Abstract
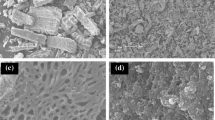
Numerous studies have explored the adsorption of cadmium (Cd) and arsenic (As) by iron (Fe)-modified biochar, but few studies have examined in-depth the similarities and differences in the adsorption behavior of different iron types on Cd and As. In this study, sewage sludge biochar (BC) was co-pyrolyzed with self-made Fe minerals (magnetite, hematite, ferrihydrite, goethite, and schwertmannite) to treat Cd and As co-contaminated water. The adsorption of Cd and As on the Fe-modified biochar was further analyzed by adsorption kinetics, adsorption isotherms, and adsorption thermodynamics combined with a series of characterization experiments. Both SEM-EDX and XRD results confirmed the successful loading of iron minerals onto BC. Both adsorption kinetics and adsorption isotherms experiments showed that the adsorption of Cd and As by BC and the other five Fe-modified biochar was mainly controlled by chemical interactions. The results also indicated that goethite biochar (GtBC) was the most effective for the adsorption of Cd among the five Fe-modified biochar. Ferrihydrite biochar (FhBC) formed more diverse complexes, coupled with the relatively stronger electrons accepting ability, thus making it more effective for As adsorption than the others. Additionally, GtBC and hematite biochar (HmBC) were found effective for the adsorption of both Cd and As, whereas MBC was not found effective for either metal. Furthermore, combined with XPS results, the adsorption of Cd by the materials was mainly governed by Cd2+-π interactions, complexation precipitation, and co-precipitation, while oxidation reactions also existed for As.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Akar T, Kaynak Z, Ulusoy S, Yuvaci D, Ozsari G, Akar ST (2009) Enhanced biosorption of nickel(II) ions by silica-gel-immobilized waste biomass: biosorption characteristics in batch and dynamic flow mode. J Hazard Mater 163(2–3):1134–1141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.07.084
Alberti G, Amendola V, Pesavento M, Biesuz R (2012) Beyond the synthesis of novel solid phases: Review on modelling of sorption phenomena. Coord Chem Rev 256(1–2):28–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2011.08.022
Alijani H, Shariatinia Z (2017) Effective aqueous arsenic removal using zero valent iron doped MWCNT synthesized by in situ CVD method using natural alpha-Fe2O3 as a precursor. Chemosphere 171:502–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.12.106
An WH, Wu C, Xue SG, Liu ZY, Liu M, Li W (2022) Effects of biochar/AQDS on As(III)-adsorbed ferrihydrite reduction and arsenic (As) and iron (Fe) transformation: Abiotic and biological conditions. Chemosphere 291(Pt 3):133126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133126
Arkaan MF, Ekaputri RF, Fatimah I, Kamari A (2020) Physicochemical and photocatalytic activity of hematite/biochar nanocomposite prepared from Salacca skin waste. Sustain Chem Pharm 16:100261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2020.100261
Brechbuhl Y, Christl I, Elzinga EJ, Kretzschmar R (2012) Competitive sorption of carbonate and arsenic to hematite: combined ATR-FTIR and batch experiments. J Colloid Interface Sci 377(1):313–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2012.03.025
Catalano JG, Zhang Z, Park C, Fenter P, Bedzyk MJ (2007) Bridging arsenate surface complexes on the hematite (012) surface. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 71(8):1883–1897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2007.01.015
Chagas JKM, Figueiredo CC, da Silva J, Paz-Ferreiro J (2021) The residual effect of sewage sludge biochar on soil availability and bioaccumulation of heavy metals: Evidence from a three-year field experiment. J Environ Manage 279:111824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111824
Chen Z, Liu T, Tang JJ, Zheng ZJ, Wang HM, Shao Q, Chen GL, Li ZX, Chen YQ, Zhu JW, Feng T (2018) Characteristics and mechanisms of cadmium adsorption from aqueous solution using lotus seedpod-derived biochar at two pyrolytic temperatures. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25(12):11854–11866. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1460-1
Cheng S, Liu YZ, Xing BL, Qin XJ, Zhang CX, Xia HY (2021) Lead and cadmium clean removal from wastewater by sustainable biochar derived from poplar saw dust. J Clean Prod 314:128074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128074
Cope CO, Webster DS, Sabatini DA (2014) Arsenate adsorption onto iron oxide amended rice husk char. Sci Total Environ 488–489:554–561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.12.120
