Abstract
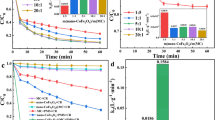
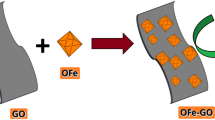
Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) was employed as a sacrificial substructure and two-dimensional support to develop magnetic cobalt ferrite-carbon nitride (CoFe2O4/g-CN) composite via a one-step solid combustion method. The catalyst activated peroxymonosulphate (PMS), through the interconversion of Co2 + /3+|surf. and Fe2 + /3+|surf. on its surface for degradation of reactive dyes (RDs). Excellent ferromagnetic nature (44.15 emu g−1) of the catalyst led to its efficient magnetic separation. With an optimum catalyst and PMS dose of 0.4 g L−1 and 1.5 g L−1, 99% RD removal was achieved for textile effluent (pH 9.5–10), under UV irradiation (48 W). In-depth radical scavenging experiments and EPR analysis confirmed the dominance of radical-based degradation process. Plausible degradation and mineralization pathways of RDs were proposed through identification of intermediates by LCMS/MS analysis. In brief, this study elucidates an exclusive strategy towards the use of g-C3N4 as fuel for facile synthesis of magnetic CoFe2O4/g-CN as a remarkable photocatalyst for activation of PMS towards mineralization of various industrially relevant RDs.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
Change history
11 April 2024
Editor's Note: Readers are alerted that the concerns have been raised with this article. Editorial action will be taken as appropriate once this matter is resolved and all parties have been given an opportunity to respond in full.
Abbreviations
- Ct :
-
Residual dye concentration at a specific time t (mg/L)
- C0 :
-
Concentration of dye in the feed solution (mg/L)
- ECB :
-
Conduction band energy
- EVB :
-
Valence band energy
- AOP:
-
Advanced oxidation process
- CB:
-
Conduction band
- EDC:
-
Endocrine-disrupting chemical
- EDTA-2Na:
-
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt
- His:
-
l-Histidine
- NOM:
-
Natural organic matter
- PBQ:
-
para-Benzoquinone
- PS:
-
Persulphate
- PMS:
-
Peroxymonosulphate
- pHPZC :
-
pH at point of zero charge
- RD:
-
Reactive dye
- R.Black:
-
Reactive black
- R.Blue:
-
Reactive blue
- R.Red:
-
Reactive red
- R.Yellow:
-
Reactive yellow
- TBA:
-
Tertiary butyl alcohol
- VB:
-
Valance band
References
Banerjee P, De S (2010) Treatment of textile effluent using advanced oxidation process and nanofiltration. Int J Environ Eng 2:56. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJEE.2010.029821
Banerjee P, DasGupta S, De S (2008) Kinetic study of advanced oxidation of eosin dye by Fenton’s reagent. Int J Chem React Eng 6. https://doi.org/10.2202/1542-6580.1756
Bansal P, Sud D (2013) Photocatalytic degradation of commercial dye, CI Reactive Red 35 in aqueous suspension: degradation pathway and identification of intermediates by LC/MS. J Mol Catal A Chem 374–375:66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2013.03.018
Bilal M, Rasheed T, Iqbal HMN et al (2018) Toxicological assessment and UV/TiO2-based induced degradation profile of reactive black 5 dye. Environ Manag 61:171–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-017-0948-7
Casbeer E, Sharma VK, Li X-Z (2012) Synthesis and photocatalytic activity of ferrites under visible light: a review. Sep Purif Technol 87:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2011.11.034
Deng Y, Zhao R (2015) Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) in wastewater treatment. Curr Pollut Rep 1:167–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40726-015-0015-z
Ding Y, Zhao J, Zhang W et al (2019) Single-walled carbon nanotubes wrapped CoFe2O4 nanorods with enriched oxygen vacancies for efficient overall water splitting. ACS Appl Energy Mater 2:1026–1032. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.8b01338
Du Y, Ma W, Liu P et al (2016) Magnetic CoFe2O4 nanoparticles supported on titanate nanotubes (CoFe2O4/TNTs) as a novel heterogeneous catalyst for peroxymonosulfate activation and degradation of organic pollutants. J Hazard Mater 308:58–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.01.035
Fang G, Liu C, Gao J et al (2015) Manipulation of persistent free radicals in biochar to activate persulfate for contaminant degradation. Environ Sci Technol 49:5645–5653. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5061512
Gmurek M, Olak-Kucharczyk M, Ledakowicz S (2017) Photochemical decomposition of endocrine disrupting compounds – a review. Chem Eng J 310:437–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.05.014
