Abstract
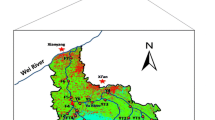
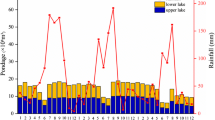
Caohai Lake is a typical natural lake-type karst plateau wetland, which is sensitive to environmental changes, and the release of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) in sediment is a potential factor of nitrogen pollution in this lake. Therefore, we aimed to reveal the temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and source analysis of DON in karst lake sediment. Surface sediment samples were collected from Caohai Lake in southwest China, and the sample locations were distributed across almost the entire wetland area, during both the wet and dry seasons. The DON content and fluorescence spectroscopy were determined and analysed using a three-dimensional fluorescence-parallel factor analysis (3DEEM-PARAFAC) model. The mean DON content in the sediment during the dry season (67.79 ± 42.96 mg/kg) was higher than that in the wet season (28.57 ± 20.97 mg/kg). There were four fluorescent components of DON in the sediment: C1 (tyrosine-like protein), C2 (terrestrial humus), C3 (tryptophan-like protein) and C4 (terrestrial humus). The DON in the surface sediment of Caohai Lake was influenced by terrestrial sources and biological activities. These findings help reveal the circulation mechanism of endogenous nitrogen in the lake and provide theoretical support for the prevention and control of nitrogen pollution in Caohai Lake.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that (the/all other) data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article (and its supplementary information files).
References
Abbt-Braun G, Lankes U, Frimmel FH (2004) Structural characterization of aquatic humic substances—the need for a multiple method approach. Aquat Sci 66(2):151–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-004-0711-z
Berman T, Bronk DA (2003) Dissolved organic nitrogen: a dynamic participant in aquatic ecosystems. Aquat Microb Ecol 3(31):279–305. https://doi.org/10.3354/ame031279
Berman T, Chava S (1999) Algal growth on organic compounds as nitrogen sources. J Plankton Res 21(8):1423–1437. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/21.8.1423
Cao X, Wu P, Han Z, Tu H, Zhang S (2016) Factors controlling the isotope composition of dissolved inorganic carbon in a karst-dominated wetland catchment, Guizhou Province, Southwest China. Environ Earth Sci 75(14):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5899-4
Cao X, Yang S, Wu P, Liu S, Liao J (2021) Coupling stable isotopes to evaluate sources and transformations of nitrate in groundwater and inflowing rivers around the Caohai karst wetland, Southwest China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28(33):45826–45839. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13827-4
Cheng YY, Guo WD (2009) Characterization of photobleaching of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in Xiamen Bay by excitation emission matrix spectroscopy. Spectrosc Spectr Anal 29(4):990–993. https://doi.org/10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2009)04-0990-04
Cory RM, Mcknight DM (2005) Fluorescence spectroscopy reveals ubiquitous presence of oxidized and reduced quinones in dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 39(21):8142–8149. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0506962
Czerwionka K (2016) Influence of dissolved organic nitrogen on surface waters. Oceanologia 58(1):39–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceano.2015.08.002
Dai LL, Yuan Q, Liu W, Lü JC, Yuan G (2022) Flora characteristics and geographical distribution of aquatic plants in Caohai Wetland of Guizhou. Guizhou Sci 40(02):6–14
Fellman JB, Hood E, Spencer RG (2010) Fluorescence spectroscopy opens new windows into dissolved organic matter dynamics in freshwater ecosystems: a review. Limnol Oceanogr 55:2452–2462
Fu P, Liu C, Wu F, Wei Z, Li W, Mei Y, Huang R (2004) Three-dimensional excitation emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopic characterization of dissolved organic matter in sediment pore water in Lake Erhai. Quat Sci 24(6):695–700. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2004.06.012
Fu PQ, Liu CQ, Wu FC (2005) Three-dimensional excitation emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopic characterization of dissolved organic matter. Spectrosc Spectr Anal 25(12):2024–2028. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1000-0593.2005.12.031
Fu G, Qi Y, Li J, Zhao C, He J, Ma Y, Zhu J (2021) Spatial distributions of nitrogen and phosphorus in surface sediments in intertidal flats of the Yellow River Delta, China. Water 13(20):2899. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13202899
Guo Y, Lin C, He T, Lin S, Zhang Q (2012) The distribution characteristics and pollution evaluation of organic carbon, nitrogen and phosphate in surface sediments of Caohai Lake. Guizhou Sci 30(01):27–32
Han Z, Zhang S, Wu P, Cao X, Tu H (2017) Distribution characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus in waters and release flux estima-tion in the sediment of Caohai basin, Guizhou, Chinese. J Ecol 36(09):2501–2506. https://doi.org/10.13292/j.1000-4890.201709.035
