Abstract
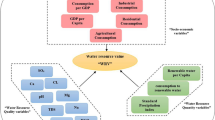
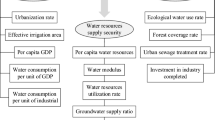
The security of water resources is of great importance to long-term sustainability. In order to better ensure the security of water resources, a significant link is to conduct water resources security evaluation, which should be considered from many perspectives as it involves natural reserves, social production, the efficiency of use, and environmental protection. In this paper, a fuzzy analytic hierarchy process sort (AHPSort) II-entropy weight (EW) method for regional water resources security evaluation is proposed based on the security of visible water and virtual water. Firstly, this paper takes into account the criterion of efficiency of water use in addition to two other criteria of quantity of water resources, pressure on water resources to establish a comprehensive water resources security evaluation system. Secondly, a combination method of hesitant fuzzy language judgment and entropy weight is employed to obtain the weight of each indicator. Thirdly, AHPSort II is used to classify the security levels of the evaluated regions, in which the security levels of regional water resources are divided into five levels. Furthermore, a case study on the cities of Hubei province, China, is conducted to show the applicability of the proposed method, the effectiveness, and reliability of the method are then verified by being compared with a subjective method and an objective method as well as sensitivity analysis. Finally, according to the comprehensive evaluation results, specific management suggestions for improving the water resources security in the case are put forward.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguaron J, Escobar M T, Moreno-Jimenez J M, Turon A (2019) AHP-Group decision making based on consistency. Mathematics 7(3):242. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7030242
Acuna-Alonso C, Fernandes A C P, Alvarez X, Valero E, Pacheco F A L, Varandas S D P, Terencio D P S, Fernandes L F S (2021) Water security and watershed management assessed through the modelling of hydrology and ecological integrity: a study in the Galicia-Costa (NW Spain). Sci Total Environ 759:143905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143905
Abbott BW, Bishop K, Zarnetske JP, Minaudo C, Chapin FS, Krause S, Hannah DM, Conner L, Ellison D, Godsey SE, Plont S, Marcais J, Kolbe T, Huebner A, Frei RJ, Hampton T, Gu S, Buhman M, Sayedi SS, Ursache O, Chapin M, Henderson KD, Pinay G (2019) Human domination of the global water cycle absent from depictions and perceptions. Nat Geosci 12(7):533-+. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-019-0374-y
Cao X C, Zeng W, Wu M Y, Li T Y, Chen S, Wang W G (2021) Water resources efficiency assessment in crop production from the perspective of water footprint. J Clean Prod 309:0959–6526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127371
Chen W M, Kang J N, Han M S (2021) Global environmental inequality: Evidence from embodied land and virtual water trade. Sci Total Environ 783:146992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146992
de Melo M C, Formiga-Johnsson R M, de Azevedo J P S, Nascimento N D, Machado F L V, Pacheco F A L, Fernandes L F S (2021) A raw water security risk model for urban supply based on failure mode analysis. J Hydrol 593:125843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125843
de Graaf IEM, Gleeson T, van Beek LPH, Sutanudjaja EH, Bierkens MFP (2019) Environmental flow limits to global groundwater pumping. Nat Int Weekly J Sci 574(7776):90-+. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1594-4
Ding X W, Chong X, Bao Z F, Xue Y, Zhang S H (2017) Fuzzy comprehensive assessment method based on the entropy weight method and its application in the water environmental safety evaluation of the Heshangshan drinking water source area, Three Gorges reservoir area. China Water 9(5):329. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9050329
Dou P F, Zuo S D, Ren Y, Rodriguez M J, Dai S Q (2021) Refined water security assessment for sustainable water management: a case study of 15 key cities in the Yangtze River Delta, China. J Environ Manag 290:112588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112588
Fu Y P, Huang G H, Liu L R, Li J Y, Zhang X Y, Zhai M Y, Pan X J (2021) Multi-hierarchy virtual-water management; a case study of Hubei Province, China. J Clean Prod 293:126244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126244
Gusain R, Kumar N, Ray S S (2020) Recent advances in carbon nanomaterial-based adsorbents for water purification. Coord Chem Rev 405:213111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2019.213111
Hubei Water Resources Bulletin in (2019) http://slt.hubei.gov.cn/
Ishizaka A, Lopez C (2018) Cost-benefit AHPSort for performance analysis of offshore providers. Int J Prod Res 57(13):4261–4277. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2018.1509393
Kang H Y, Lee A H I, Chan Y C (2019) An integrated fuzzy multi-criteria decision-making approach for evaluating business process information systems. Mathematics 7(10):982. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7100982
Kang S Z, Hao X M, Du T S, Tong L, Su X L, Lu H N, Li X L, Huo Z L, Li S E, Ding R S (2017) Improving agricultural water productivity to ensure food security in China under changing environment: From research to practice. Agric Water Manag 179:5–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2016.05.007
Li B, Wu Q, Zhang W P, Liu Z J (2020) Water resources security evaluation model based on grey relational analysis and analytic network process: a case study of Guizhou Province. J Water Process Eng 37:101429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101429
Li Z M, Zhang Q, Liao H C (2018) Efficient-equitable-ecological evaluation of regional water resource coordination considering both visible and virtual water. Omega 83:223–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2018.06.003
Liu Y L, Zhuo L, Varis O, Fang K, Liu G, Wu P (2021) Enhancing water and land efficiency in agricultural production and trade between Central Asia and China. Sci Total Environ 780:146584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146584
Li ZM, Xu JP, Lev B, Gang J (2015) Multi-criteria group individual research output evaluation based on context-free grammar judgments with assessing attitude. Omega 57:282–293 B. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2015.09.001
