Abstract
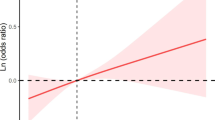
Previous studies indicate that pesticide use may play an important role in the occurrence and development of rheumatoid arthritis (RA); however, little is known about the effect of specific pesticides on RA. The objective of this study was to evaluate whether pyrethroid exposure was linked to RA in adults. Data were originated from the 2007–2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). The levels of pyrethroid exposure were assessed by 3-phenoxybenzoic acid (3-PBA) concentrations in urine samples. We built multivariate logistic regression models to assess associations between pyrethroid exposure and RA among US adults. A restricted cubic spline plot (three knots) was applied to test whether there was a nonlinear relationship between exposure to pyrethroid pesticides and the prevalence of RA. Finally, 4384 subjects were included in our analysis with 278 RA patients. In crude model, higher level of 3-PBA (creatinine-adjusted) was positively associated with RA (OR: 1.51, 95% CI: 1.07, 2.15). After adjustment for sex, race/ethnicity, education, body mass index, family poverty income, level of education, marital status, smoking status, alcohol usage, physical activity, hypertension, and urinary creatinine, the highest (vs lowest) quartile of 3-PBA was associated with an increased prevalence of RA (OR: 1.23, 95% CI: 0.86, 1.79). Significantly positive associations between 3-PBA concentration and RA were observed in the population aged between 40 and 59 years and with lower level of education. The restricted cubic spline plot presented an increase in trend and indicated that pyrethroid exposure was linearly associated with occurrence of RA (p for nonlinearity = 0.728). In conclusion, our study indicated that pyrethroid pesticide exposure was associated with an increased risk of RA. Higher levels of pyrethroid exposure were linearly associated with increased prevalence of RA in adults. Certainly, our findings are in great need of further corroboration by prospective studies with strict design.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are mentioned in the body of the manuscript, tables, and figure.
References
Abella V, Pérez T, Scotece M, Conde J, Pirozzi C, Pino J, Lago F, González-Gay MÁ, Mera A, Gómez R, Gualillo O (2016) Pollutants make rheumatic diseases worse: facts on polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) exposure and rheumatic diseases. Life Sci 157:140–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2016.06.010
Ahluwalia N, Dwyer J, Terry A, Moshfegh A, Johnson C (2016) Update on NHANES dietary data: focus on collection, release, analytical considerations, and uses to inform public policy. Adv Nutr 7:121–134. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.115.009258
Arleevskaya M, Takha E, Petrov S, Kazarian G, Renaudineau Y, Brooks W, Larionova R, Korovina M, Valeeva A, Shuralev E, Mukminov M, Kravtsova O, Novikov A (2022) Interplay of environmental, individual and genetic factors in rheumatoid arthritis provocation. Int J Mol Sci 23 https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158140
Corsini E, Sokooti M, Galli CL, Moretto A, Colosio C (2013) Pesticide induced immunotoxicity in humans: a comprehensive review of the existing evidence. Toxicology 307:123–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2012.10.009
Cross M, Smith E, Hoy D, Carmona L, Wolfe F, Vos T, Williams B, Gabriel S, Lassere M, Johns N, Buchbinder R, Woolf A, March L (2014) The global burden of rheumatoid arthritis: estimates from the Global Burden of Disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis 73:1316–1322. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204627
Cutolo M, Villaggio B, Craviotto C, Pizzorni C, Seriolo B, Sulli A (2002) Sex hormones and rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Rev 1:284–289
De Roos AJ, Cooper GS, Alavanja MC, Sandler DP (2005) Rheumatoid arthritis among women in the Agricultural Health Study: risk associated with farming activities and exposures. Ann Epidemiol 15:762–770
Deane KD, Demoruelle MK, Kelmenson LB, Kuhn KA, Norris JM, Holers VM (2017) Genetic and environmental risk factors for rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 31 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.berh.2017.08.003
Gold LS, Ward MH, Dosemeci M, De Roos AJ (2007) Systemic autoimmune disease mortality and occupational exposures. Arthritis Rheum 56:3189–3201
