Abstract
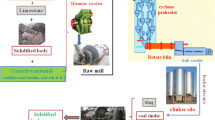
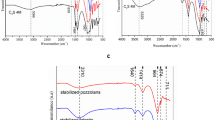
In order to reduce the environmental impact of shale gas production and towards the attenuation of artificial pozzolanic materials production cost, new oil-based drilling cuttings (OBDCs) pozzolanic materials have been introduced. After calcination, the chemical composition and the pozzolanic activity of oil-based drilling cuttings residue (OBDCRs) were investigated. The combination of X-ray diffraction (XRD), thermogravimetric analysis (TG), and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) techniques shed light on impacts of pretreatment, calcination temperature, and Ba2+ on minerals’ structure and pozzolanic activity. The results showed that, after high temperature calcination, the components of Si or Al in the OBDCRs particle surface and structure were activated and recombined to produce corresponding activity. Ba2+ could promote the pozzolanic activity of OBDCRs. The 28-day-compressive strength of OBDCRs was bigger than 31.33Mpa, and the compression strength ratios of cement mortar were bigger than 65%. Therefore, the pozzolanic reactivity of the treated OBDCs was competitive with that of conventional shale, which indicates that the heat treatment of OBDCs produces a cement substitute without any secondary pollution.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abdul-Wahab SA, Al-Rawas GA et al (2016) Impact of the addition of oil-based mud on carbon dioxide emissions in a cement plant. J Clean Prod 112:4214–4225
Abdul-Wahab SA, Al-Dhamri H, Ram G et al (2020) The use of oil-based mud cuttings as an alternative raw material to produce high sulfate-resistant oil well cement. J Clean Prod 269:1–10
Al Dhamri HS, Abdul-Wahabb SA (2020) Oil-based mud cutting as an additional raw material in clinker production. J Hazard Mater 384:1–17
Ball AS, Stewart RJ, Schliephake K (2012) A Review of the current options for the treatment and safe disposal of drill cuttings. Waste Manag Res 30(5):457–473
Berenguer R, Lima N, Pinto L et al (2021) Cement-based materials: pozzolanic activities of mineral additions are compromised by the presence of reactive oxides. J Build Eng 41:102358 1-13
Bernardo G, Marroccoli M, Nobili M et al (2007) The use of oil well-derived drilling waste and electric arc furnace slag as alternative raw materials in clinker production. Resour Conserv Recycl 52:95–102
China, (1996) State Environmental Protection Administration. Integrated wastewater discharge standard. GB8978-1996, 1-6
China, (1999) General Administration of quality supervision, inspection and Quarantine. Method of testing cements--Determinationof strength. GB/T 17671-1999, 1-10
China (2005a), General Administration of quality supervision, inspection and Quarantine. Test method for activity of industrial waste slag used as addition to cement. GB/T 12957-2005, 1-10
China, (2005b) General Administration of quality supervision, inspection and Quarantine. Test method for fluidity of cement mortar. GB/T 2419-2005, 1-10
China, (2005c) General Administration of quality supervision, inspection and Quarantine. Pozzolanic materials used for cement production. GB/T2847-2005, 1-10
China, (2010) General Administration of quality supervision, inspection and Quarantine. Limits of radionuclides in building materials. GB6566-2010, 1-10
China, (2015) General Administration of quality supervision, inspection and Quarantine.Technical specification for co-processing of solid waste in cement kiln. GB 30760-2014:1-13
China, (2017) General Administration of quality supervision, inspection and Quarantine. Methods for chemical analysis of cement. GB/T 176-2017, 21-22
China, (2018a) General Administration of quality supervision, inspection and Quarantine. Methods for chemical analysis of cement. GB/T 176-2017, 1-50
China, (2018b) Ministry of ecology and environment, State Administration of market supervision and Administration. Soil environmental quality standard –Risk control standards for soil pollution of construction land (Trial). GB36600-2018, 1-5
Donatello S, Tyrer M, Cheeseman CR (2010a) Comparison of test methods to assess pozzolanic activity. Cem Concr Compos 32:121–127
Donatello S, Freeman-Pask A, Tyrer M, Cheeseman CR (2010b) Effect of milling and acid washing on the pozzolanic activity of incinerator sewage sludge ash. Cem Concr Compos 32:54–61
