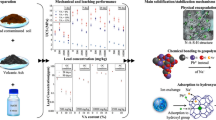
Abstract
Complexes formed by organic matter and clay minerals, which are active components of soil systems, play an important role in the migration and transformation of pollutants in nature. In this study, humic-acid–montmorillonite (HA–MT) and humic-acid–kaolin (HA–KL) complexes were prepared, and their structures before and after the adsorption of aniline were analyzed. The aniline adsorption–desorption characteristics of complexes with different clay minerals and varying HA contents were explored using the static adsorption–desorption equilibrium method. Compared with the pristine clay minerals, the flaky and porous structure of the complexes and the aromaticity were enhanced. The adsorption of aniline on the different clay mineral complexes was nonlinear, and the adsorption capacity increased with increasing HA content. Additionally, the adsorption capacity of HA–MT was higher than that of HA–KL. After adsorption, the specific surface area of the complexes decreased, the surfaces became more complicated, and the aromaticity decreased because aniline is primarily adsorption onto the complexes via aromatic rings. Aniline was adsorbed onto the complexes via spontaneous exothermic physical adsorption. The amount of aniline desorbed from the complexes increased with increasing HA content, and a lag in desorption was observed, with a greater lag for HA–KL than for HA–MT.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data and materials generated or analyzed during this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Arroyave JM, Waiman CC, Zanini GP, Avena MJ (2016) Effect of humic acid on the adsorption/desorption behavior of glyphosate on goethite. Isotherms Kinetics Chemosphere 145:34–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.11.082
Belousov P, Semenkova A, Egorova T, Romanchuk A, Zakusin S, Dorzhieva O, Tyupina E, Izosimova Y, Tolpeshta I, Chernov M, Krupskaya V (2019) Cesium sorption and desorption on glauconite, bentonite, zeolite and diatomite. Minerals 9(10):625. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9100625
Campos B, Aguilar-Carrillo J, Algarra M, Gonçalves MA, Rodríguez-Castellón ED, Silva JCG, Bobos I (2013) Adsorption of uranyl ions on kaolinite, montmorillonite, humic acid and composite clay material. Appl Clay Sci 85:53–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2013.08.046
Chen H, Koopal LK, Xiong J, Avena M, Tan W (2017) Mechanisms of soil humic acid adsorption onto montmorillonite and kaolinite. J Colloid Interface Sci 504:457–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.05.078
Cheng J, Ye Q, Lu Z, Zhang J, Zeng L, Parikh SJ, Ma W, Tang C, Xu J, He Y (2021) Quantification of the sorption of organic pollutants to minerals via an improved mathematical model accounting for associations between minerals and soil organic matter. Environ Pollut 280:116991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116991
Chianese S, Fenti A, Iovino P, Musmarra D, Salvestrini S (2020) Sorption of organic pollutants by humic acids: a review. Molecules 25(4):918. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25040918
Doretto KM, Rath S (2013) Sorption of sulfadiazine on Brazilian soils. Chemosphere 90(6):2027–2034. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.10.084
El-Sayed MEA, Khalaf MMR, Gibson D, Rice JA (2019a) Assessment of clay mineral selectivity for adsorption of aliphatic/aromatic humic acid fraction. Chem Geol 511:21–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.02.034
El-Sayed MEA, Khalaf MMR, Rice JA (2019b) Isotherm and kinetic studies on the adsorption of humic acid molecular size fractions onto clay minerals. Acta Geochimica 38(6):863–871. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-019-00330-4
Fu Z, He N, Zhou P, Xie H, Fu Z, Liu C, Chen J (2019) Grand canonical Monte Carlo simulation on adsorption of aniline on the ice surface. J Mol Liq 290:111221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111221
Georgiou, K, Jackson, RB, Vindušková, O, Abramoff, RZ, Ahlström A, Feng W, Harden JW, Pellegrini AFA, Polley HW, Soong JL, Riley WJ, Torn MS (2022) Global stocks and capacity of mineral-associated soil organic carbon. Nat Commun 13(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-31540-9
Guo F, Zhou M, Xu J, Fein JB, Yu Q, Wang Y, Huang Q, Rong X (2021) Glyphosate adsorption onto kaolinite and kaolinite-humic acid composites: experimental and molecular dynamics studies. Chemosphere 263:127979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127979
Guo X, Tu B, Ge J, Yang C, Song X, Dang Z (2016) Sorption of tylosin and sulfamethazine on solid humic acid. J Environ Sci 43:208–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2015.10.020