Cuong DV, Wu PC, Chen LI, Hou CH (2021) Active MnO2/biochar composite for efficient As(III) removal: Insight into the mechanisms of redox transformation and adsorption. Water Res 188:116495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116495
de la Luz-Asunción M, Pérez-Ramírez EE, Martínez-Hernández AL, García-Casillas PE, Luna-Bárcenas JG, Velasco-Santos C (2020) Adsorption and kinetic study of Reactive Red 2 dye onto graphene oxides and graphene quantum dots. Diam Relat Mater 109:108002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2020.108002
Deng S, Wang P, Zhang GS, Dou Y (2016) Polyacrylonitrile-based fiber modified with thiosemicarbazide by microwave irradiation and its adsorption behavior for Cd(II) and Pb(II). J Hazard Mater 307:64–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.01.002
Foo KY, Hameed BH (2010) Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem Eng J 156(1):2–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.09.013
Goldberg S, Johnston CT (2001) Mechanisms of Arsenic adsorption on amorphous oxides evaluated using macroscopic measurements, vibrational spectroscopy, and surface complexation modeling. J Colloid Interface Sci 234(1):204–216. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.2000.7295
Gunay A, Arslankaya E, Tosun I (2007) Lead removal from aqueous solution by natural and pretreated clinoptilolite: adsorption equilibrium and kinetics. J Hazard Mater 146(1–2):362–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.12.034
Guo JH, Yan CZ, Luo ZX, Fang HD, Hu SG, Cao YL (2019) Synthesis of a novel ternary HA/Fe-Mn oxides-loaded biochar composite and its application in cadmium(II) and arsenic(V) adsorption. J Environ Sci (china) 85:168–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2019.06.004
Hazrati S, Farahbakhsh M, Cerda A, Heydarpoor G (2021) Functionalization of ultrasound enhanced sewage sludge-derived biochar: physicochemical improvement and its effects on soil enzyme activities and heavy metals availability. Chemosphere 269:128767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128767
Hu XH, Wen J, Zhang HB, Wang Q, Yan CY, Xing L (2020) Can epicatechingallate increase Cr(VI) adsorption and reduction on ZIF-8? Chem. Eng. J 391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123501
Huang M, Li ZW, Huang B, Luo NL, Zhang Q, Zhai XQ, Zeng GM (2018) Investigating binding characteristics of cadmium and copper to DOM derived from compost and rice straw using EEM-PARAFAC combined with two-dimensional FTIR correlation analyses. J Hazard Mater 344:539–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.10.022
Huang YM, Lee XQ, Grattieri M, Yuan MW, Cai R, Macazo FC, Minteer SD (2020) Modified biochar for phosphate adsorption in environmentally relevant conditions. Chem Eng J 380:122375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122375
Iqbal T, Iqbal S, Batool F, Thomas D, Iqbal MMH (2021) Utilization of a Newly developed nanomaterial based on loading of biochar with hematite for the removal of cadmium ions from aqueous media. Sustain 13(4):2191. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13042191
Irshad MK, Noman A, Alhaithloul HAS, Adeel M, Rui Y, Shah T, Zhu S, Shang J (2020) Goethite-modified biochar ameliorates the growth of rice (Oryza sativa L) plants by suppressing Cd and As-induced oxidative stress in Cd and As co-contaminated paddy soil. Sci. Total. Environ 717:137086. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137086
Jennings AA (2013) Analysis of worldwide regulatory guidance values for the most commonly regulated elemental surface soil contamination. J Environ Manage 118:72–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.12.032
Li F-Y, Gui X-Y, Xu J-H, Ma J-R, Wen Z-W, Cai Y-B, Wang J-F (2019) Spectral analysis of dissolved organic matter from biochar. Spectrosc Spectral Anal (beijing, China) 39(11):3475–3481
Li JH, Cheng R, Chen JA, Lan JR, Li SY, Zhou M, Zeng TY, Hou HB (2021a) Microscopic mechanism about the selective adsorption of Cr(VI) from salt solution on nitrogen-doped carbon aerogel microsphere pyrolysis products. Sci Total Environ 798:149331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149331
Li YF, Wen J, Xue ZZ, Yin XY, Yuan L, Yang CL (2021b) Removal of Cr(VI) by polyaniline embedded polyvinyl alcohol/sodium alginate beads - extension from water treatment to soil remediation. J Hazard Mater 426:127809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127809
