening stably low cadmium and moderately high micronutrients wheat cultivars under three different agricultural environments of China. Chemosphere 241:125065. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125065
Mahmoud AWM, Abdeldaym EA, Abdelaziz SM, El-Sawy MB, Mottaleb SA (2019) Synergetic effects of zinc, boron, silicon, and zeolite nanoparticles on confer tolerance in potato plants subjected to salinity. Agronomy 10:19
Memari-Tabrizi EF, Yousefpour-Dokhanieh A, Babashpour-Asl M (2021) Foliar-applied silicon nanoparticles mitigate cadmium stress through physio-chemical changes to improve growth, antioxidant capacity, and essential oil profile of summer savory (Satureja hortensis L.). Plant Physiol Biochem 165:71–79
Mukarram M, Khan MMA, Corpas FJ (2021) Silicon nanoparticles elicit an increase in lemongrass (Cymbopogon flexuosus (Steud.) Wats) agronomic parameters with a higher essential oil yield. J Hazard Material 412:125254
Nasirzadeh L, Kvarnheden A, Sorkhilaleloo B, Hervan EM, Fatehi F (2022) Foliar-applied selenium nanoparticles can alleviate soil-cadmium stress through physio-chemical and stomatal changes to optimize yield, antioxidant capacity, and fatty acid profile of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 22(2):2469–2480
Ozfidan-Konakci C, Yildiztugay E, Bahtiyar, M Kucukoduk M (2018) The humic acid-induced changes in the water status,chlorophyll fluorescence and antioxidant defense systems of wheat leaves with cadmium stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 155:66–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.02.071
Qi WY, Li Q, Chen H, Liu J, Xing SF, Xu M, Wang SG (2021) Selenium nanoparticles ameliorate Brassica napus L. cadmium toxicity by inhibiting the respiratory burst and scavenging reactive oxygen species. J Hazard Material 417:125900
Rioba NB, Itulya FM, Saidi M, Dudai N, Bernstein N (2015) Effects of nitrogen, phosphorus and irrigation frequency on essential oil content and composition of sage (Salvia officinalis L.). J Applied Res Med Arom Plant 2:21–29
Rizwan M, Ali S, Ali B, Adrees M, Arshad M, Hussain A, Waris AA (2019a) Zinc and iron oxide nanoparticles improved the plant growth and reduced the oxidative stress and cadmium concentration in wheat. Chemosphere 214:269–277
Rizwan M, Ali S, Malik S, Adrees M, Qayyum MF, Alamri SA, Ahmad P (2019b) Effect of foliar applications of silicon and titanium dioxide nanoparticles on growth, oxidative stress, and cadmium accumulation by rice (Oryza sativa). Acta Physiol Plant 41:1–12
Saleh SR, Kandeel MM, Ghareeb D, Ghoneim TM, Talha NI, Alaoui-Sossé B, Abdel-Daim MM (2020) Wheat biological responses to stress caused by cadmium, nickel and lead. Sci Total Environ 706:136013
Sardar R, Ahmed S, Shah AA, Yasin NA (2022) Selenium nanoparticles reduced cadmium uptake, regulated nutritional homeostasis and antioxidative system in Coriandrum sativum grown in cadmium toxic conditions. Chemosphere 287:132332
Sefidkon F, Abbasi K, Khaniki GB (2006) Influence of drying and extraction methods on yield and chemical composition of the essential oil of Satureja hortensis. Food Chem 99:19–23
Shahhoseini R, Azizi M, Asili J, Moshtaghi N, Samiei L (2020) Effects of zinc oxide nanoelicitors on yield, secondary metabolites, zinc and iron absorption of Feverfew (Tanacetum parthenium (L.) Schultz Bip.). Acta Physiol Plant 42:1–18
Sharifan H, Moore J, Ma X (2020) Zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles elevated iron and copper contents and mitigated the bioavailability of lead and cadmium in different leafy greens. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 191:110177
Sheppard LJ, Franssen I, Cape JN (1995) Frost hardiness of Norway spruce treated with acid mist. Evaluation of the electrolyte leakage rate technique. Environ Exp Bot 35:139–149
Siddiqui H, Ahmed KBM, Sami F, Hayat S (2020) Silicon nanoparticles and plants: current knowledge and future perspectives. Sustainable agriculture reviews 41: Nanotechnology for plant growth and development, pp 129–142
Venkatachalam P, Jayaraj M, Manikandan R, Geetha N, Rene ER. Sharma NC, Sahi SV (2017) Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) alleviate heavy metal-induced toxicity in Leucaena leucocephala seedlings: a physiochemical analysis. Plant Physiol Biochemi 110:59-69.
Wang C, Cheng T, Liu H, Zhou F, Zhang J. Zhang M, Cao T (2021a) Nano-selenium controlled cadmium accumulation and improved photosynthesis in indica rice cultivated in lead and cadmium combined paddy soils. J Environ Sci 103:336–346
Wang M, Chen Z, Song W, Hong D, Huang L, Li Y (2021b) A review on cadmium exposure in the population and intervention strategies against cadmium toxicity. Bullut Environ Contamin Toxicol 106:65–74
Zámboriné Németh É, Thi Nguyen H (2020) Thujone, a widely debated volatile compound: What do we know about it? Phytochem Rev 19:405–423
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The data were prepared by Mitra Bakhtiari, Fereshteh Raeisi Sadati, and Seyede Yalda Raeisi; the initial draft was prepared by Mitra Bakhtiari and revised by Fereshteh Raeisi Sadati and Seyede Yalda Raeisi Sadati.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Ethical approval was not required for this work.
Consent to participate
All authors agreed to submit the manuscript to Environmental Science and Pollution Research.
Consent for publication
All authors approved the final manuscript to publish in Environmental Science and Pollution Research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bakhtiari, M., Raeisi Sadati, F. & Raeisi Sadati, S.Y. Foliar application of silicon, selenium, and zinc nanoparticles can modulate lead and cadmium toxicity in sage (Salvia officinalis L.) plants by optimizing growth and biochemical status. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 54223–54233 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25959-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25959-w