Hohman SP, Smyth AR, Bean EZ, Reisinger AJ (2021) Internal nitrogen dynamics in stormwater pond sediments are influenced by pond age and inorganic nitrogen availability. Biogeochemistry:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-021-00843-2
Huguet A, Vacher L, Relexans S, Saubusse S, Froidefond JM, Parlanti E (2009) Properties of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in the Gironde Estuary. Org Geochem 40(6):706–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2009.03.002
Jacquin C, Lesage G, Traber J, Pronk W, Heran M (2017) Three-dimensional excitation and emission matrix fluorescence (3DEEM) for quick and pseudo-quantitative determination of protein- and humic-like substances in full-scale membrane bioreactor (MBR). Water Res 118:82–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.04.009
Jef H, Codd GA, Paerl HW, Ibelings BW, Verspagen JMH, Visser PM (2018) Cyanobacterial blooms. Nat Rev Microbiol 16:471–483. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-018-0040-1
Kang J, Song GF, Liu SL, Song CQ, Gao X (2021) Spectral characterization of the effect of gas–water ratio on dissolved organic nitrogen variation along a drinking water biological aerated filter. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(46):65743–65751. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15528-4
Lin Y, Wang L, Xu K, Huang H, Ren H (2021) Algae biofilm reduces microbe-derived dissolved organic nitrogen discharges: performance and mechanisms. Environ Sci Technol 9(55):6227–6238. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c06915
Long Y, Jiang J, Hu X, Hu J, Ren C, Zhou S (2021) The response of microbial community structure and sediment properties to anthropogenic activities in Caohai wetland sediments. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 211:111936. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.111936
Lusk MG, Toor GS (2016) Dissolved organic nitrogen in urban streams: biodegradability and molecular composition studies. Water Res 96:225–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.03.060
McKnight DM, Boyer EW, Westerhoff PK, Doran PT, Kulbe T, Andersen DT (2001) Spectrofluorometric characterization of dissolved organic matter for indication of precursor organic material and aromaticity. Limnol Oceanogr 46(1):38–48. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2001.46.1.0038
Mladenov N, Parsons D, Kinoshita AM, Pinongcos F, Mueller M, Garcia D, Lipson DA, Grijalva LM, Zink TA (2021) Groundwater-surface water interactions and flux of organic matter and nutrients in an urban, Mediterranean stream. Sci Total Environ 811:152379. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2021.152379
Murphy DV, Macdonald AJ, Stockdale EA, Kwt G, Fortune S, Gaunt JL, Poulton PR, Wakefield JA, Webster CP, Wilmer WS (2000) Soluble organic nitrogen in agricultural soils. Biol Fertil Soils 30(5-6):374–387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050018
Peng F, He T, Li Z, Chen M, Qian X, Zeng L, Xu Y (2018) Enrichment characteristics and risk assessment of Hg in bird feathers from Caohai wetland in Guizhou Province, China. Acta Geochim 37(4):526–536 CNKI:SUN:DQHB.0.2018-04-004
Ren W, Wu X, Ge X, Lin G, Zhou M, Long Z, Yu X, Tian W (2021) Characteristics of dissolved organic matter in lakes with different eutrophic levels in southeastern Hubei Province, China. J Oceanol Limnol (prepublish). https://doi.org/10.1007/S00343-020-0102-X
Shi L (2018) The characteristics of dissolved organic nitrogen of sediment-water interface and particle-water interface at Erhai Lake. Yunnan University, Yunnan
Sinha E, Michalak AM, Balaji V (2017) Eutrophication will increase during the 21st century as a result of precipitation changes. Science (New York, N.Y) 357(6349):405–408. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aan2409
Sipler RE, Bronk DA (2015) Dynamics of dissolved organic nitrogen. biogeochemistry of marine dissolved organic matter (2nd Edition), 127-232. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-405940-5.00004-2
Stedmon CA, Markager S, Bro R (2003) Tracing dissolved organic matter in aquatic environments using a new approach to fluorescence spectroscopy. Mar Chem 82(3):239–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4203(03)00072-0
Su M, Zhang J, Huo S, Xi B, Hua F, Zan F, Qian G, Liu J (2016) Microbial bioavailability of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) in the sediments of Lake Shankou, Northeastern China. J Environ Sci 42:79–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2015.08.011
Wu S, Xia P, Lin T, Yang J, Wang R, Chen Y (2019) Contents and distribution characteristics of nitrogen forms in sediments of Guizhou Lake Caohai under different water level levels. J Lake Sci 31(02):407–415. https://doi.org/10.18307/2019.0210
Wu D, Hu C, Zhang M, Li Z, Su H (2020) Foraging habitat selection of overwintering Black-necked Cranes in the farming area surrounding the Caohai Wetland, Guizhou Province, China. Avian Res 11(01):76–84. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40657-020-00192-y
