Abstract
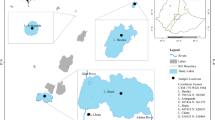
Gaining a deeper understanding of factors that influence changes in phytoplankton community has significant implications for shallow lake management. The present study examined changes in the algae community of three shallow eutrophic lakes of the Taoge water system between 2008 and 2018 and the related factors influencing these changes. The composition of the algal community varied significantly during this period with the relative diatom biomass in lakes Changdanghu and Gehu increasing between 2014 and 2016 and again decreasing after 2017. However, relative cyanobacteria biomass initially decreased and later increased; meanwhile, the proportion of biomass of other phyla decreased continuously in the study period. Lake Zhushanhu showed similar trends, although it eventually returned to its initial state with absolute Microcystis dominance. Furthermore, the analysis of driving factors revealed that the concentrations of total nitrogen (TN), nitrate (NO3), and orthophosphate (PO4) were significantly associated with a significant increase in Microcystis biomass. Meteorological conditions also influenced changes in total algal and diatom biomasses, which were inversely related to the daily mean and daily maximum wind speeds. Monthly cumulative precipitation was only significantly associated with diatom biomass. Meanwhile, rainfall primarily affected the algal community structure between 2013 and 2017; an increase in the relative biomass of diatoms coincided with increased precipitation. Coordinating nitrogen and phosphorous use within the Taoge water system should improve lake habitat management; a broader perspective in attempts to control global and regional climate change may be needed.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the Department of Ecology and Environment of Jiangsu Province, which were used under license for the current study, and so are not publicly available. Data are however available from the authors upon reasonable request and with permission of the Department of Ecology and Environment of Jiangsu Province (http://www.jiangsu.gov.cn/ysqgk/front/main.do?sysid=2&groupid=42).
References
Almanza V, Pedreros P, Dail Laughinghouse H, Félez J, Parra O, Azócar M, Urrutia R (2019) Association between trophic state, watershed use and blooms of cyanobacteria in south-central Chile. Limnologica 75:30–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.limno.2018.11.004
Andersen IM, Williamson TJ, González MJ, Vanni MJ (2020) Nitrate, ammonium, and phosphorus drive seasonal nutrient limitation of chlorophytes, cyanobacteria, and diatoms in a hyper-eutrophic reservoir. Limnol Oceanogr 65:962–978. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.11363
Arhonditsis GB, Winder M, Brett MT, Schindler DE (2004) Patterns and mechanisms of phytoplankton variability in Lake Washington (USA). Water Res 38:4013–4027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.06.030
Borics G, Nagy L, Miron S, Grigorszky I, László-Nagy Z, Lukács BA, G-Tóth L, Várbíró G (2013) Which factors affect phytoplankton biomass in shallow eutrophic lakes? Hydrobiologia 714:93–104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1525-6
Borics G, Abonyi A, Salmaso N, Ptacnik R (2021) Freshwater phytoplankton diversity: models, drivers and implications for ecosystem properties. Hydrobiologia 848:53–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-020-04332-9
Cao X, Wang J, Liao J, Sun J, Huang Y (2016) The threshold responses of phytoplankton community to nutrient gradient in a shallow eutrophic Chinese lake. Ecol Indic 61:258–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.09.025
Chaffin JD, Bridgeman TB, Bade DL, Mobilian CN (2014) Summer phytoplankton nutrient limitation in Maumee Bay of Lake Erie during high-flow and low-flow years. J Great Lakes Res 40:524–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jglr.2014.04.009
Clarke KR (1993) Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust J Ecol 18:117–143. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-9993.1993.tb00438.x
Conley DJ, Paerl HW, Howarth RW, Boesch DF, Seitzinger SP, Havens KE, Lancelot C, Likens GE (2009) Controlling eutrophication: nitrogen and phosphorus. Science 323:1014–1015. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1167755
Davidsona K, Gowen RJ, Tett P, Bresnan E, Harrison PJ, Mckinney A, Milligan S, Mills DK, Silke J, Crooks AM (2012) Harmful algal blooms: how strong is the evidence that nutrient ratios and forms influence their occurrence? Estuar Coast and Shelf S 115:399–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2012.09.019
Davis J, Sim L, Chambers J (2010) Multiple stressors and regime shifts in shallow aquatic ecosystems in antipodean landscapes. Freshwater Biol 55:5–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2009.02376.x
Deng J, Chen F, Liu X, Peng J, Hu W (2016) Horizontal migration of algal patches associated with cyanobacterial blooms in an eutrophic shallow lake. Ecol Eng 87:185–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.12.017
Dixon P (2003) VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J Veg Sci 14:927–930. https://doi.org/10.1658/1100-9233(2003)014[0927:VAPORF]2.0.CO;2
Dugdale RC, Wilkerson FP, Hogue VE, Marchi A (2007) The role of ammonium and nitrate in spring bloom development in San Francisco Bay. Estuar Coast and Shelf S 73:17–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2006.12.008
Erratt KJ, Creed IF, Trick CG (2020) Differential drawdown of ammonium, nitrate, and urea by freshwater chlorophytes and cyanobacteria. J Phycol 56:458–468. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpy.12960
