Abstract
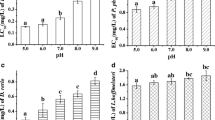
Lactic and formic acid are two commonly found monocarboxylic organic acids. Lactic acid is discharged into the water bodies as acidic industrial effluent from the food, cosmetic, chemical, and pharmaceutical industries, whereas formic acid is discharged from various paper, leather tanning, and textile processing industries. The present study investigated the toxicity of both organic acids upon the benthic oligochaete worm Tubifex tubifex. The 96-h median lethal concentration (LC50) values for lactic and formic acid are determined as 143.81 mg/l and 57.99 mg/l respectively. The effects of two sublethal concentrations (10% and 30% of 96 h LC50) of these acids on differential expression of oxidative stress enzymes are investigated. The comparative analysis of acute toxicity demonstrates that formic acid exposure is more detrimental to T. tubifex than lactic acid. The in silico structural analysis predicts that formic acid can interact with cytochrome c oxidase of the electron transport system and thereby inhibits its functionality and induces reactive oxygen species production. Integrated biomarker response (IBR) analysis illustrates that overall oxidative stress of formic acid to T. tubifex is significantly higher than that of lactic acid, which supports the structural analysis. It is concluded from this study that toxicokinetic–toxicodynamic and species sensitivity distributions studies are helpful for ecological risk management of environmental toxicants.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the authors upon reasonable request.
References
Abbott DA, Abbott DA, Suir E, Duong GH, De Hulster E, Pronk JT, Van Maris AJA (2009) Catalase overexpression reduces lactic acid-induced oxidative stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:2320. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00009-09
Abdel-Rahman MA, Tashiro Y, Sonomoto K (2013) Recent advances in lactic acid production by microbial fermentation processes. Biotechnol Adv 31:877–902. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIOTECHADV.2013.04.002
Ashauer R, Hintermeister A, Caravatti I, Kretschmann A, Escher BI (2010) Toxicokinetic and toxicodynamic modeling explains carry-over toxicity from exposure to diazinon by slow organism recovery. Environ Sci Technol 44:3963–3971. https://doi.org/10.1021/es903478b
Banaee M, Sureda A, Mirvaghefi AR, Ahmadi K (2013) Biochemical and histological changes in the liver tissue of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) exposed to sub-lethal concentrations of diazinon. Fish Physiol Biochem 39:489–501. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10695-012-9714-1
Bansal N (2018) Industrial development and challenges of water pollution in coastal areas: the case of Surat, India. IOP Conf Ser: Earth Environ Sci 120:012001. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/120/1/012001
Beauchamp C, Fridovich I (1971) Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 44:276–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(71)90370-8
Beers RF, Sizer IW (1952) A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J Biol Chem 195:133–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9258(19)50881-x
Beliaeff B, Burgeot T (2002) Integrated biomarker response: a useful tool for ecological risk assessment. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:1316–1322. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620210629
Bertrand L, Monferrán MV, Mouneyrac C et al (2016) Sensitive biomarker responses of the shrimp Palaemonetes argentinus exposed to chlorpyrifos at environmental concentrations: roles of alpha-tocopherol and metallothioneins. Aquat Toxicol 179:72–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AQUATOX.2016.08.014
Bhagat J, Ingole BS, Singh N (2016) Glutathione s-transferase, catalase, superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase, and lipid peroxidation as biomarkers of oxidative stress in snails: a review. Invertebr Surv J 13: 336–349. https://doi.org/10.25431/1824-307X/isj.v13i1.336-349
Bhattacharya R, Chatterjee A, Saha NC (2019) Acute toxicity and ethological responses of oligochaete worm Tubifex tubifex (Muller) exposed to a cationic surfactant Cetylpyridinium chloride. International Journal of Scientific Research in Biological Sciences 6:8–14. https://doi.org/10.26438/ijsrbs/v6i2.814
Bhattacharya R, Chatterjee A, Chatterjee S, Saha NC (2021) Oxidative stress in benthic oligochaete worm, Tubifex tubifex induced by sublethal exposure to a cationic surfactant cetylpyridinium chloride and an anionic surfactant sodium dodecyl sulfate. Comp Biochem Physiol Part - C Toxicol Pharmacol 240:108906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2020.108906
Bouché ML, Habets F, Biagianti-Risbourg S, Vernet G (2000) Toxic effects and bioaccumulation of cadmium in the aquatic oligochaete Tubifex tubifex. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 46:246–251. https://doi.org/10.1006/EESA.2000.1919