Liu JQ, Wu PX, Li SS, Chen MQ, Cai WT, Zou DH, Zhu NW, Dang Z (2019) Synergistic deep removal of As(III) and Cd(II) by a calcined multifunctional MgZnFe-CO3 layered double hydroxide: photooxidation, precipitation and adsorption. Chemosphere 225:115–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.03.009
Liu K, Li FB, Cui JH, Yang SY, Fang LP (2020) Simultaneous removal of Cd(II) and As(III) by graphene-like biochar-supported zero-valent iron from irrigation waters under aerobic conditions: synergistic effects and mechanisms. J Hazard Mater 395:122623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122623
Luo MK, Lin H, He YH, Li B, Dong YB, Wang L (2019) Efficient simultaneous removal of cadmium and arsenic in aqueous solution by titanium-modified ultrasonic biochar. Bioresour Technol 284:333–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.03.108
Ma JC, Huang W, Zhang XS, Li YC, Wang N (2021) The utilization of lobster shell to prepare low-cost biochar for high-efficient removal of copper and cadmium from aqueous: sorption properties and mechanisms. J Environ Chem Eng 9(1):104703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104703
Manning BA, Fendorf SE, Goldberg S (1998) Surface structures and stability of arsenic(iii) on goethite: spectroscopic evidence for inner-sphere complexes. Environ Sci Technol 32(16):2383–2388. https://doi.org/10.1021/es9802201
Meng XQ, Wang XM, Zhang CM, Yan S, Zheng GY, Zhou LX (2021) Co-adsorption of As(III) and phenanthrene by schwertmannite and Fenton-like regeneration of spent schwertmannite to realize phenanthrene degradation and As(III) oxidation. Environ Res 195:110855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.110855
Navarathna CM, Karunanayake AG, Gunatilake SR, Pittman CU Jr, Perez F, Mohan D, Mlsna T (2019) Removal of arsenic(III) from water using magnetite precipitated onto Douglas fir biochar. J Environ Manage 250:109429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109429
Peng HH, Yang JCE, Fu ML, Yuan BL (2020) Nanocrystalline ferrihydrite activated peroxymonosulfate for butyl-4-hydroxybenzoate oxidation: performance and mechanism. Chemosphere 242:125140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125140
Peter A, Chabot B, Loranger E (2021) Enhanced activation of ultrasonic pre-treated softwood biochar for efficient heavy metal removal from water. J Environ Manage 290:112569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112569
Poulin S, França R, Moreau-Bélanger L, Sacher E (2010) Confirmation of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy peak attributions of nanoparticulate iron oxides, using symmetric peak component line shapes. J Phys Chem C 114(24):10711–10718. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp100964x
Qiu Y, Zhang Q, Li M, Fan ZX, Sang WJ, Xie CFY, Niu DY (2019) Adsorption of Cd(II) from aqueous solutions by modified biochars: comparison of modification methods. Water Air Soil Pollut 230(4):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4135-8
Reddy DHK, Lee SM (2014) Magnetic biochar composite: Facile synthesis, characterization, and application for heavy metal removal. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 454:96–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2014.03.105
Regenspurg S, Brand A, Peiffer S (2004) Formation and stability of schwertmannite in acidic mining lakes. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68(6):1185–1197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2003.07.015
Revellame ED, Fortela DL, Sharp W, Hernandez R, Zappi ME (2020) Adsorption kinetic modeling using pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws: a review. Clean Eng Technol 1:100032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clet.2020.100032
Shakoor MB, Ali S, Rizwan M, Abbas F, Bibi I, Riaz M, Khalil U, Niazi NK, Rinklebe J (2020) A review of biochar-based sorbents for separation of heavy metals from water. Int J Phytoremediation 22(2):111–126. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2019.1647405
Sitthichai S, Pilapong C, Thongtem T, Thongtem S (2015) CMC-coated Fe 3 O 4 nanoparticles as new MRI probes for hepatocellular carcinoma. Appl Surf Sci 356:972–977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.08.140
Sun DZ, Li FY, Jin JW, Khan S, Eltohamy KM, He MM, Liang XQ (2022) Qualitative and quantitative investigation on adsorption mechanisms of Cd(II) on modified biochar derived from co-pyrolysis of straw and sodium phytate. Sci Total Environ 829:154599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154599