Gogoi D, Makkar P, Ghosh NN (2021) Solar light-irradiated photocatalytic degradation of model dyes and industrial dyes by a magnetic CoFe 2 O 4 –gC 3 N 4 S-scheme heterojunction photocatalyst. ACS Omega 6:4831–4841. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c05809
Guo X, Ai S, Yang D et al (2019) Synergistic photocatalytic and Fenton-like degradation of organic contaminants using peroxymonosulfate activated by CoFe2O4@ g-C3N4 composite. Environ Technol 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2019.1697378
Hafeez HY, Lakhera SK, Narayanan N et al (2019) Environmentally sustainable synthesis of a CoFe 2 O 4 –TiO 2 /rGO ternary photocatalyst: a highly efficient and stable photocatalyst for high production of hydrogen (solar fuel). ACS Omega 4:880–891. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b03221
Hao OJ, Kim H, Chiang P-C (2000) Decolorization of wastewater. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 30:449–505. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643380091184237
Huang S, Xu Y, Xie M et al (2015) Synthesis of magnetic CoFe2O4/g-C3N4 composite and its enhancement of photocatalytic ability under visible-light. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 478:71–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2015.03.035
Jourshabani M, Lee B-K, Shariatinia Z (2020) From traditional strategies to Z-scheme configuration in graphitic carbon nitride photocatalysts: recent progress and future challenges. Appl Catal B Environ 276:119157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119157
Koprivanac N, Bosanac G, Grabaric Z, Papic S (1993) Treatment of wastewaters from dye industry. Environ Technol 14:385–390. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593339309385304
Li M, Song C, Wu Y et al (2019) Novel Z-scheme visible-light photocatalyst based on CoFe2O4/BiOBr/graphene composites for organic dye degradation and Cr(VI) reduction. Appl Surf Sci 478:744–753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.02.017
Ma Y, Liu E, Hu X et al (2015) A simple process to prepare few-layer g-C3N4 nanosheets with enhanced photocatalytic activities. Appl Surf Sci 358:246–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.08.174
Martínez-Huitle CA, Brillas E (2009) Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods: a general review. Appl Catal B Environ 87:105–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2008.09.017
Oh W-D, Dong Z, Lim T-T (2016) Generation of sulfate radical through heterogeneous catalysis for organic contaminants removal: current development, challenges and prospects. Appl Catal B Environ 194:169–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.04.003
Rafique M, Hajra S, Tahir MB et al (2022) A review on sources of heavy metals, their toxicity and removal technique using physico-chemical processes from wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18638-9
Ren Y, Lin L, Ma J et al (2015) Sulfate radicals induced from peroxymonosulfate by magnetic ferrospinel MFe2O4 (M = Co, Cu, Mn, and Zn) as heterogeneous catalysts in the water. Appl Catal B Environ 165:572–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.10.051
Roy D, Neogi S, De S (2021) Multicomponent transport model-based scaling up of long-term fixed bed adsorption of reactive dyes from textile effluent using aminated PAN beads. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:43483–43506. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13661-8
Roy D, Neogi S, De S (2022a) Visible light assisted activation of peroxymonosulfate by bimetallic MOF based heterojunction MIL-53(Fe/Co)/CeO2 for atrazine degradation: Pivotal roles of dual redox cycle for reactive species generation. Chem Eng J 430:133069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.133069
Roy D, Neogi S, De S (2022b) Mechanistic investigation of photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol-A using MIL-88A(Fe)/MoS2 Z-scheme heterojunction composite assisted peroxymonosulfate activation. Chem Eng J 428:131028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.131028
Sarkar P, Roy D, Bera B et al (2022) Efficient photocatalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin using novel dual Z-scheme gCN/CuFe2O4/MoS2 mediated peroxymonosulphate activation. Chem Eng J 430:132834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.132834
Sathishkumar P, Pugazhenthiran N, Mangalaraja RV et al (2013) ZnO supported CoFe2O4 nanophotocatalysts for the mineralization of Direct Blue 71 in aqueous environments. J Hazard Mater 252–253:171–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.02.030