Feng PZ, Li J (1994) Study of the effects of minor ions on the hydraulicity of C2S. J Wuhan Univ Technol 16(3):32–36
Georgopoulos G, Badogiannis E, Tsivilis S et al (2021) Thermally and mechanically treated Greek palygorskite clay as a pozzolanic material. Appl Clay Sci 215:106306 1-13
Hong JP, Chen YB, Li YS, Chen YR (2008) Study on activity of burnt shale as cement admixture. J Kunming Univ Sci Technol (Science and Technology) 33(3):24–30
Lai H, Lv S, Lai Z et al (2020) Utilization of oil-based mud drilling cuttings wastes from shale gas extraction for cement clinker production. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(26):33075–33084
Lechtenberg D, Diller H (2012) Alternative fuels and raw materials (AFR) review oil mud drillings. In: Alternative Fuels and Raw Materials Handbook for the Cement and Lime Industry, 2nd edn. MVW Lechtenberg & Partner, Dusseldorf, pp 303–320
Li XD, Poon CS, Sun H et al (2001) Heavy metal speciation and leaching behaviors in cement based solidified/stabilized waste materials. J Hazard Mater 82(3):215–230
Long SZ, Liao GL, Zhao SY (1996) Study on some problems of sintering barium calcium sulphoaluminate minerals. China Build Mater Sci Technol 5(3):11–16
Mitrovic A, Zdujic M (2014) Preparation of pozzolanic addition by mechanical treatment of kaolin clay. Int J Miner Process 132:59–66
Mou SB, Sun ZY (2002) Hydration activity of burnt shale and its application mechanism in cement mixture. Non-Metallic Mines 25(1):29–30
Page P W, Greaves C, Lawson R, et al., (2003). Options for the recycling of drilling cuttings. SPE80583, 1-5
Ren GH, Sun ZY, Mou SB et al (1996) Study on pozzolanic activity of burned shale. J Wuhan Univ Technol 6:31–32
Sabir BB, Wild S, Bai J (2001) Metakaolin and calcined clays as pozzolans for concrete: a review. Cem Concr Compos 23(6):441–454
Sarma H, Sonowala S, Prasad MNV (2019) Plant-microbiome assisted and biochar-amended remediation of heavy metals and polyaromatic compounds - a microcosmic study. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 176:288–299
Shen W, Huang WX, Min PR (2003) Cement technology. Wuhan Industrial University Press, Wuhan, pp 1–50
Soeder DJ, Sharma S, Pekney N et al (2014) An approach for assessing engineering risk from shale gas wells in the United States. Int J Coal Geol 126:4–19
Souri A, Kazemi-Kamyab H, Snellings R, Naghizadeh R, Golestani-Fard F, Scrivener K (2015) Pozzolanic activity of mechanochemically and thermally activated kaolins in cement. Cem Concr Res 77:47–59
Vizcayno C, Gutiérrez RM, Castello R et al (2010) Pozzolan Obtained by mechanochemical and thermal treatments of kaolin. Appl Clay Sci 49:405–413
Xiong DM, Liao P, Tian J et al (2021) Experimental research on preparation of cement clinker from oil-based drilling cuttings. J Yangtze Univ (Natural Science Edition) 18(3):67–73
Xu AM, Sarkar SL (1991) Microstructural study of gypsum activated fly ash hydration in cement paste. Cem Concr Res 21(6):1137–1147
Acknowledgements
The authors want to thank the technology support of Chongqing Jiaotong University and Yangtze Normal University.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Youth project of science and technology research program of Chongqing Education Commission of China (No KJQN202203113).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Deming Xiong: framework design and experiments, data and relevant mechanism analysis, writing-original draft, writing-review, revised, and editing. Chaoqiang Wang: framework design and experiments, assisting with research, experiments, and data analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Any experimental research on animals should follow the internationally recognized guidelines. However, in this study, we did not conduct any human or animal experiments, so we do not need the moral consent of the relevant departments.
Consent to participate
Nobody participated in the human or animal experiment.
Consent for publication
All authors agreed to publish the article.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, D., Wang, C. The pozzolanic activity of calcined oil-based drilling cuttings—aluminosilicate composites. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 80222–80236 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23389-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23389-8