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:1–2. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Chang T, Wei B, Wang Q et al (2020) Toxicity assessment of municipal sewage treatment plant effluent by an integrated biomarker response in the liver of crucian carp (Carassius auratus). Environ Sci Pollut Res 27.https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07463-2
Chapman PM (2001) Utility and relevance of aquatic oligochaetes in Ecological Risk Assessment. Hydrobiologia 463:149–169. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013103708250
Chatterjee A, Bhattacharya R, Saha NC (2019) Zinc oxide (ZnO) induced toxicity and behavioural changes to oligochaete worm Tubifex tubifex (Muller). Int J Sci Res Biol Sci 6:35–42. https://doi.org/10.26438/ijsrbs/v6i2.3542
Chatterjee A, Bhattacharya R, Chatterjee S, Saha NC (2021) Acute toxicity of organophosphate pesticide profenofos, pyrethroid pesticide λ cyhalothrin and biopesticide azadirachtin and their sublethal effects on growth and oxidative stress enzymes in benthic oligochaete worm, Tubifex tubifex. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 242:108943. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CBPC.2020.108943
Cheremisinoff NP (2011) Pollution and pollution prevention. Handb Pollut Prev Clean Prod Best Pract Agrochem Ind 3:25–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-4377-7825-0.00002-9
DeLano WL (2002) Pymol: an open-source molecular graphics tool CCP4 Newsletter on protein crystallography 40:82–92. http://www.ccp4.ac.uk/newsletters/newsletter40/11_pymol.pdf
Devin S et al (2014) The integrated biomarker response revisited: optimization to avoid misuse. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:2448–2454. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2169-9
Dhara K, Mukherjee D, Saha NC (2015) Acute toxicity of cadmium to benthic oligochaete worm, Branchiura sowerbyi Beddard, 1982 and juvenile catfish, Clarias batrachus Linnaeus, 1758. Proc Zool Soc 68:116–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12595-014-0106-7
Eiroa M, Vilar A, Kennes C, Veiga MC (2006) Biological treatment of industrial wastewater containing formaldehyde and formic acid. Water SA 32:115–118
Emsley P, Lohkamp B, Scott WG, Cowtan K (2010) Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr Sect D Biol Crystallogr 66:486–501. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444910007493
Faggio C, Pagano M, Alampi R et al (2016) Cytotoxicity, haemolymphatic parameters, and oxidative stress following exposure to sub-lethal concentrations of quaternium-15 in Mytilus galloprovincialis. Aquat Toxicol 180:258–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AQUATOX.2016.10.010
Faheem M, Lone KP (2018) Oxidative stress and histopathologic biomarkers of exposure to bisphenol-A in the freshwater fish, Ctenopharyngodon idella. Braz J Pharm Sci 53:e17003. https://doi.org/10.1590/s2175-9790201700031700
Ferreira NGC, Cardoso DN, Morgado R, Soares AMVM, Loureiro S (2015) Longterm exposure of the isopod Porcellionides pruinosus to nickel: costs in the energy budget and detoxification enzymes. Chemosphere 135:354–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.04.025
Fillaudeau L, Bories A, Decloux M (2008) Brewing, winemaking and distilling: an overview of wastewater treatment and utilisation schemes. In: Handbook of Water and Energy Management in Food Processing. pp 929–995
Finney JOIDJ, Tattersfield F (1947) Probit analysis: a statistical treatment of the sigmoid response curve. J R Stat Soc 110:263–266. https://doi.org/10.2307/2981407
Garai P, Banerjee P, Mondal P, Saha NC (2021) Effect of heavy metals on fishes: toxicity and bioaccumulation. J Clin Toxicol 11:1000001
Gautam PK, Gautam RK, Banerjee S, Chattopadhyaya MC, Pandey JD (2016) Heavy metals in the environment: fate, transport, toxicity and remediation technologies. Toxicity and Remediation Techniques. ISBN: 978–1–63484–740–7
Ghelichpour M, Mirghaed AT, Jimenez AP (2019) LC50 determination and intoxication symptoms of a new pyridine carboxamide pesticide Flonicamid on common carp Cyprinus carpio. Rudn J Agron Anim Ind 14:279–288. https://doi.org/10.22363/2312-797x-2019-14-3-279-288
Harper DM, Rosenberg DA, Resh VH (1994) Freshwater biomonitoring and benthic macroinvertebrates. J Appl Ecol 31: X, 488. https://doi.org/10.2307/2404174
He L, He T, Farrar S et al (2017) Antioxidants maintain cellular redox homeostasis by elimination of reactive oxygen species. Cell Physiol Biochem 44:532–553. https://doi.org/10.1159/000485089
Holland PL (2008) Electronic structure and reactivity of three-coordinate iron complexes. Acc Chem Res 41:905. https://doi.org/10.1021/AR700267B
Keyhani J, Keyhani E (1980) EPR study of the effect of formate on cytochrome c oxidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 92:327–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-291X(80)91556-9
Kumari S, Kishor R (2020) Chitin and chitosan: origin, properties, and applications. Handb Chitin Chitosan 1:1–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-817970-3.00001-8