Escalas A, Catherine A, Maloufi S, Cellamare M, Hamlaoui S, Yéprémian C, Louvard C, Troussellier M, Bernard C (2019) Drivers and ecological consequences of dominance in periurban phytoplankton communities using networks approaches. Water Res 163:114893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.114893
Ge Y, Zhang K, Yang X (2018) Long-term succession of aquatic plants reconstructed from palynological records in a shallow freshwater lake. Sci Total Environ 643:312–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.203
Guo L (2007) Doing battle with the green monster of Taihu Lake. Science 317:1166. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.317.5842.1166
Han Z, An W, Yang M, Zhang Y (2020) Assessing the impact of source water on tap water bacterial communities in 46 drinking water supply systems in China. Water Res 172:115469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.115469
Hillebrand H, Dürselen CD, Kirschtel D, Pollingher U, Zohary T (1999) Biovolume calculation for palagic and benthic microalgae. J Phycol 35:403–424. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1529-8817.1999.3520403.x
Ho JC, Michalak AM (2020) Exploring temperature and precipitation impacts on harmful algal blooms across continental U.S. lakes. Limnol Oceanogr 65:992–1009. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.11365
Hu HJ, Wei YX (2006) The freshwater algae of China: systematics, taxonomy and ecology. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese)
Huo D, Gan N, Geng R, Cao Q, Song L, Yu G, Li R (2021) Cyanobacterial blooms in China: diversity, distribution, and cyanotoxins. Harmful Algae 109:102106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2021.102106
Izaguirre G, Taylor WD (2004) A guide to geosmin- and MIB-producing cyanobacteria in the United States. Water Sci Technol 49:19–24. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2004.0524
Kuha J, Arvola L, Hanson PC, Huotari J, Huttula T, Juntunen J, Järvinen M, Kallio K, Ketola M, Kuoppamäki K, Lepistö A, Lohila A, Paavola R, Vuorenmaa J, Winslow L, Karjalainen J (2016) Response of boreal lakes to episodic weather-induced events. Inland Waters 6:523–534. https://doi.org/10.5268/IW-6.4.886
Lepšová-Skácelová O, Fibich P, Wild J, Lepš J (2018) Trophic gradient is the main determinant of species and large taxonomic groups representation in phytoplankton of standing water bodies. Ecol Indic 85:262–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.10.034
Lin Y, He Z, Yang Y, Stoffella PJ, Phlips EJ, Powell CA (2008) Nitrogen versus phosphorus limitation of phytoplankton growth in Ten Mile Creek, Florida, USA. Hydrobiologia 605:247–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-008-9360-x
Liu X, Lu X, Chen Y (2011) The effects of temperature and nutrient ratios on Microcystis blooms in Lake Taihu, China: An 11-year investigation. Harmful Algae 10:337–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2010.12.002
Luimstra VM, Verspagen JMH, Xu T, Schuurmans JM, Huisman J (2020) Changes in water color shift competition between phytoplankton species with contrasting light-harvesting strategies. Ecology 101:e02951. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecy.2951
Ma J, Qin B, Wu P, Zhou J, Niu C, Deng J, Niu H (2015) Controlling cyanobacterial blooms by managing nutrient ratio and limitation in a large hyper-eutrophic lake: Lake Taihu, China. J Environ Sci 27:80–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2014.05.042
Maileht K, Nõges T, Nõges P, Ott I, Mischke U, Carvalho L, Dudley B (2013) Water colour, phosphorus and alkalinity are the major determinants of the dominant phytoplankton species in European lakes. Hydrobiologia 704:115–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-012-1348-x
Nishizawa E, Kurokawa T, Yabe M (2006) Policies and resident’s willingness to pay for restoring the ecosystem damaged by alien fish in Lake Biwa, Japan. Environ Sci Policy 9:448–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2006.03.006
Padisák J, Borics G, Fehér G, Grigorszky I, Oldal I, Schmidt A, Zámbóné-Doma Z (2003) Dominant species, functional assemblages and frequency of equilibrium phases in late summer phytoplankton assemblages in Hungarian small shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 502:157–168. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:HYDR.0000004278.10887.40
Padisák J, Crossetti LO, Naselli-Flores L (2009) Use and misuse in the application of the phytoplankton functional classification: a critical review with updates. Hydrobiologia 621:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-008-9645-0
Paerl HW, Huisman J (2008) Blooms like it hot. Science 320:57–58. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1155398
Paerl HW, Otten TG (2013) Harmful cyanobacterial blooms: causes, consequences, and controls. Microb Ecol 65:995–1010. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-012-0159-y
Paerl HW, Hall NS, Calandrino ES (2011) Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a world experiencing anthropogenic and climatic-induced change. Sci Total Environ 409:1739–1745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.02.001
Pannard A, Bormans M, Lagadeuc Y (2008) Phytoplankton species turnover controlled by physical forcing at different time scales. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 65:47–60. https://doi.org/10.1139/f07-149
Qin B, Zhang Y, Deng J, Zhu G, Liu J, Hamilton DP, Paerl HW, Brookes JD, Wu T, Peng K, Yao Y, Ding K, Ji X (2021) Polluted lake restoration to promote sustainability in the Yangtze River Basin. China Natl Sci Rev 9:nwab207. https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwab207