Guo X, Wang H, Song Q, Li N, Liang Q, Su W, Liang M, Ding X, Sun C, Lowe S, Sun Y (2022) Association between exposure to organophosphorus pesticides and the risk of diabetes among US Adults: cross-sectional findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Chemosphere 301:134471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134471
Han Y, Xia Y, Han J, Zhou J, Wang S, Zhu P, Zhao R, Jin N, Song L, Wang X (2008) The relationship of 3-PBA pyrethroids metabolite and male reproductive hormones among non-occupational exposure males. Chemosphere 72:785–790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.03.058
Holsapple MP (2002) Autoimmunity by pesticides: a critical review of the state of the science. Toxicol Lett 127:101–109
IMARC (2021) Pyrethroids market: global industry trends, share, size, growth, opportunity and forecast https://www.marketresearch.com/IMARC-v3797/Pyrethroids-Global-Trends-Share-Size-14625527/ Accessed on 5 May 2022
Jeong H, Baek SY, Kim SW, Eun YH, Kim IY, Kim H, Lee J, Koh EM, Cha HS (2017) Comorbidities of rheumatoid arthritis: results from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. PLoS One 12:e0176260. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0176260
Kåss AS, Lea TE, Torjesen PA, Gulseth HC, Førre ØT (2010) The association of luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone with cytokines and markers of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis: a case-control study. Scand J Rheumatol 39:109–117. https://doi.org/10.3109/03009740903270607
Kim U-J, Hong M, Choi Y-H (2021) Environmental pyrethroid exposure and cognitive dysfunction in U.S. older adults: the NHANES 2001–2002. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18 https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182212005
Koureas M, Tsakalof A, Tsatsakis A, Hadjichristodoulou C (2012) Systematic review of biomonitoring studies to determine the association between exposure to organophosphorus and pyrethroid insecticides and human health outcomes. Toxicol Lett 210:155–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2011.10.007
Koureas M, Rachiotis G, Tsakalof A, Hadjichristodoulou C (2017) Increased frequency of rheumatoid arthritis and allergic rhinitis among pesticide sprayers and associations with pesticide use. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14 https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14080865
Lee G-H, Choi K-C (2020) Adverse effects of pesticides on the functions of immune system. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 235:108789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2020.108789
Lee D-H, Steffes M, Jacobs DR (2007) Positive associations of serum concentration of polychlorinated biphenyls or organochlorine pesticides with self-reported arthritis, especially rheumatoid type, in women. Environ Health Perspect 115:883–888
Lehmler H-J, Simonsen D, Liu B, Bao W (2020) Environmental exposure to pyrethroid pesticides in a nationally representative sample of U.S. adults and children: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007–2012. Environ Pollut 267:115489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115489
Li AJ, Kannan K (2018) Urinary concentrations and profiles of organophosphate and pyrethroid pesticide metabolites and phenoxyacid herbicides in populations in eight countries. Environ Int 121:1148–1154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.10.033
Li J, Li X, Xia Y, Fan H, Fan D, Xi X, Ye Q, Zhu Y, Xiao C (2021) Subgroup analysis of the relationship between polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and rheumatoid arthritis: data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2003–2014. Sci Total Environ 775:145841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145841
Lundberg I, Alfredsson L, Plato N, Sverdrup B, Klareskog L, Kleinau S (1994) Occupation, occupational exposure to chemicals and rheumatological disease. A register based cohort study. Scand J Rheumatol 23:305–310
Maeda Y, Kurakawa T, Umemoto E, Motooka D, Ito Y, Gotoh K, Hirota K, Matsushita M, Furuta Y, Narazaki M, Sakaguchi N, Kayama H, Nakamura S, Iida T, Saeki Y, Kumanogoh A, Sakaguchi S, Takeda K (2016) Dysbiosis contributes to arthritis development via activation of autoreactive T cells in the intestine. Arthritis Rheumatol 68:2646–2661. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.39783