LaMonte G, Tang X, Chen JL-Y et al (2013) Acidosis induces reprogramming of cellular metabolism to mitigate oxidative stress. Cancer Metab 1:23. https://doi.org/10.1186/2049-3002-1-23
Li ZH, Velisek J, Grabic R, Li P, Kolarova J, Randak T (2011) Use of hematological and plasma biochemical parameters to assess the chronic effects of a fungicide propiconazole on a freshwater teleost. Chemosphere 83:572–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.12.024
Li X, Wu Q, Holsapple CW, Goldsby T (2017) An empirical examination of firm financial performance along dimensions of supply chain resilience. Management Research Review 40:254–269. https://doi.org/10.1108/MRR-02-2016-0030
Liesivuori J, Savolainen AH (1991) Methanol and Formic acid toxicity: biochemical mechanisms. Pharmacol Toxicol 69:157–163. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0773.1991.tb01290.x
Lin KJ, Yo SP (2008) The effect of organic pollution on the abundance and distribution of aquatic oligochaetes in an urban water basin, Taiwan. Hydrobiologia 596:213–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-007-9098-x
Lucan-Bouché ML, Biagianti-Risbourg S, Arsac F, Vernet G (1999) An original decontamination process developed by the aquatic oligochaete Tubifex tubifex exposed to copper and lead. Aquat Toxicol 45:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-445X(98)00091-5
Masindi V, Muedi KL (2018) Environmental contamination by heavy metals. Heavy Metals. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.76082
Meller M, Egeler P, Römbke J, Schallnass H, Nagel R, Streit B (1998) Short-term toxicity of lindane, hexachlorobenzene, and copper sulfate to tubificid sludgeworms (Oligochaeta) in artificial media. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 39:10–20. https://doi.org/10.1006/EESA.1997.1603
Michel H (1999) Cytochrome c oxidase: catalytic cycle and mechanisms of proton pumping-A discussion. Biochemistry 38:15129–15140. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi9910934
Milbrink G (1987) Biological characterization of sediments by standardized tubificid bioassays. Hydrobiologia 155:267–275. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00025659
Miller C et al (2018) Industrial production of lactic acid and its applications. Comprehensive Biotechnology 1:42–54
Mondal P, Garai P, Chatterjee A, Saha NC (2020a) Toxicological and therapeutic effects of neem (Azadirachta indica) leaf powder in hole-in-the-head (HITH) disease of fish Anabas testudineus. Aquac Res 52:715–723. https://doi.org/10.1111/ARE.14928
Mondal P, Chatterjee A, Garai P, Mukherjee A, Chandra Saha NC (2020b) Therapeutic effects of metronidazole benzoate in combination with melatonin in diplomonad parasite infection on Anabas testudineus. Biosci Biotechnol Res Commun 13:1993–2000. https://doi.org/10.21786/BBRC/13.4/54
Mosleh YY, Palacios SP, Ahmed MT, Mahmoud FM, Osman MA, Risbourg SB (2007) Effects of chitosan on oxidative stress and metallothioneins in aquatic worm Tubifex tubifex (Oligochaeta, Tubificidae). Chemosphere 67:167–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.09.019
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738-3
Posthuma L, de Zwart D (2012) Predicted mixture toxic pressure relates to observed fraction of benthic macrofauna species impacted by contaminant mixtures. Environ Toxicol Chem 31:2175–2188. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.1923
Posthuma L, van Gils J, Zijp MC, van de Meent D, de Zwartd D (2019) Species sensitivity distributions for use in environmental protection, assessment, and management of aquatic ecosystems for 12 386 chemicals. Environ Toxicol Chem 38:703–711. https://doi.org/10.1002/ETC.4373
Ram J, Sukhija J, Behera D, Gupta A (2010) Ocular and systemic morbidity profile in mass formic acid injuries. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging 41:123–127. https://doi.org/10.3928/15428877-20091230-22
Riemann A, Schneider B, Ihling A, Nowak M, Sauvant C, Thews O, Acidic GM (2011) Acidic environment leads to ROS-induced MAPK signaling in cancer cells. PLoS ONE 6:e22445. https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0022445
Saha NC, Bhunia F, Kaviraj A (2006) Comparative toxicity of three organic acids to freshwater organisms and their impact on aquatic ecosystems. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 12:192–202. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807030500430625
Šali A, Blundell TL (1993) Comparative protein modelling by satisfaction of spatial restraints. J Mol Biol 234:779–815. https://doi.org/10.1006/JMBI.1993.1626
Šali A, Overington JP (1994) Derivation of rules for comparative protein modeling from a database of protein structure alignments. Protein Sci 3:1582–1596. https://doi.org/10.1002/PRO.5560030923
Sauer M, Porro D, Mattanovich D, Branduardi P (2008) Microbial production of organic acids: expanding the markets. Trends Biotechnol 26:100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TIBTECH.2007.11.006
