Abstract
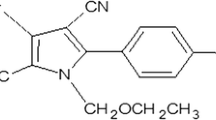
Pesticide residues are always an unsolved problem in the world despite all kinds of prevention measures. The present research work is based on a scientific hypothesis, i.e., “The removal of average pesticide residue is inversely proportional to the thickness of cuticle.” The effects of boron-containing products and plant-based surfactants were tested for the removal of five pesticides (lambda-cyhalothrin, chlorpyrifos, diflubenzuron, metaflumizone, acetamiprid) on tomatoes and apples. Boron-containing products were able to remove the pesticide residues on average between 58.0 and 72.6% in tomatoes and 33.2–58.8% in an apple. While plant-based surfactants removed residues on average between 58.5 and 66.6% in tomatoes and 41.0–53.2% in an apple. The highest removal rate was 72% with etidot at 1%. The solution of 1% C8–C10 provided 66.6% average removal for tomatoes. Less removal was achieved in apples. For an apple, Log Kow and molecular mass (independent variables) were significant with p < 0.01, and the coefficient of determination (R2) was > 0.87. However, the multiple linear regression analysis for ground colemanite was significant with R2 of 0.96. In tomatoes, neither Log Kow nor molecular mass as significant. The correlation was found between the physical and chemical properties of pesticides, but it is estimated that the thickness of the cuticle is effective in removing pesticides.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are given in the manuscript.
References
Amqam H, Ane R, Manynyulei S, et al. (2019) Chlorpyrifos residue in washed and unwashed tomatoes. In: Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Environmental Risks and Public Health, ICER-PH 2018, 26–27, October 2018, Makassar, Indonesia. EAI, pp 2–7
Anastassiades M, Lehotay SJ, Štajnbaher D, Schenck FJ (2003) Fast and easy multiresidue method employing acetonitrile extraction/partitioning and “dispersive solid-phase extraction” for the determination of pesticide residues in produce. J AOAC Int. https://doi.org/10.1093/jaoac/86.2.412
Angioni A, Dedola F, Garau A et al (2011) Chlorpyrifos residues levels in fruits and vegetables after field treatment. J Environ Sci Heal - Part B Pestic Food Contam Agric Wastes 46:544–549. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2011.583880
Archer TE (1968) Location, Extraction, and removal of endrin residues on alfalfa hay. J Dairy Sci 51:1606–1611. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(68)87239-X
Bonnechere A, Hanot V, Jolie R et al (2012) Processing factors of several pesticides and degradation products in carrots by household and industrial processing. J Food Res 1:68. https://doi.org/10.5539/jfr.v1n3p68
Carvalho FP (2006) Agriculture, pesticides, food security and food safety. Environ Sci Policy 9:685–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2006.08.002
Chatterjee NS, Gupta S (2012) Persistence of metaflumizone on cabbage ( Brassica oleracea Linne ) and soil , and its risk assessment. Env Monit Assess 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-3017-y
Chen W, Liu Y, Jiao B (2016) Dissipation behavior of five organophosphorus pesticides in kumquat sample during honeyed kumquat candied fruit processing. Food Control 66:87–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.01.033
Craven A (2003) Book review Pesticide residues in coastal tropical ecosystems. Pest Manag Sci 1360:2003. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.797
El-sayed EM, Salman S (2021) Investigation of the effects of household processing on the reduction rate of chlorpyrifos, metalaxyl and diazinon residues in orange fruit Investigation of the effects of household processing on the reduction rate of chlorpyrifos, metalaxyl and diazino. Hell Plant Prot J 14:64–75. https://doi.org/10.2478/hppj-2021-0007
González-Rodríguez RM, Rial-Otero R, Cancho-Grande B et al (2011) A review on the fate of pesticides during the processes within the food-production Chain. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 51:99–114. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408390903432625