Tan KL, Hameed BH (2017) Insight into the adsorption kinetics models for the removal of contaminants from aqueous solutions. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 74:25–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.01.024
Tshemese SJ, Mhike W, Tichapondwa SM (2021) Adsorption of phenol and chromium (VI) from aqueous solution using exfoliated graphite: equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamic studies. Arab J Chem 14(6):103160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103160
Vikrant K, Kim KH (2019) Nanomaterials for the adsorptive treatment of Hg(II) ions from water. Chem Eng J 358:264–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.10.022
Wahlqvist M, Shchukarev A (2007) XPS spectra and electronic structure of group IA sulfates. J Electron Spectros Relat Phenomena 156–158:310–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elspec.2006.11.032
Wamba AGN, Lima EC, Ndi SK, Thue PS, Kayem JG, Rodembusch FS, Dos Reis GS, de Alencar WS (2017) Synthesis of grafted natural pozzolan with 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane: preparation, characterization, and application for removal of Brilliant Green 1 and Reactive Black 5 from aqueous solutions. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24(27):21807–21820. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9825-4
Wang F, Jin LT, Guo CN, Min LJ, Zhang P, Sun HW, Zhu HK, Zhang CP (2021a) Enhanced heavy metals sorption by modified biochars derived from pig manure. Sci Total Environ 786:147595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147595
Wang H, Wang XJ, Ma JX, Xia P, Zhao JF (2017a) Removal of cadmium (II) from aqueous solution: a comparative study of raw attapulgite clay and a reusable waste-struvite/attapulgite obtained from nutrient-rich wastewater. J Hazard Mater 329:66–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.01.025
Wang L, Li ZT, Wang Y, Brookes PC, Wang F, Zhang QC, Xu JM, Liu XM (2021b) Performance and mechanisms for remediation of Cd(II) and As(III) co-contamination by magnetic biochar-microbe biochemical composite: competition and synergy effects. Sci Total Environ 750:141672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141672
Wang N, Xue XM, Juhasz AL, Chang ZZ, Li HB (2017b) Biochar increases arsenic release from an anaerobic paddy soil due to enhanced microbial reduction of iron and arsenic. Environ Pollut 220(Pt A):514–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.09.095
Wang SS, Gao B, Zimmerman AR, Li YC, Ma L, Harris WG, Migliaccio KW (2015) Removal of arsenic by magnetic biochar prepared from pinewood and natural hematite. Bioresour Technol 175:391–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.10.104
Wen J, Xue ZZ, Yin XY, Wang X (2022) Insights into aqueous reduction of Cr(VI) by biochar and its iron-modified counterpart in the presence of organic acids. Chemosphere 286(Pt 3):131918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131918
Wongrod S, Simon S, van Hullebusch ED, Lens PNL, Guibaud G (2018) Changes of sewage sludge digestate-derived biochar properties after chemical treatments and influence on As(III and V) and Cd(II) sorption. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 135:96–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2018.10.001
Wu C, An WH, Liu ZY, Lin J, Qian ZY, Xue SG (2020a) The effects of biochar as the electron shuttle on the ferrihydrite reduction and related arsenic (As) fate. J Hazard Mater 390:121391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121391
Wu JZ, Li ZT, Huang D, Liu XM, Tang CX, Parikh SJ, Xu JM (2020b) A novel calcium-based magnetic biochar is effective in stabilization of arsenic and cadmium co-contamination in aerobic soils. J Hazard Mater 387:122010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.122010
Xiao ZX, Yang LZ, Chen C, Chen D, Zhou X (2022) Redox reaction between solid-phase humins and Fe(III) compounds: toward a further understanding of the redox properties of humin and its possible environmental effects. J Environ Manage 310:114793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114793
Xin Y, Gu PW, Long HY, Meng MJ, Yaseen M, Su HF (2021) Fabrication of ferrihydrite-loaded magnetic sugar cane bagasse charcoal adsorbent for the adsorptive removal of selenite from aqueous solution. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 614:126131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.126131
Yan CY, Wen J, Wang Q, Xing L, Hu XH (2021) Mobilization or immobilization? The effect of HDTMA-modified biochar on As mobility and bioavailability in soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 207:111565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111565