Schenková J, Helešic J (2006) Habitat preferences of Aquatic Oligochaeta (Annelida) in the Rokytná River, Czech Republic – a small highland stream. Hydrobiologia 564:117–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-1713-0
Shahangian S, Ash KO (1986) Formic and lactic acidosis in a fatal case of methanol intoxication. Clin Chem 32:395–397. https://doi.org/10.1093/clinchem/32.2.395
Sharbidre AA, Metkari V, Patode P (2011) Effect of diazinon on acetylcholinesterase activity and lipid peroxidation of Poecilia reticulata. Res J Environ Toxicol 5:152–161. https://doi.org/10.3923/rjet.2011.152.161
Sigurdsson J, Björnsson A, Gudmundsson ST (1983) Formic acid burn–local and systemic effects. Report of a case. Burns Incl Therm Inj 9:358–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-4179(83)90084-0
Stewart JSS (1969) Tissue hypoxia and metabolic acidosis-significant factors? Postgrad Med J 45:518–521. https://doi.org/10.1136/pgmj.45.526.518
Thompson M (1992) NTP technical report on the toxicity studies of Formic Acid (CAS No. 64–18-6) administered by inhalation to F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice. Toxic Rep Ser 19:1-D3
Tornero V, Hanke G (2016) Chemical contaminants entering the marine environment from sea-based sources: A review with a focus on European seas. Mar Pollut Bull 112:17–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.06.091
Ura H, Hirata K, Katsuramaki T (1999) Mechanisms of cell death in hypoxic stress. Nippon Geka Gakkai Zasshi 100:656–662
US Environmental Protection Agency (2004) SSD Generator. Center for Public Health and Environmental Assessment (CPHEA), Washington, DC. [cited 2020 December 19]. Available from: https://www.epa.gov/caddis-vol4/caddis-volume-4-data-analysis-download-software Google Scholar
Valavanidis A, Vlahogianni T, Dassenakis M, Scoullos M (2006) Molecular biomarkers of oxidative stress in aquatic organisms in relation to toxic environmental pollutants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 64:178–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.03.013
Valk DS, Khadem AF, Foreman CM, Lier JBV, Kreuk MKD (2017) Physical and biochemical changes in sludge upon Tubifex tubifex predation. Environ Technol (UK) 38:1524–1538. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2016.1236150
Vijayakumar J, Aravindan R, Viruthagiri T (2007) Lactic acid and its potential applications in industries. Chem Eng World 42:101–103
Vyata V, Durugu S, Jitta SR et al (2020) An atypical presentation of formic acid poisoning. Cureus 12.https://doi.org/10.7759/CUREUS.7988
Wu Y, Hua C, Liu Z, Yang J, Huang R, Li M, Liu K, Miao R, Fang Y (2021) High-performance sensing of formic acid vapor enabled by a newly developed nanofilm-based fluorescent sensor. Anal Chem 93:7094–7101. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.ANALCHEM.1C00576
Yildiz S (2016) Habitat preferences of aquatic oligochaeta (Annelida) species in the Lake District (Turkey). Fresenius Environ Bull 25:4362–4373
Zhang X, Tian Y, Wang Q, Chen L, Wang X (2012) ‘Heavy metal distribution and speciation during sludge reduction using aquatic worms. Biores Technol 126:41–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.09.015
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to the Department of Zoology, The University of Burdwan, West Bengal, India, for providing the infrastructural facilities and necessary financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Pramita Garai: Conception or design of the work; Material preparation; data collection; analysis and writing of the first draft of the manuscript.
Priyajit Banerjee: Conception or design of the work; Material preparation; data collection; analysis and writing.
Pramita Sharma: Conception or design of the work; Material preparation; data collection; analysis.
Arnab Chatterjee: Conception or design of the work; Material preparation; data collection; analysis.
Ritwick Bhattacharya: Conception or design of the work; Material preparation; data collection; analysis.
Nimai Chandra Saha: Conception or design of the work; Material preparation; data collection; analysis; supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article contains no animal studies by any of the authors requiring endorsement from the ethical committee. In fact, according to the current regulatory studies, no ethical authorization is required for invertebrates like Tubifex tubifex.
Consent to participate
All the authors have consent to participate.
Consent for publication
All the authors have consent to publish.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Chris Lowe
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garai, P., Banerjee, P., Sharma, P. et al. Mechanistic insights to lactic and formic acid toxicity on benthic oligochaete worm Tubifex tubifex. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 87319–87333 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21361-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21361-0