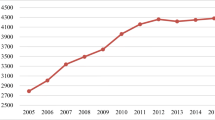
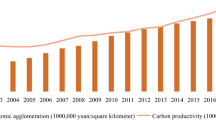
Abstract
The study explored the influencing mechanism of population agglomeration in large cities on carbon emissions, including technological innovation, industrial structure, and transportation effects. Moreover, we attempt to explore the nonlinear impact of population agglomeration in large cities on carbon emissions. We used the panel data of 207 big cities with a permanent resident population of more than 1 million to study the relationship between population agglomeration and carbon emissions. We found that population agglomeration to big cities increased urban carbon emissions significantly. The results of the mechanism analysis showed that population agglomeration to big cities raised carbon emissions by the channel of industrial structure and transportation effects. The channel of technological innovation effect decreased carbon emissions but did not offset the growth of carbon emissions caused by industrial structure and transportation effects. Nonlinear estimation findings demonstrated that the impact of population agglomeration on carbon emissions was different in big cities with varying levels of population.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available in the National Bureau of Statistics of China, https://data.stats.gov.cn/easyquery.htm?cn=C01.
Notes
Yao X, Pan S, Sun C (2017) Urban scale, spatial agglomeration and power intensity. Econ Res J 52(11):165
References
Al-Mulali U, Sab CNBC, Fereidouni HG (2012) Exploring the bi-directional long run relationship between urbanization, energy consumption, and carbon dioxide emission. Energy 46(1):156–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2012.08.043
Andreoni J, Levinson A (2001) The simple analytics of the environmental Kuznets curve. J Public Econ 80(2):269–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0047-2727(00)00110-9
Arrow K, Bolin B, Costanza R et al (1995) Economic growth, carrying capacity, and the environment. Ecol Econ 15(2):91–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/0921-8009(95)00059-3
Chen J, Wang L, Li Y (2020) Research on the impact of multi-dimensional urbanization on China's carbon emissions under the background of COP21. J Environ Manag 273:111123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111123
Chen Q (2013) Advanced econometrics and stata application. Adv Educ Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese)
Cole MA, Neumayer E (2004) Examining the impact of demographic factors on air pollution. Popul Environ 26(1):5–21. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:POEN.0000039950.85422.eb
Fan Y, Liu L, Wu G, Wei Y (2006) Analyzing impact factors of CO2 emissions using the STIRPAT model. Environ Impact Assess Rev 26(4):377–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2005.11.007
Fang Q, Tao S (2017) Driving factors of China's carbon cmission: from the perspective of population and urbanization. Contemp Financ Econ 03:304
Gan T, Yang H, Liang W, Liao X (2021) Do economic development and population agglomeration inevitably aggravate haze pollution in China? New evidence from spatial econometric analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:5063–5079. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10847-4
Glaeser EL, Resseger MG (2010) The complementarity between cities and skills. J Reg Sci 50(1):221–244. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9787.2009.00635.x
Hanif I (2018) Impact of economic growth, nonrenewable and renewable energy consumption, and urbanization on carbon emissions in Sub-Saharan Africa. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(15):15057–15067. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1753-4
Hankey S, Marshall JD (2010) Impacts of urban form on future US passenger-vehicle greenhouse gas emissions. Energy Policy 38(9):4880–4887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2009.07.005
He X (2019) Population agglomeration, industrial agglomeration and environmental pollution:research based on two types of environmental pollution. J Southwest Minzu Univ (Humanit Soc Sci) 40(02):87–97. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1004-3926.2019.02.015 (in Chinese)
Hong J (2017) Non-linear influences of the built environment on transportation emissions: focusing on densities. J Trans Land Use 10(1):229–240. https://doi.org/10.5198/jtlu.2015.815
Hsiao C (1986) Analysis of panel data. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Econometric society monographs, vol 11. Cambridge University Press, New York. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511754203
Kasman A, Duman YS (2015) CO2 emissions, economic growth, energy consumption, trade and urbanization in new EU member and candidate countries:a panel data analysis. Econ Model 44:97–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2014.10.022
Li C, Fu C (2016) The dynamic stability of relationships between population size and waste watere missions. Resour Sci 38(06):1169–1178. https://doi.org/10.18402/resci.2016.06.16. (in Chinese)
Li Q, Ma H (2017) Influences on environment pollution by population agglomeration and foreign direct investment. Urban Problems (12):56–64. https://doi.org/10.13239/j.bjsshkxy.cswt.171208. (in Chinese)
Li X, Zhou M, Zhang W, Yu K, Meng X (2022) Study on the mechanism of haze pollution affected by urban population agglomeration. Atmosphere 13(2):278. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020278
Li Y, Zhang P (2013) Have industrial agglomeration aggravated regional environmental pollution—Chinese provincial level empirical evidence. J Huazhong Univ Sci Tech (Soc Sci) 27(05):97-106. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1671-7023.2013.05.016. (in Chinese)
Liddle B (2004) Demographic dynamics and per capita environmental impact: using panel regressions and household decompositions to examine population and transport. Popul Environ 26(1):23–39. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:POEN.0000039951.37276.f3
Liu X, Song D (2013) Influence on urban environment by industrial agglomeration. Urban Problems (03):9-15. 10.13239/j.bjsshkxy.cswt.2013.03.006. (in Chinese)
Liu Y, Leng Q (2020) Urbanization,population agglomeration and haze changes:based on threshold regression and spatial partition. Ecol Econ 36(03):92–98 (in Chinese)