Reynolds CS (1984) Phytoplankton periodicity: the interactions of form, function and environmental variability. Freshwater Biol 14:111–142. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.1984.tb00027.x
Reynolds CS, Huszar V, Kruk C, Naselli-Flores L, Melo S (2002) Towards a functional classification of the freshwater phytoplankton. J Plankton Res 24:417–428. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/24.5.417
Rice EW (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association, Washington DC
Scheffer M, Hosper SH, Meijer ML, Moss B, Jeppesen E (1993) Alternative equilibria in shallow lakes. Trends Ecol Evol 8:275–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-5347(93)90254-M
Schindler DW, Hecky RE, Findlay DL, Stainton MP, Parker BR, Paterson MJ, Beaty KG, Lyng M, Kasian SE (2008) Eutrophication of lakes cannot be controlled by reducing nitrogen input: results of a 37-year whole-ecosystem experiment. PNAS 105:11254–11258. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0805108105
Schindler DW, Hecky RE, McCullough GK (2012) The rapid eutrophication of Lake Winnipeg: greening under global change. J Great Lakes Res 38:6–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jglr.2012.04.003
Shi K, Zhang Y, Zhou Y, Liu X, Zhu G, Qin B, Gao G (2017) Long-term MODIS observations of cyanobacterial dynamics in Lake Taihu: responses to nutrient enrichment and meteorological factors. Sci Rep 7:40326. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep40326
Stockwell JD, Doubek JP, Adrian R et al (2020) Storm impacts on phytoplankton community dynamics in lakes. Glob Change Biol 26:2756–2784. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.15033
Sun J, Liu D (2003) Geometric models for calculating cell biovolume and surface area for phytoplankton. J Plankton Res 25:1331–1346. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbg096
USEPA (2017) National lakes assessment 2012: Technical report, EPA 841-R-16-114. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington DC. https://www.epa.gov/national-aquatic-resource-surveys/nla
Wentzky VC, Tittel J, Jäger CG, Rinke K (2018) Mechanisms preventing a decrease in phytoplankton biomass after phosphorus reductions in a German drinking water reservoir - results from more than 50 years of observation. Freshwater Biol 63:1063–1076. https://doi.org/10.1111/fwb.13116
Wilhelm SW, Farnsley SE, LeCleir GR, Layton AC, Satchwell MF, DeBruyn JM, Boyer GL, Zhu G, Paerl HW (2011) The relationships between nutrients, cyanobacterial toxins and the microbial community in Taihu (Lake Tai), China. Harmful Algae 10:207–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2010.10.001
Wu T, Qin B, Brookes JD, Shi K, Zhu G, Zhu M, Yan W, Wang Z (2015) The influence of changes in wind patterns on the areal extension of surface cyanobacterial blooms in a large shallow lake in China. Sci Total Environ 518:24–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.02.090
Xu H, Paerl HW, Qin B, Zhu G, Gao G (2010) Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Limnol Oceanogr 55:420–432. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2010.55.1.0420
Xu X, Zhang Y, Chen Q, Li N, Shi K, Zhang Y (2020) Regime shifts in shallow lakes observed by remote sensing and the implications for management. Ecol Indic 113:106285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106285
Yuan LL, Jones JR (2020) Rethinking phosphorus–chlorophyll relationships in lakes. Limnol Oceanogr 65:1847–1857. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.11422
Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Gao Y, Zhang H, Cao J, Cai J, Kong X (2011) Water pollution control technology and strategy for river-lake systems: a case study in Gehu Lake and Taige Canal. Ecotoxicology 20:1154–1159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-011-0676-3
Zhang Y, Song C, Ji L, Liu Y, Xiao J, Cao X, Zhou Y (2018) Cause and effect of N/P ratio decline with eutrophication aggravation in shallow lakes. Sci Total Environ 627:1294–1302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.327
Zhou Y, Ma J, Zhang Y, Qin B, Jeppesen E, Shi K, Brookes JD, Spencer RGM, Zhu G, Gao G (2017) Improving water quality in China: environmental investment pays dividends. Water Res 118:152–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.04.035
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank everyone who helped during field campaigns and sample analysis. We are grateful to Dr. Jiancai Deng and Dr. Zhaoliang Peng for their thoughtful and constructive suggestions. We also thank the anonymous reviewers for their useful comments on the earlier draft of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment (grant nos. 2012ZX07506 and 2018ZX07208).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qiao Chen: methodology, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing—original draft, and visualization.
Weiping Hu: conceptualization, methodology, resources, supervision, writing—review and editing, and project administration.
Lijuan Shen: validation, investigation and visualization.
Wei Shen: investigation and visualization.
Xiang Zhang: investigation and visualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Thomas Hein
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Q., Hu, W., Shen, L. et al. The role of nutrients, wind speed, and rainfall in determining the composition of the algal community of shallow lakes in the Taoge water system, upstream from Lake Taihu, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 16195–16209 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22935-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22935-8