Yang D, Wang L, Li ZT, Tang XJ, He MJ, Yang SY, Liu XM, Xu JM (2020) Simultaneous adsorption of Cd(II)andAs(III)by a novel biochar-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron in aqueous systems. Sci Total Environ 708:134823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134823
Yang F, Li X-Q, Wang B, Sun L, He Y-Y, Huang Y-M, Li Y (2015) Effects of Different feedstocks on physicochemical characteristics of pyrolyzed biochars. J Agro-Environ Sci 34(9):1822–1828
Yang G, Chen HL, Qin HD, Feng YJ (2014) Amination of activated carbon for enhancing phenol adsorption: Effect of nitrogen-containing functional groups. Appl Surf Sci 293:299–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.12.155
Yang WJ, Ding P, Zhou L, Yu JG, Chen XQ, Jiao FP (2013) Preparation of diamine modified mesoporous silica on multi-walled carbon nanotubes for the adsorption of heavy metals in aqueous solution. Appl Surf Sci 282:38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.05.028
Yin DX, Wang X, Peng B, Tan CY, Ma LQ (2017) Effect of biochar and Fe-biochar on Cd and As mobility and transfer in soil-rice system. Chemosphere 186:928–937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.07.126
Yu YL, Xu ZB, Xu XY, Zhao L, Qiu H, Cao XD (2021) Synergistic role of bulk carbon and iron minerals inherent in the sludge-derived biochar for As(V) immobilization. Chem Eng J 417:129183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129183
Yuan L, Wen J, Xue ZZ, Li YF, Yang CL, Yin XY (2021) Microscopic investigation into remediation of cadmium and arsenite Co-contamination in aqueous solution by Fe-Mn-incorporated titanosilicate. Sep Purif Technol 279:119809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119809
Zhang F, Wang X, Ji XH, Ma LJ (2016) Efficient arsenate removal by magnetite-modified water hyacinth biochar. Environ Pollut 216:575–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.06.013
Zhang M, Gao B (2013) Removal of arsenic, methylene blue, and phosphate by biochar/AlOOH nanocomposite. Chem Eng J 226:286–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.04.077
Zhang W, Ma XY, Li R, Yang WZ, Li Q, Sun XY, Li JS, Shen JY (2021) Rapid sequestration of chelated Cr(III) by ferrihydrite: adsorption and overall transformation of Cr(III) complexes. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 625:126819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126819
Zhao ZX, Jia YF, Xu LY, Zhao SL (2011) Adsorption and heterogeneous oxidation of As(III) on ferrihydrite. Water Res 45(19):6496–6504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.09.051
Zhu SH, Qu T, Irshad MK, Shang JY (2020a) Simultaneous removal of Cd(II) and As(III) from co-contaminated aqueous solution by α-FeOOH modified biochar. Biochar 2(1):81–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42773-020-00040-8
Zhu SH, Zhao JJ, Zhao N, Yang X, Chen C, Shang JY (2020b) Goethite modified biochar as a multifunctional amendment for cationic Cd(II), anionic As(III), roxarsone, and phosphorus in soil and water. J Clean Prod 247:119579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119579
ZoroufchiBenis K, Soltan J, McPhedran KN (2021) Electrochemically modified adsorbents for treatment of aqueous arsenic: pore diffusion in modified biomass vs biochar. Chem Eng J 423:130061. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.130061
Funding
This work was supported by the Open Funding of State Environmental Protection Key Laboratory of Monitoring for Heavy Metal Pollutants (Grant No. SKLMHM202211) and the Natural Science Foundation of Changsha City (No. kq2208020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qi Wang: methodology, experiment, data curation, and writing—original draft. Jia Wen: methodology, funding acquisition, writing—review and editing, and supervision. Lisha Yang: writing—review and editing. Hongsheng Cui: writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Zhihong Xu
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This manuscript was only submitted on Environmental Science and Pollution Research.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Wen, J., Yang, L. et al. Exploration on the role of different iron species in the remediation of As and Cd co-contamination by sewage sludge biochar. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 39154–39168 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24952-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24952-z