Liu Y, Ma X, Yang R (2019) Interaction among population agglomeration, economic agglomeration, and environmental pollution:an PECM model analysis. Populat Res 43(03):90–101 (in Chinese)
Lu M, Feng H (2014) Agglomeration and emission reduction: an empirical study on the influence of urban scale gap on industrial pollution intensity. J Worl Econ 37(7):86–114 (in Chinese)
Lv Q, Liu H, Yang D, Liu H (2019) Effects of urbanization on freight transport carbon emissions in China: common characteristics and regional disparity. J Clean Prod 211:481–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.11.182
Nejat P, Jomehzadeh F, Taheri MM, Gohari M, Majid MZA (2015) A global review of energy consumption, CO2 emissions and policy in the residential sector (with an over view of the top ten CO2 emitting countries). Renew Sust Energ Rev 43:843–862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.11.066
Nickell S (1981) Biases in dynamic models with fixed effects. Econometrica 49:1399–1416. https://doi.org/10.2307/1911408
Oliveira EA, Andrade JS, Makse HA (2014) Large cities are less green. Sci Rep 4(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep04235
Parikh J, Shukla V (1995) Urbanization, energy use and greenhouse effects in economic development: results from a cross-national study of developing countries. Glob Environ Chang 5(2):87–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/0959-3780(95)00015-G
Poumanyvong P, Kaneko S (2010) Does urbanization lead to less energy use and lower CO2 emissions? Ecol Econ 70(2):434–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2010.09.029
Qu R, Jiang S (2012) Examining the impact of demographic factors on regional carbon emission:an empirical study based on Chinese provincial panel data. Populat Econ 02:10–17 (in Chinese)
Romer PM (1986) Increasing returns and long-run growth. J Polit Econ 94(5):1002–1037. https://doi.org/10.1086/261420
Shao S, Li X, Cao J (2019) Urbanization promotion and haze pollution governance in China. Econ Res J 54(02):148–165 (in Chinese)
Shefer D (1973) Localization economies in SMSA's: a production function analysis. J Reg Sci 13(1):55–64. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9787.1973.tb00377.x
Song D, Xu A (2011) Regional difference and influential factors of China's urban carbon emissions. China Popul,Resour Environ 21(11):8-14 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2011.11.002. (in Chinese)
Sun Y, Li H, Andlib Z, Genie MG (2022) How do renewable energy and urbanization cause carbon emissions? Evidence from advanced panel estimation techniques. Renew Energy 185:996–1005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.12.112
Tao C, Peng Y (2017) Population agglomeration, greening level and environmental pollution:an analysis of spatial heterogeneity based on urban data. J Jiangxi Univ Finance Econ (06):21-31. 10.13676/j.cnki.cn36-1224/f.2017.06.002. (in Chinese)
Timmons D, Zirogiannis N, Lutz M (2016) Location matters: population density and carbon emissions from residential building energy use in the United States. Energy Res Soc Sci 22:137–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.erss.2016.08.011
Wang F, Zhou X (2013) Study of the effects of demographic factors on environmental pollution in China:evidence from provincial panel data. South China Population 28(6):8-18. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1004-1613.2013.06.002. (in Chinese)
Wang S, Liu X, Zhou C, Hu J, Ou J (2017) Examining the impacts of socioeconomic factors, urban form, and transportation networks on CO2 emissions in China's megacities. Appl Energy 185:189–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.10.052
Wang X, Xie G, Yue S (2015) Impact of economic growth and population aggregation on urban environmental quality and its regional differentiation:a case study of 74 cities implemented the new standard for air quality during the first stage. Econ Geogr 35(02):71-76+91. https://doi.org/10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2015.02.010 (in Chinese)
Wang WZ, Liu LC, Liao H, Wei YM (2021) Impacts of urbanization on carbon emissions: An empirical analysis from OECD countries. Energy Policy 151:112171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2021.112171
Wu C (2010) Impact of opening up, population growth to China's SO2 emission. China Popul, Resour Environ 20(11):143–146. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2010.11.025 (in Chinese)
Xu H, Yang Y (2017) Influence of fiscal decentralization on heterogeneity of environmental pollution. Soft Sci 31(11):83-87. https://doi.org/10.13956/j.ss.1001-8409.2017.11.19. (in Chinese)
Yang B, Ding L, Tian Y (2021) The influence of population agglomeration on air pollution: An empirical study based on the mediating effect model. Earth Environ Sci 687(1):012014. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/687/1/012014
Yang S, Kong Q, Xu L (2020) Impact of industry and population agglomeration on environmental pollution: empirical evidence at the provincial level. Statistics & Decision 36(14):55-60. https://doi.org/10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2020.14.012 (in Chinese)
Zheng Y, Lu M (2018) Are large cities less green?an analysis based on scale effect and peer effect. Fudan Journal (Social Sciences Edition) 60(01):133-144. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0257-0289.2018.01.015 (in Chinese)
Zhou H, Li X (2010) Research on urbanization and environmental sustainability in China. J Nanjing University (Philosophy,Humanities and Social Sciences) 47(04):66–75 (in Chinese)
Funding
This research is supported by the National Normal Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 71772139).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yanchun Yi designed this study and participated in all phases; Dong Chen analyzed the data; Ji Qi contributed analysis tools; Ji Qi and Yanchun Yi revised the paper together. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: V.V.S.S. Sarma
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix Flowchart
Appendix Flowchart

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, Y., Qi, J. & Chen, D. Impact of population agglomeration in big cities on carbon emissions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 86692–86706 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21722-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21722-9