McInnes IB, Schett G (2017) Pathogenetic insights from the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 389:2328–2337. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31472-1
Meeker JD, Barr DB, Hauser R (2009) Pyrethroid insecticide metabolites are associated with serum hormone levels in adult men. Reprod Toxicol 27:155–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2008.12.012
Mohammadi H, Ghassemi-Barghi N, Malakshah O, Ashari S (2019) Pyrethroid exposure and neurotoxicity: a mechanistic approach. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol 70:74–89. https://doi.org/10.2478/aiht-2019-70-3263
Mostafalou S, Abdollahi M (2013) Pesticides and human chronic diseases: evidences, mechanisms, and perspectives. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 268:157–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2013.01.025
Nowak K, Jabłońska E, Ratajczak-Wrona W (2019) Immunomodulatory effects of synthetic endocrine disrupting chemicals on the development and functions of human immune cells. Environ Int 125:350–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.01.078
Olsson AR, Skogh T, Axelson O, Wingren G (2004) Occupations and exposures in the work environment as determinants for rheumatoid arthritis. Occup Environ Med 61:233–238
Park J, Park SK, Choi Y-H (2019) Environmental pyrethroid exposure and diabetes in U.S. adults. Environ Res 172:399–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2018.12.043
Parks CG, Walitt BT, Pettinger M, Chen J-C, de Roos AJ, Hunt J, Sarto G, Howard BV (2011) Insecticide use and risk of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus in the Women’s Health Initiative Observational Study. Arthritis Care Res (hoboken) 63:184–194. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.20335
Parks CG, D’Aloisio AA, Sandler DP (2018) Childhood residential and agricultural pesticide exposures in relation to adult-onset rheumatoid arthritis in women. Am J Epidemiol 187:214–223. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwx224
Parks CG, Meyer A, Beane Freeman LE, Hofmann JN, Sandler DP (2019a) Farming tasks and the development of rheumatoid arthritis in the Agricultural Health Study. Occup Environ Med 76:243–249. https://doi.org/10.1136/oemed-2018-105361
Parks CG, Santos AdSE, Lerro CC, DellaValle CT, Ward MH, Alavanja MC, Berndt SI, Beane Freeman LE, Sandler DP, Hofmann JN (2019b) Lifetime pesticide use and antinuclear antibodies in male farmers from the Agricultural Health Study. Front Immunol 10:1476. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01476
Ravula AR, Yenugu S (2021) Pyrethroid based pesticides - chemical and biological aspects. Crit Rev Toxicol 51:117–140. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408444.2021.1879007
Rodzaj W, Wileńska M, Klimowska A, Dziewirska E, Jurewicz J, Walczak-Jędrzejowska R, Słowikowska-Hilczer J, Hanke W, Wielgomas B (2021) Concentrations of urinary biomarkers and predictors of exposure to pyrethroid insecticides in young, Polish, urban-dwelling men. Sci Total Environ 773:145666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145666
Rosenberg AM, Semchuk KM, McDuffie HH, Ledingham DL, Cordeiro DM, Cessna AJ, Irvine DG, Senthilselvan A, Dosman JA (1999) Prevalence of antinuclear antibodies in a rural population. J Toxicol Environ Health A 57:225–236
Rosenfeld CS (2017) Gut dysbiosis in animals due to environmental chemical exposures. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 7:396. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2017.00396
Saillenfait A-M, Ndiaye D, Sabaté J-P (2015) Pyrethroids: exposure and health effects–an update. Int J Hyg Environ Health 218:281–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2015.01.002
Salliot C, Nguyen Y, Boutron-Ruault M-C, Seror R (2020) Environment and lifestyle: their influence on the risk of RA. J Clin Med 9 https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103109
Singh AK, Parashar A, Singh AK, Singh R (2013) Pre-natal/juvenile chlorpyrifos exposure associated with immunotoxicity in adulthood in Swiss albino mice. J Immunotoxicol 10:141–149. https://doi.org/10.3109/1547691X.2012.700653
Skolarczyk J, Pekar J, Nieradko-Iwanicka B (2017) Immune disorders induced by exposure to pyrethroid insecticides. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (online) 71:446–453
Sparks JA (2019) Rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Intern Med 170 https://doi.org/10.7326/AITC201901010