Harinathareddy A, Prasad NBL, Devi KL (2014) Effect of household processing methods on the removal of pesticide residues in tomato vegetable. J Environ Res Dev 9:50–57
Hou R, Zhang Z, Pang S et al (2016) Alteration of the nonsystemic behavior of the pesticide ferbam on tea leaves by engineered gold nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 50:6216–6223. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b01336
Huan Z, Xu Z, Jiang W et al (2015) Effect of Chinese traditional cooking on eight pesticides residue during cowpea processing. Food Chem 170:118–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.08.052
Hwang KW, Yoo SC, Lee SE, Moon JK (2018) Residual level of chlorpyrifos in lettuces grown on chlorpyrifos-treated soils. Appl Sci 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122343
Kithure JGN, Murung JI, Tum PK et al (2017) Fate of lambda-cyhalothrin in kales, tomatoes and cabbage from rural settings in Kenya. Int J Sci Res Innov Technol 4:12–18
Kwon H, Kim TK, Hong SM et al (2015) Effect of household processing on pesticide residues in field-sprayed tomatoes. Food Sci Biotechnol 24:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-015-0001-7
Lee S, Ko R, Lee K et al (2022) Dissipation patterns of acrinathrin and metaflumizone in Aster scaber. Appl Biol Chem 65:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13765-022-00681-2
Levot GW, Lund RD, Black R (2004) Diazinon and diflubenzuron residues in soil following surface disposal of spent sheep dip wash. Aust J Exp Agric 44:975–982. https://doi.org/10.1071/EA03085
Lewis CT (1980) The Penetration of cuticle by insecticide. In: Miller T A (ed) Cuticle Techniques in Arthropods, 1st edn. Springer, New York, pp 367–400
Ling Y, Wang H, Yong W et al (2011) The effects of washing and cooking on chlorpyrifos and its toxic metabolites in vegetables. Food Control 22:54–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2010.06.009
Lozowicka B, Jankowska M, Hrynko I, Kaczynski P (2016) Removal of 16 pesticide residues from strawberries by washing with tap and ozone water, ultrasonic cleaning and boiling. Environ Monit Assess 188:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4850-6
Marican A, Durán-Lara EF (2018) A review on pesticide removal through different processes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:2051–2064. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0796-2
Medina MB, Munitz MS, Resnik SL (2021) Effect of household rice cooking on pesticide residues. Food Chem 342:128311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128311
Nawaz A, Ilyas M, Shahid S, Shah H (2015) Int J Food Allied Sci 1:63–66. https://doi.org/10.21620/ijfaas.2015263-66
Nejmanová J, Cvačka J, Hrdý I et al (2006) Residues of diflubenzuron on horse chestnut (Aesculus hippocastanum) leaves and their efficacy against the horse chestnut leafminer, Cameraria ohridella. Pest Manag Sci 62:274–278. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.1165
Anonymous (2021) World - tomato - market analysis, forecast, size, trends and insights. Globe Newswire. Dublin. https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2020/02/14/1985135/0/en. Accessed 21 January 2022
Pihlström T (2011) Method Validation and quality control procedures for pesticide residues analysis in food and feed. Natl Food Adm Uppsala, Sweden
Polat B, Tiryaki O (2020) Assessing washing methods for reduction of pesticide residues in Capia pepper with LC-MS/MS. J Environ Sci Heal - Part B Pestic Food Contam Agric Wastes 55:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2019.1660563
Qi H, Huang Q, Hung Y (2018) Effectiveness of electrolyzed oxidizing water treatment in removing pesticide residues and its effect on produce quality. Food Chem 239:561–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.06.144
Romeh AA, Hendawi MY (2013) Effect of processing on acetamiprid residues in eggplant fruits, Solanum melongena L. African J Agric Res 8:2033–2037. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJAR2013.7240
Sanco (2010) Method validation and quality control procedures for pesticide residues analysis. Document No. SANCO/3131/2007
Seenivasan S, Muraleedharan NN (2009) Residues of lambda-cyhalothrin in tea. Food Chem Toxicol 47:502–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2008.12.010