Huang Y, Liu Z, He Y, Li Y (2015) Impact of soil primary size fractions on sorption and desorption of atrazine on organo-mineral fractions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(6):4396–4405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3684-z
Liu H, Lin H, Song B, Sun X, Xu R, Kong T, Xu F, Li B, Sun W (2020) Stable-isotope probing coupled with high-throughput sequencing reveals bacterial taxa capable of degrading aniline at three contaminated sites with contrasting pH. Sci Total Environ 771:144807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144807
Li Y, Koopal LK, Tan W, Chai Y, Chen Y, Wu C, Tang X (2022) Effect of humic acid on lysozyme interaction with montmorillonite and kaolinite. Sci Total Environ 834:155370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155370
Lu H, Wang J, Li F, Huang X, Tian B, Hao H (2018) Highly efficient and reusable montmorillonite/Fe3O4/humic acid nanocomposites for simultaneous removal of Cr (VI) and aniline. Nanomaterials 8(7):537. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8070537
Mohammed M, Mekala LP, Chintalapati S, Chintalapati VR (2020) New insights into aniline toxicity: aniline exposure triggers envelope stress and extracellular polymeric substance formation in Rubrivivax benzoatilyticus JA2. J Hazard Mater 385:121571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121571
Peng H, Liang N, Li H, Chen F, Zhang D, Pan B, Xing B (2015) Contribution of coated humic acids calculated through their surface coverage on nano iron oxides for ofloxacin and norfloxacin sorption. Environ Pollut 204:191–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.04.029
Qian G, Xu L, Li N, Wang K, Qu Y, Xu Y (2022) Enhanced arsenic migration in tailings soil with the addition of humic acid, fulvic acid and thiol-modified humic acid. Chemosphere 286:131784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131784
Qu C, Chen W, Hu X, Cai P, Chen C, Yu X, Huang Q (2019) Heavy metal behaviour at mineral-organo interfaces: mechanisms, modelling and influence factors. Environ Int 131:104995. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.104995
Ren J, Ren X, Chen J, Guo W, Yang B, Du P (2021) Humic-mineral interactions modulated by pH conditions in bauxite residues – implications in stable aggregate formation. Geoderma 385:114856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114856
Ruan X, Zhu L, Chen B, Qian G, Frost RL (2015) Combined 1 H NMR and LSER study for the compound-specific interactions between organic contaminants and organobentonites. J Colloid Interface Sci 460:119–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.08.034
Sabah E, Ouki S (2017) Sepiolite and sepiolite-bound humic acid interactions in alkaline media and the mechanism of the formation of sepiolite-humic acid complexes. Int J Miner Process 162:69–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2017.03.005
Sander M, Pignatello J (2005) Characterization of charcoal adsorption sites for aromatic compounds: insights drawn from single-solute and bi-solute competitive experiments. Environ Sci Technol 39(6):1606–1615. https://doi.org/10.1021/es049135l
Sissou Z, Liu H, Zhou H (2019) Transport velocities of aniline and nitrobenzene in sandy sediment. J Soils Sediments 19:2570–2579. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-019-02287-6
Sun Q, Meng J, Sarkar B, Lan Y, Lin L, Li H, Yang X, Yang T, Chen W, Wang H (2020) Long-term influence of maize stover and its derived biochar on soil structure and organo-mineral complexes in Northeast China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(22):28374–28383. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08171-y
Sun W, Li Y, McGuinness LR, Luo S, Huang W, Kerkhof LJ, Mack E, Häggblom MM, Fennell DE (2015) Identification of anaerobic aniline-degrading bacteria at a contaminated industrial site. Environ Sci Technol 49(18):11079–11088. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b02166
Tang Z, Li Y, Yang Z, Liu D, Tang M, Yang S, Tang Y (2019) Characteristic and mechanism of sorption and desorption of benzene on humic acid. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(20):20277–20285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05095-0
Turlapati SA, Minocha R, Long S, Ramsdell J, Minocha SC (2015) Oligotyping reveals stronger relationship of organic soil bacterial community structure with N-amendments and soil chemistry in comparison to that of mineral soil at Harvard Forest, MA, USA. Front Microbiol 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00049