Xia P, Ma L, Sun R, Yang Y, Tang X, Yan D, Lin T, Zhang Y, Yi Y (2020) Evaluation of potential ecological risk, possible sources and controlling factors of heavy metals in surface sediment of Caohai Wetland, China. Sci Total Environ 740:140231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140231
Yan Z, Yang N, Liang Z, Yan M, Zhong X, Zhang Y, Xu W, Xin Y (2021) Active dissolved organic nitrogen cycling hidden in large river and environmental implications. Sci Total Environ 795:148882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148882
Yang H, Chen J, Liu W, Wang J, Li J, Ji Y, Chen Y (2016) Distribution characteristics and controlling factors of total organic carbon, total nitrogen, and total phosphorus in sediments of Caohai Lake, China. Earth Environ 44(03):297–303. https://doi.org/10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2016.03.003
Yang X, Wei X, Xu X, Zhang Y, Li J, Wan J (2019) Characteristics of dissolved organic nitrogen in the sediments of six water sources in Taihu Lake, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16(6):929. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16060929
Yao X, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Zhu G, Qin B, Zhou Y, Xue J (2020) Emerging role of dissolved organic nitrogen in supporting algal bloom persistence in Lake Taihu, China: emphasis on internal transformations. Sci Total Environ 736:139497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139497
Zhang Q (2012) The stability of carbon sink effect related to carbonate rock dissolution: a case study of the Caohai Lake geological carbon sink. Acta Geosci Sin 33(06):947–952. https://doi.org/10.3975/cagsb.2012.06.14
Zhang Z (2020) Spatial-temporal distribution and sources of organic matter in Caohai Lake, Guizhou Provice. Xi'an University of Science and Technology, Xi'an
Zhang YL, Yang LY, Qin BQ, Gao G, Luo LC, Zhu GW, Liu ML (2008) Spatial distribution of COD and the correlations with other parameters in the northern region of Lake Taihu. Environ Sci 29(06):1457–1462. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.2008.06.006
Zhang Y, Zhang E, Yan Y, Mav D, Qin B (2010) Characteristics and sources of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in lakes of the Yungui Plateau, China, differing in trophic state and altitude. Limnol Oceanogr 55(6):2645–2659
Zhang J, Lin S, Zhang Q, He T, Lin C (2014) Seasonal and vertical distribution characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus content in the sediment and overlying water of Caohai in Guizhou. Guangdong. Agric Sci 41(09):184–188. https://doi.org/10.16768/j.issn.1004-874x.2014.09.011
Zhang L, Fang W, Li X, Lu W, Li J (2020) Strong linkages between dissolved organic matter and the aquatic bacterial community in an urban river. Water Res 184:116089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116089
Zheng F, Wang J, Xiao R, Chai W, Xing D, Lu H (2021) Dissolved organic nitrogen in wastewater treatment processes: transformation, biosynthesis and ecological impacts. Environ Pollut 273:116436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116436
Zhou C, Yu LF, Cai GJ, An M, Xia HP (2016) Spatial-temporal variation of water quality in Caohai Lake. J Hydroecol 37(01):24–30. https://doi.org/10.15928/j.1674-3075.2016.01.004
Zhu P, Hua ZL, Li HM (2013) PARAFAC method used for analysis of three-dimensional fluorescence spectra of DOM in Taihu Lake. Spectrosc Spectr Anal 33(06):1619–1625. https://doi.org/10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2013)06-1619-07
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank the anonymous reviewers and editors for their critical comments and suggestions on our manuscript, and everyone who funded the research.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41807376), the Talent Introduction Project of Guizhou University (No. [2019]24), and the Project of Talent Base in Guizhou Province (No. RCJD2018-21).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. The first draft of the manuscript and the drawing of the diagram were completed by Xinting Yan, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. Manuscript writing guidance and the first draft revision were completed by Associate Prof. Xingxing Cao and Prof. Zhiwei Han. Experimental operation was done by Jiahao Liao and Xinting Yan. Data collation and sample collection were performed by Jiahao Liao. Associate Prof. Xingxing Cao provided funding. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent for publication
All authors agree to publish this research (including any individual details, images, or videos) in Environmental Science and Pollution Research.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, X., Liao, J., Cao, X. et al. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and source analysis of dissolved organic nitrogen in the surface sediment of the Caohai Lake, southwest China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 12844–12856 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22953-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22953-6