Shalaby A (2017) Residues of lambda-cyhalothrin insecticide and its biochemical effects on sweet pepper fruits. J Product Dev 22:65–81. https://doi.org/10.21608/jpd.2017.41707
Shukor NSA, Khazaai SNM, Hussin ZM, Jan SLM (2015) Degradation behaviour of Chlorpyrifos in Spinac (Spinacia Oleracea) and soil. Malaysian J Anal Sci 19:722–729
Soliman KM (2001) Changes in concentration of pesticide residues in potatoes during washing and home preparation. Food Chem Toxicol 39:887–891. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0278-6915(00)00177-0
Sreenivasa Rao C, Shashi Bhushan V, Narayana Reddy P, Kelageri SS (2017) Residues, risk assessment and decontamination of lambda cyhalothrin residues from tomato fruits. J Entomol Zool Stud 5:1764–1768
Tari VS, Patil PY (2014) Study of effect of chemical pesticide on mango plantation in Ratnagiri District. In: Nakade D B (ed) Proceeding of National conference on Resource management and agricultural Development in India. Jaysingpur, India, pp 36–40
Tari VSS, Patil PY, Kannan K (2020) Pesticide residue in mango orchards and health risk. Acta Sci Microbiol 3:8–14. https://doi.org/10.31080/asmi.2020.03.0669
Tilman D, Cassman KG, Matson PA et al (2002) Agricultural sustainability and intensive production practices. Nature 418:671–677
Tomer VJKS (2013) Vegetable processing at household level: effective tool against pesticide residue exposure. IOSR J Environ Sci Toxicol Food Technol 6:43–53. https://doi.org/10.9790/2402-0624353
United States Department of Agriculture (2021) Fresh apples, grapes, and pears: world markets and trade. https://downloads.usda.library.cornell.edu/usda-esmis/files/1z40ks800/nc581j510/zw130269m/fruit.pdf. Accessed 20 Jan 2022
Anonymous (2019) Chlorpyrifos Residues in fruits: the case for a europe-wide ban to protect consumers. Heal Environ Alliance Pestic Action Netw Eur. https://www.env-health.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/June-2019-PAN-HEAL-Briefing-chlorpyrifos_web.pdf. Accessed 20 Jan 2022
Wang Z, Huang J, Chen J, Li F (2013) Effectiveness of dishwashing liquids in removing chlorothalonil and chlorpyrifos residues from cherry tomatoes. Chemosphere 92:1022–1028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.03.039
Wanwimolruk S, Duangsuwan W, Phopin K, Boonpangrak S (2017) Food safety in Thailand 5: the effect of washing pesticide residues found in cabbages and tomatoes. J Fur Verbraucherschutz Und Leb 12:209–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00003-017-1116-y
Woods WG (1994) An introduction to boron: history, sources, uses and chemistry. Environ Health Perspectives 102:5–11. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.94102s75
Yang T, Zhao B, Kinchla A, He L (2017) Effectiveness of commercial and homemade washing agents in removing pesticide residues on and in apples. J Agric Food Chem A-I. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b03118
Yap CA, Jarroop Z (2018) Residue levels and dissipation behaviors of chlorpyrifos in black pepper berries and soil. Food Res 2:587–593. https://doi.org/10.26656/fr.2017.2(6).127
Zhang ZY, Liu XJ, Hong XY (2007) Effects of home preparation on pesticide residues in cabbage. Food Control 18:1484–1487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2006.11.002
Funding
This project was supported by National Boron Research Institute (BORON), Turkey (Project no: 2012.Ç0331).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Conceptualization: Nalan TURGUT, Cengiz GÖKBULUT; methodology: Melis YALÇIN, Cengiz GÖKBULUT, Cafer TURGUT; formal analysis and investigation: Melis YALÇIN, Nalan TURGUT, Serhan MERMER, Cafer TURGUT; writing—original draft preparation: Melis YALÇIN, Sait SOFUOĞLU, Cafer TURGUT; writing—review and editing: Sait SOFUOĞLU, Vinaya TARİ.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yalçın, M., Turgut, N., Gökbulut, C. et al. Removal of pesticide residues from apple and tomato cuticle. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 15821–15829 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23269-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23269-1