Tezcanli-Guyer G, Ince N (2003) Degradation and toxicity reduction of textile dyestuff by ultrasound. Ultrason Sonochem 10:235–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1350-4177(03)00089-0
Thomas A, Fischer A, Goettmann F et al (2008) Graphitic carbon nitride materials: variation of structure and morphology and their use as metal-free catalysts. J Mater Chem 18:4893. https://doi.org/10.1039/b800274f
Tian H, Liu M, Zheng W (2018) Applied Catalysis B : Environmental Constructing 2D graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets / layered MoS 2 / graphene ternary nanojunction with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Appl Catal B Environ 225:468–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.12.019
Torrellas SÁ, García Lovera R, Escalona N et al (2015) Chemical-activated carbons from peach stones for the adsorption of emerging contaminants in aqueous solutions. Chem Eng J 279:788–798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.05.104
Wang J, Wang S (2018) Activation of persulfate (PS) and peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and application for the degradation of emerging contaminants. Chem Eng J 334:1502–1517
Wang Y, Wang X, Antonietti M (2012) Polymeric graphitic carbon nitride as a heterogeneous organocatalyst: from photochemistry to multipurpose catalysis to sustainable chemistry. Angew Chem Int Ed 51:68–89. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201101182
Wang Q, Shao Y, Gao N et al (2017) Activation of peroxymonosulfate by Al2O3-based CoFe2O4 for the degradation of sulfachloropyridazine sodium: kinetics and mechanism. Sep Purif Technol 189:176–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.07.046
Xu M, Li J, Yan Y et al (2019) Catalytic degradation of sulfamethoxazole through peroxymonosulfate activated with expanded graphite loaded CoFe2O4 particles. Chem Eng J 369:403–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.075
Yang Q, Ma Y, Chen F et al (2019) Recent advances in photo-activated sulfate radical-advanced oxidation process (SR-AOP) for refractory organic pollutants removal in water. Chem Eng J 378:122149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122149
Yaseen DA, Scholz M (2019) Textile dye wastewater characteristics and constituents of synthetic effluents: a critical review. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:1193–1226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2130-z
Yu X-J, Qu J, Yuan Z et al (2019) Anisotropic CoFe 2 O 4 @graphene hybrid aerogels with high flux and excellent stability as building blocks for rapid catalytic degradation of organic contaminants in a flow-type setup. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:34222–34231. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b10287
Zheng Y, Liu J, Liang J et al (2012) Graphitic carbon nitride materials: controllable synthesis and applications in fuel cells and photocatalysis. Energy Environ Sci 5:6717. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ee03479d
Zou H, Yan X, Ren J et al (2015) Photocatalytic activity enhancement of modified g-C3N4 by ionothermal copolymerization. J Mater 1:340–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmat.2015.10.004
Funding
This work is supported by a grant from the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, under the scheme no. DST/TM/WTI/WIC/2K17/84(G), Dt. 15-01-2019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Poulomi Sarkar: Experimentation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing, Editing- Original draft preparation; Debashis Roy: synthesis and characterization, draft editing; Biswajit Bera: Characterization and draft editing; Sudarsan Neogi: Investigation, Reviewing and Editing, Conceptualization, Supervision, Sirshendu De: Investigation, Reviewing and Editing, Conceptualization, Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests
Disclaimer
Any opinions, findings and conclusions expressed in this paper are those of the authors.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Sami Rtimi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sarkar, P., Roy, D., Bera, B. et al. Enhanced photodegradation of reactive dyes in textile effluent with CoFe2O4/g-CN heterostructure–mediated peroxymonosulphate activation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 50566–50583 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18944-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18944-2