Luo Y, Chen X D, Yao L M (2020) Flood disaster resilience evaluation of Chinese regions: integrating the hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets with prospect theory. Nat Hazards 105(1):667–690. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-04330-z
Liu Z H, Jiang Z Z J, Xu C, Cai G J, Zhan J (2021) Assessment of provincial waterlogging risk based on entropy weight TOPSIS-PCA method. Nat Hazards 108(2):1545–1567. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-021-04744-3
Luo P P, Sun Y T, Wang S T, Wang S M, Lyu J Q, Zhou M M, Nakagami K, Takara k Nover D (2020) Historical assessment and future sustainability challenges of Egyptian water resources management. J Clean Prod 263:121154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121154
Ministry of Environmental Protection of China. Report on the State of the Environment in China (2015) Environmental information centre, ministry of environmental protection of the people’s republic of china: Beijing, China
Mishra V (2020) Long-term (1870-2018) drought reconstruction in context of surface water security in India. J Hydrol 580:124228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124228
Miccoli F, Ishizaka A (2017) Sorting municipalities in Umbria according to the risk of wolf attacks with AHPSort II. Ecol Indic 73:741–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.10.034
Meng F Y, Tang J (2019) New ranking order for linguistic hesitant fuzzy sets. J Oper Res Soc 70:531–540. https://doi.org/10.1080/01605682.2018.1447252
Nilsson M, Griggs D, Visbeck M (2016) Map the interactions between Sustainable Development Goals. Nature 534(7607):320–322. https://doi.org/10.1038/534320a
National Bureau of statistics (2019) http://www.stats.gov.cn/
Sun C, Li S Y, Deng Y (2020) Determining weights in multi-criteria decision making based on negation of probability distribution under uncertain environment. Mathematics 8(2):191. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8020191
Sutadian A D, Muttil N, Yilmaz A G, Perera B J C (2017) Using the analytic hierarchy process to identify parameter weights for developing a water quality index. Ecol Indic 75:220–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.12.043
Song M L, Zhu Q Y, Peng J, Gonzalez E D R S (2017) Improving the evaluation of cross efficiencies: a method based on Shannon entropy weight. Comput Ind Eng 112:99–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2017.07.023
Tu Y, Wang H Y, Zhou X Y, Shen W J, Lev B, Klemes J J (2021) Comprehensive evaluation of security, equity, and efficiency on regional water resources coordination using a hybrid multi-criteria decision-making method with different hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets. J Clean Prod 310:127447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127447
The Ministry of Water Resources releases 2019 China Water Resources Bulletin (2019) https://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:SJYF.0.2020-09-018
The United Nations World Water Development Report (2019) https://https://unhabitat.org/world-water-development-report-2019
Vorosmarty C J, McIntyre P B, Gessner M O, Dudgeon D, Prusevich A, Green P, Glidden S, Bunn S E, Sullivan C A, Reidy Liermann C, Davies P M (2010) Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature 467(7315):555–561. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature.2010.09440
Wang X X, Chen Y N, Li Z, Fang G H, Wang Y (2020) Development and utilization of water resources and assessment of water security in Central Asia. Agric Water Manag 240:106297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106297
Xu Z W, Yao L M, Zhang Q, Dowaki K, Long Y (2020) Inequality of water allocation and policy response considering virtual water trade: a case study of Lanzhou city, China. J Clean Prod 269:122326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122326
Yin B L, Guan D J, Zhou L L, Zhou J, He X J (2020) Sensitivity assessment and simulation of water resource security in karst areas within the context of hydroclimate change. J Clean Prod 258:120994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120994
Xu Z, Qin J D, Liu J, Martinez L (2019) Sustainable supplier selection based on AHPSort II in interval type-2 fuzzy environment. Inf Sci 483:273–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.01.013
Yan H B, Ma T J, Huynh V N (2016) On qualitative multi-attribute group decision making and its consensus measure: a probability based perspective. Omega 70:94–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2016.09.004
Zhang Y X, Xu Z S, Liao H C (2019) Water security evaluation based on the TODIM method with probabilistic linguistic term sets. Soft Comput 23(15):6215–6230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-018-3276-9
Zhang C Q, Wang C, Zhang Z M, Tian D Z (2019) A novel technique for multiple attribute group decision making in interval-valued hesitant fuzzy environments with incomplete weight information. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 10(6):2429–2445. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-018-0912-2
Zhang H, Li Y P, Sun J, Liu J, Huang G H, Ding Y K, Wu X J (2021) A two-stage factorial-analysis-based input-output model for virtual-water quantification and metabolic-network identification in Kyrgyzstan. J Clean Prod 301:126960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126960
Zhao J, Chen YQ, Xu JC, Jin JL, Wang GQ, Shamseldin A, Guo Y, Cheng L (2021) Regional water security evaluation with risk control model and its application in Jiangsu Province, China. Environ Sci Pollution Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14547-5
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 71801177), the Humanities and Social Sciences Fund of Ministry of Education of China (grant number 18YJC630163), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (grant number WUT: 2020VI006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Marcus Schulz
Author contribution
YD: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing - original draft; YT: Methodology, Writing - review & editing; ZL: Writing - review & editing; LN: Formal analysis.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, Y., Tu, Y., Li, Z. et al. Regional water resources security grading evaluation considering both visible and virtual water: a case study on Hubei province, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 25824–25847 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17506-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17506-2