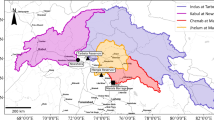
Abstract
Remote sensing has long been an effective method for water quality monitoring because of its advantages such as high coverage and low consumption. For non-optically active parameters, traditional empirical and analytical methods cannot achieve quantitative retrieval. Machine learning has been gradually used for water quality retrieval due to its ability to capture the potential relationship between water quality parameters and satellite images. This study is based on Sentinel-2 images and compared the ability of four machine learning algorithms (eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost), Support Vector Regression (SVR), Random Forest (RF), and Artificial Neural Network (ANN)) to retrieve chlorophyll-a (Chl-a), dissolved oxygen (DO), and ammonia-nitrogen (NH3-N) for inland reservoirs. The results indicated that XGBoost outperformed the other three algorithms. We used XGBoost to reconstruct the spatial-temporal patterns of Chl-a, DO, and NH3-N for the period of 2018–2020 and further analyzed the interannual, seasonal, and spatial variation characteristics. This study provides an efficient and practical way for optically and non-optically active parameters monitoring and management at the regional scale.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Achmad AR, Syifa M, Park SJ et al (2019) Geomorphological transition research for affecting the coastal environment due to the volcanic eruption of Anak Krakatau by satellite imagery. J Coast Res 90:214. https://doi.org/10.2112/SI90-026.1
Alcantara E, Bernardo N, Rodrigues T et al (2017) Modeling the spatio-temporal dissolved organic carbon concentration in Barra Bonita reservoir using OLI/Landsat-8 images. Model Earth Syst Environ 3:11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-017-0275-2
Barnes BB, Hu C (2016) Dependence of satellite ocean color data products on viewing angles: a comparison between SeaWiFS, MODIS, and VIIRS. Remote Sens Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2015.12.048
Bierman P, Lewis M, Ostendor B et al (2011) A review of methods for analysing spatial and temporal patterns in coastal water quality. Ecol Indic 11:103–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2009.11.001
Botchkarev A (2018) Performance metrics (error measures) in machine learning regression, forecasting and prognostics: properties and typology. Interdiscip J Inf Knowl Manag 14:45–79. https://doi.org/10.28945/4184
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45:5–32. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010933404324
Breitburg D, Levin LA, Oschlies A et al (2018) Declining oxygen in the global ocean and coastal waters. Science 359:eaam7240. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aam7240
Chai T, Draxler RR (2014) Root mean square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE)?–arguments against avoiding RMSE in the literature. Geosci Model Dev 7:1247–1250. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-7-1247-2014
Chawla I, Karthikeyan L, Mishra AK (2020) A review of remote sensing applications for water security: quantity, quality, and extremes. J Hydrol 585:124826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.124826
Chen T, Guestrin C (2016) Xgboost: a scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp 785–794. https://doi.org/10.1145/2939672.2939785
Chi L, Song X, Yuan Y et al (2020) Main factors dominating the development, formation and dissipation of hypoxia off the Changjiang Estuary (CE) and its adjacent waters, China. Environ Pollut 265:115066. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115066
Diaz-Gonzalez FA, Vuelvas J, Correa CA et al (2022) Machine learning and remote sensing techniques applied to estimate soil indicators–review. Ecol Indic 135:108517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108517
Dong G, Hu Z, Liu X et al (2020) Spatio-temporal variation of total nitrogen and ammonia nitrogen in the water source of the middle route of the south-to-north water diversion project. Water 12:2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092615
Fernanda W, Enner A, Thanan R et al (2015) Estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration and the trophic state of the Barra Bonita hydroelectric reservoir using OLI/Landsat-8 images. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12:10391–10417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120910391
Gao Y, Gao J, Yin H et al (2015) Remote sensing estimation of the total phosphorus concentration in a large lake using band combinations and regional multivariate statistical modeling techniques. J Environ Manag 151:33–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.11.036
Gitelson A (1992) The peak near 700 nm on radiance spectra of algae and water: relationships of its magnitude and position with chlorophyll concentration. Int J Remote Sens 13:3367–3373. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431169208904125
Gons HJ (1999) Optical teledetection of chlorophyll a in turbid inland waters. Environ Sci Technol 33:1127–1132. https://doi.org/10.1021/es9809657
Guo H, Huang JJ, Chen B et al (2021a) A machine learning-based strategy for estimating non-optically active water quality parameters using Sentinel-2 imagery. Int J Remote Sens 42:1841–1866. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2020.1846222
Guo H, Huang JJ, Zhu X et al (2021b) A generalized machine learning approach for dissolved oxygen estimation at multiple spatiotemporal scales using remote sensing. Environ Pollut 288:117734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117734
Hunter PD, Tyler AN, Gilvear DJ et al (2009) Using remote sensing to aid the assessment of human health risks from blooms of potentially toxic cyanobacteria. Environ Sci Technol 43:2627–2633. https://doi.org/10.1021/es802977u
Kaire T, Tiit K, Alo L et al (2016) First experiences in mapping lake water quality parameters with Sentinel-2 MSI imagery. Remote Sens 8:640. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8080640
Kim S, Kim H (2016) A new metric of absolute percentage error for intermittent demand forecasts. Int J Forecast 32:669–679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijforecast.2015.12.003
Kim YW, Kim T, Shin J et al (2022) Validity evaluation of a machine-learning model for chlorophyll a retrieval using Sentinel-2 from inland and coastal waters. Ecol Indic 137:108737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108737