Sun L, Ye Z, Ling Y, Cai S, Xu J, Fan C, Zhong Y, Shen Q, Li Y (2020) Relationship between polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and rheumatoid arthritis in US general population, NHANES 2003–2012. Sci Total Environ 704:135294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135294
Tang W, Wang D, Wang J, Wu Z, Li L, Huang M, Xu S, Yan D (2018) Pyrethroid pesticide residues in the global environment: an overview. Chemosphere 191 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.115
Venetsanopoulou AI, Alamanos Y, Voulgari PV, Drosos AA (2022) Epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis: genetic and environmental influences. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 1-9https://doi.org/10.1080/1744666x.2022.2106970
Wang X, He B, Kong B, Wei L, Wang R, Zhou C, Shao Y, Lin J, Jin Y, Fu Z (2017) β-Cypermethrin and its metabolite 3-phenoxybenzoic acid exhibit immunotoxicity in murine macrophages. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (shanghai) 49:1083–1091. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gmx111
Werthmann DW, Rabito FA, Stout DM, Tulve NS, Adamkiewicz G, Calafat AM, Ospina M, Chew GL (2021) Pyrethroid exposure among children residing in green versus non-green multi-family, low-income housing. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 31:549–559. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41370-021-00312-w
Wielgomas B, Nahorski W, Czarnowski W (2013) Urinary concentrations of pyrethroid metabolites in the convenience sample of an urban population of Northern Poland. Int J Hyg Environ Health 216:295–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2012.09.001
Xue Q, Pan A, Wen Y, Huang Y, Chen D, Yang C-X, Hy WuJ, Yang J, Pan J, Pan X-F (2021) Association between pyrethroid exposure and cardiovascular disease: a national population-based cross-sectional study in the US. Environ Int 153:106545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2021.106545
Ye M, Beach J, Martin JW, Senthilselvan A (2016) Urinary concentrations of pyrethroid metabolites and its association with lung function in a Canadian general population. Occup Environ Med 73:119–126. https://doi.org/10.1136/oemed-2015-102839
Zepeda-Arce R, Rojas-García AE, Benitez-Trinidad A, Herrera-Moreno JF, Medina-Díaz IM, Barrón-Vivanco BS, Villegas GP, Hernández-Ochoa I, Sólis Heredia MdJ, Bernal-Hernández YY (2017) Oxidative stress and genetic damage among workers exposed primarily to organophosphate and pyrethroid pesticides. Environ Toxicol 32:1754–1764. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22398
Zhou S, Dong J, Liu Y, Yang Q, Xu N, Yang Y, Ai X (2021) Effects of acute deltamethrin exposure on kidney transcriptome and intestinal microbiota in goldfish (Carassius auratus). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 225:112716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112716
Acknowledgements
All authors in this study thank the NHANES for providing publicly available data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xianwei Guo: conceptualization, methodology, software, data curation, formal analysis, visualization, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing.
Ning Li: methodology, validation, formal analysis, software, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing.
Hao Wang: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, writing—review and editing.
Wanying Su: validation and visualization.
Qiuxia Song: methodology, writing—original draft, software.
Qiwei Liang: methodology, formal analysis, writing—review and editing.
Chenyu Sun: conceptualization, writing—review and editing.
Mingming Liang: software, visualization.
Xiuxiu Ding: writing—review and editing.
Scott Lowe: writing—review and editing.
Yehuan Sun: conceptualization, supervision, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The NCHS Research Ethics Review Board reviewed and approved the protocol of the NHANES study, and all participants signed informed consent forms.
Consent for publication
There is no conflict of interest that exists in this manuscript, and it is approved by all authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, X., Li, N., Wang, H. et al. Exploratory analysis of the association between pyrethroid exposure and rheumatoid arthritis among US adults: 2007–2014 data analysis from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 14413–14423 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23145-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23145-y