Abstract
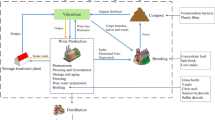
Environmental problems caused by the food processing industry have always been one of the concerns for the public. Herein, for the first time, a gate-to-gate life cycle assessment (LCA) was employed to evaluate the environmental impact of rice bran oil production. Four subsystems, namely, transportation of the raw rice bran to oil factory, crude oil extraction, oil refining, and oil storage, were established. The product sustainability software GaBi and the method CML 2001-Jan. 2016 were used to calculate and analyze the environmental burdens at each stage of the rice bran oil production chain. The results show the oil refining stage had the greatest environmental impact, followed by the oil extraction stage. High demands for coal and electricity make a critical difference in generating vast majority of environmental impacts. Modifying the electricity source and replacing traditional fuels with cleaner ones will do bring benefits to the sustainable development of the industry.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Ben-Othman S, Jõudu I, Bhat R (2020) Bioactives from agri-food wastes: present insights and future challenges. Molecules 25:510
Bommarco R, Kleijn D, Potts SG (2013) Ecological intensification: harnessing ecosystem services for food security. Trends Ecol Evol 28:230–238
Bórawski P, Bełdycka-Bórawska A, Szymańska EJ, Jankowski KJ, Dubis B, Dunn JW (2019) Development of renewable energy sources market and biofuels in The European Union. J Clean Prod 228:467–484
De Marco I, Riemma S, Iannone R (2018) Uncertainty of input parameters and sensitivity analysis in life cycle assessment: an Italian processed tomato product. J Clean Prod 177:315–325
Friedman M (2013) Rice brans, rice bran oils, and rice hulls: composition, food and industrial uses, and bioactivities in humans, animals, and cells. J Agric Food Chem 61:10626–10641
Gallyas F, Lee S, Yu S, Park HJ, Jung J, Go G-W, Kim W (2019) Rice bran oil ameliorates inflammatory responses by enhancing mitochondrial respiration in murine macrophages. PLoS ONE 14:10
Ghasemzadeh A, Baghdadi A, Z E Jaafar H, Swamy MK, Megat Wahab PE (2018) Optimization of flavonoid extraction from red and brown rice bran and evaluation of the antioxidant properties. Molecules 23, 1863.
Gul K, Yousuf B, Singh AK, Singh P, Wani AA (2015) Rice bran: nutritional values and its emerging potential for development of functional food—a review. Bioactive Carbohydrates and Dietary Fibre 6:24–30
Hou H, Shao S, Zhang Y, Kang H, Qin C, Sun X, Zhang S (2019) Life cycle assessment of sea cucumber production: a case study, China. J Clean Prod 213:158–164
Kalhor P, Ghandi K (2019) Deep eutectic solvents for pretreatment, extraction, and catalysis of biomass and food waste. Molecules 24:4012
Khanali M, Mousavi SA, Sharifi M, Keyhani Nasab F, Chau K-W (2018) Life cycle assessment of canola edible oil production in Iran: a case study in Isfahan province. J Clean Prod 196:714–725
Khatri P, Jain S (2017) Environmental life cycle assessment of edible oils: a review of current knowledge and future research challenges. J Clean Prod 152:63–76
Khatri P, Jain S, Pandey S (2017) A cradle-to-gate assessment of environmental impacts for production of mustard oil using life cycle assessment approach. J Clean Prod 166:988–997
Lai WT, Khong NMH, Lim SS, Hee YY, Sim BI, Lau KY, Lai OM (2017) A review: Modified agricultural by-products for the development and fortification of food products and nutraceuticals. Trends Food Sci Technol 59:148–160
Lai O-M, Jacoby JJ, Leong W-F, Lai W-T (2019) Chapter 2 - Nutritional studies of rice bran oil, in: Cheong, L.-Z., Xu, X. (Eds.), Rice bran and rice bran oil. AOCS Press, pp. 19–54.