von Oepen B, Kördel W, Klein W (1991) Sorption of nonpolar and polar compounds to soils: processes, measurements and experience with the applicability of the modified OECD-Guideline 106. Chemosphere 22(3):285–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-6535(91)90318-8
Wang F, He J, He B, Zhu X, Qiao X, Peng L (2018) Formation process and mechanism of humic acid-kaolin complex determined by carbamazepine sorption experiments and various characterization methods. J Environ Sci 69:251–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2017.10.020
Wang L, Li X, Tsang DCW, Jin F, Hou D (2020) Green remediation of Cd and Hg contaminated soil using humic acid modified montmorillonite: immobilization performance under accelerated ageing conditions. J Hazard Mater 387:122005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.122005
Wen X, Du C, Wan J, Zeng G, Huang D, Yin L, Deng R, Tan S, Zhang J (2019) Immobilizing laccase on kaolinite and its application in treatment of malachite green effluent with the coexistence of Cd (П). Chemosphere 217:843–850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.073
Xu N, Huangfu X, Li Z, Wu Z, Li D, Zhang M (2019) Nanoaggregates of silica with kaolinite and montmorillonite: sedimentation and transport. Sci Total Environ 669:893–902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.099
Xu P, Wu J, Wang H, Tang S, Cheng W, Li M, Bu R, Han S, Geng M (2022) Combined application of chemical fertilizer with green manure increased the stabilization of organic carbon in the organo-mineral complexes of paddy soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22315-2
Yang K, Yan X, Xu J, Jiang L, Wu W (2021) Sorption of organic compounds by pyrolyzed humic acids. Sci Total Environ 781:146646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146646
Yeasmin S, Singh B, Kookana RS, Farrell M, Sparks DL, Johnston CT (2014) Influence of mineral characteristics on the retention of low molecular weight organic compounds: a batch sorption–desorption and ATR-FTIR study. J Colloid Interface Sci 432:246–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2014.06.036
Yousef RI, El-Eswed B, Al-Muhtaseb AAH (2011) Adsorption characteristics of natural zeolites as solid adsorbents for phenol removal from aqueous solutions: kinetics, mechanism, and thermodynamics studies. Chem Eng J 171(3):1143–1149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.05.012
Zhang S, Shao T, Bekaroglu SSK, Karanfil T (2010) Adsorption of synthetic organic chemicals by carbon nanotubes: effects of background solution chemistry. Water Res 44(6):2067–2074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.12.017
Zhou W, Yang Q, Chen C, Wu Q, Zhu L (2015) Fixed-bed study and modeling of selective phenanthrene removal from surfactant solutions. Colloids Surf A 470:100–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2015.01.077
Zhu X, He J, Su S, Zhang X, Wang F (2016) Concept model of the formation process of humic acid–kaolin complexes deduced by trichloroethylene sorption experiments and various characterizations. Chemosphere 151:116–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.02.068
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the efforts of all the researchers whose articles were included in this study. The authors would like to thank the editor and anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions for improving the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant number 41701353]; the Yue Qi Young Scholar Project, China University of Mining & Technology, Beijing [grant number 2019QN09]; and the National Innovative Experiment Program for College Students of China [grant number 202103050].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Methodology, project administration, and writing – review and editing – were performed by Yan Ma. Investigation, methodology, and writing – original draft – were performed by Xinyi Wu. Investigation, material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Tong Wang. Investigation and writing – review and editing – were performed by Shengkun Zhou. Methodology and visualization were performed by Biying Cui. Investigation and writing – review and editing – were performed by Haoqun Sha. Conceptualization, formal analysis, and supervision were performed by Bowen Lv.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Y., Wu, X., Wang, T. et al. Elucidation of aniline adsorption–desorption mechanism on various organo–mineral complexes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 39871–39882 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-25096-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-25096-w