Lee Z, Carder KL, Arnone RA (2002) Deriving inherent optical properties from water color: a multiband quasi-analytical algorithm for optically deep waters. Appl Opt 41:5755–5772. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.41.005755
Li Y, Zhang Y, Shi K et al (2018) Spatiotemporal dynamics of chlorophyll-a in a large reservoir as derived from Landsat 8 OLI data: understanding its driving and restrictive factors. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:1359–1374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0536-7
Liu G, Li L, Song K et al (2020) An OLCI-based algorithm for semi-empirically partitioning absorption coefficient and estimating chlorophyll a concentration in various turbid case-2 waters. Remote Sens Environ 239:111648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2020.111648
Lu S, Deng R, Liang Y et al (2020) Remote sensing retrieval of total phosphorus in the pearl river channels based on the GF-1 remote sensing data. Remote Sens 12:1420. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12091420
Maritorena S, Siegel DA, Peterson AR (2002) Optimization of a semianalytical ocean color model for global-scale applications. Appl Opt 41:2705–2714. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.41.002705
Matthews MW, Odermatt D (2015) Improved algorithm for routine monitoring of cyanobacteria and eutrophication in inland and near-coastal waters. Remote Sens Environ 156:374–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2014.10.010
Matthews MW, Bernard S, Robertson L (2012) An algorithm for detecting trophic status (chlorophyll- a ), cyanobacterial-dominance, surface scums and floating vegetation in inland and coastal waters. Remote Sens Environ 124:637–652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2012.05.032
Mouw CB, Greb S, Aurin D et al (2015) Aquatic color radiometry remote sensing of coastal and inland waters: challenges and recommendations for future satellite missions. Remote Sens Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2015.02.001
Neil C, Spyrakos E, Hunter PD et al (2019) A global approach for chlorophyll-a retrieval across optically complex inland waters based on optical water types. Remote Sens Environ 229:159–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.04.027
Nguyen H-Q, Ha N-T, Pham T-L (2020) Inland harmful cyanobacterial bloom prediction in the eutrophic Tri An reservoir using satellite band ratio and machine learning approaches. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:9135–9151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07519-3
O’Reilly JE, Maritorena S, Mitchell BG et al (1998) Ocean color chlorophyll algorithms for SEAWIFS. J Geophys Res 103:24937. https://doi.org/10.1029/98JC02160
Saberioon M, Brom J, Nedbal V et al (2020) Chlorophyll-a and total suspended solids retrieving and mapping using Sentinel-2 and machine learning for inland waters. Ecol Indic 113:106236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106236
Sagan V, Peterson KT, Maimaitijiang M et al (2020) Monitoring inland water quality using remote sensing: potential and limitations of spectral indices, bio-optical simulations, machine learning, and cloud computing. Earth-Sci Rev 205:103187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103187
Smith B, Pahlevan N, Schalles J et al (2021) A chlorophyll-a algorithm for Landsat-8 based on mixture density networks. Front Remote Sens 1:623678. https://doi.org/10.3389/frsen.2020.623678
Song K, Lin L, Li S et al (2012) Hyperspectral remote sensing of total phosphorus (TP) in three Central Indiana water supply reservoirs. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:1481–1502. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-0959-6
Vanhellemont Q (2019) Adaptation of the dark spectrum fitting atmospheric correction for aquatic applications of the Landsat and Sentinel-2 archives. Remote Sens Environ 225:175–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.03.010
Varol M (2020) Use of water quality index and multivariate statistical methods for the evaluation of water quality of a stream affected by multiple stressors: a case study. Environ Pollut 266:115417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115417
Wang Z, Wei L, He C et al (2021) Ammonia nitrogen monitoring of urban rivers with UAV-borne hyperspectral remote sensing imagery. In: 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS. IEEE, Brussels, pp 3713–3716
Xiao H, Krauss M, Floehr T et al (2016) Effect-directed analysis of Aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists in sediments from the three Gorges reservoir, China. Environ Sci Technol 50:11319–11328. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b03231
Xiong Y, Ran Y, Zhao S et al (2019) Remotely assessing and monitoring coastal and inland water quality in China: progress, challenges and outlook. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol:1–37. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2019.1656511
Zhang Y, Fitch P, Vilas MP et al (2019) Applying multi-layer artificial neural network and mutual information to the prediction of trends in dissolved oxygen. Front Environ Sci 7:46. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2019.00046
Zhu M, Wang J, Yang X et al (2022) A review of the application of machine learning in water quality evaluation. Eco-Environ Health. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eehl.2022.06.001
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2021YFC3200400).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shang Tian: put forward ideas, performed the experiments, and wrote the draft.
Hongwei Guo: performed the experiments and revised the draft.
Jinhui Jeanne Huang: supervised research activity and revised draft.
Xiaotong Zhu: trained machine learning models.
Bo Wang: processed data.
Wang Xu: provided study materials.
Qinghuai Zeng: provided study materials.
Youquan Mai: provided study materials.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Xianliang Yi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, S., Guo, H., Xu, W. et al. Remote sensing retrieval of inland water quality parameters using Sentinel-2 and multiple machine learning algorithms. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 18617–18630 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23431-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23431-9