Liu J, Li YP, Huang GH, Zhuang XW, Fu HY (2017) Assessment of uncertainty effects on crop planning and irrigation water supply using a Monte Carlo simulation based dual-interval stochastic programming method. J Clean Prod 149:945–967
Ma X, Wang Y, Wang C (2017) Low-carbon development of China’s thermal power industry based on an international comparison: review, analysis and forecast. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 80:942–970
Notarnicola B, Sala S, Anton A, McLaren SJ, Saouter E, Sonesson U (2017) The role of life cycle assessment in supporting sustainable agri-food systems: a review of the challenges. J Clean Prod 140:399–409
Park H-Y, Lee K-W, Choi H-D (2017) Rice bran constituents: immunomodulatory and therapeutic activities. Food Funct 8:935–943
Perez-Ternero C, Alvarez de Sotomayor M, Herrera MD (2017) Contribution of ferulic acid, γ-oryzanol and tocotrienols to the cardiometabolic protective effects of rice bran. Journal of Functional Foods 32:58–71
Prasad S, Singh A, Korres NE, Rathore D, Sevda S, Pant D, (2020) Sustainable utilization of crop residues for energy generation: a life cycle assessment (LCA) perspective. Bioresource Technology 303, 122964.
Quispe I, Navia R, Kahhat R (2019) Life Cycle Assessment of rice husk as an energy source. A Peruvian case study. J Clean Prod 209:1235–1244
Rico X, Gullon B, Alonso JL, Yanez R (2020) Recovery of high value-added compounds from pineapple, melon, watermelon and pumpkin processing by-products: An overview. Food Research International 132, 109086.
Samad N (2015) Rice bran oil prevents neuroleptic-induced extrapyramidal symptoms in rats: possible antioxidant mechanisms. J Food Drug Anal 23:370–375
Soussana J-F (2014) Research priorities for sustainable agri-food systems and life cycle assessment. J Clean Prod 73:19–23
Thengane SK, Burek J, Kung KS, Ghoniem AF, Sanchez DL (2020) Life cycle assessment of rice husk torrefaction and prospects for decentralized facilities at rice mills. J Clean Prod 275:123177
Tsarouhas P, Achillas C, Aidonis D, Folinas D, Maslis V (2015) Life Cycle Assessment of olive oil production in Greece. J Clean Prod 93:75–83
Tukker A, Jansen B (2006) Environmental impacts of products: a detailed review of studies. J Ind Ecol 10:159–182
Unrean P, Lai Fui BC, Rianawati E, Acda M (2018) Comparative techno-economic assessment and environmental impacts of rice husk-to-fuel conversion technologies. Energy 151:581–593
Wang C, Engels A, Wang Z (2018) Overview of research on China’s transition to low-carbon development: the role of cities, technologies, industries and the energy system. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 81:1350–1364
Wang C, Cheng X, Shuai C, Huang F, Zhang P, Zhou M, Li R (2020) Evaluation of energy and environmental performances of solar photovoltaic-based targeted poverty alleviation plants in China. Energy Sustain Dev 56:73–87
Wimbadi RW, Djalante R (2020) From decarbonization to low carbon development and transition: a systematic literature review of the conceptualization of moving toward net-zero carbon dioxide emission (1995–2019). J Clean Prod 256:120307
Yuan Q, Song G, Fullana-i-Palmer P, Wang Y, Semakula HM, Mekonnen MM, Zhang S (2017) Water footprint of feed required by farmed fish in China based on a Monte Carlo-supported von Bertalanffy growth model: a policy implication. J Clean Prod 153:41–50
Zhang H, Sun H, Zhou S, Bai N, Zheng X, Li S, Zhang J, Lv W (2019) Effect of straw and straw biochar on the community structure and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in rice-wheat rotation ecosystems. Sci Rep 9:9367
Zhao L, Ji Y, Yao J, Long S, Li D, Yang Y (2017) Quantifying the fate and risk assessment of different antibiotics during wastewater treatment using a Monte Carlo simulation. J Clean Prod 168:626–631
Acknowledgements
The authors warmly thank Dr. Haochen Hou for the technical support in Monte Carlo simulations.
Funding
This study was supported by the General Project of the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (2019-MS-044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lihui Sun: Conceptualization; Project administration; Roles/Writing — original draft; Writing — review and editing;
Yuying Wang: Roles/Writing — original draft; Investigation; Data curation;
Yuqing Gong: Resources; Validation;
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Loubet
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, LH., Wang, YY. & Gong, YQ. Life cycle assessment of rice bran oil production: a case study in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 39847–39859 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18172-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18172-0