Abstract
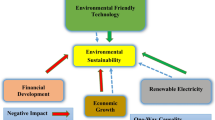
This paper explored the asymmetrical relationships between green and sustainable technology research and environmental sustainability among the BRICS states from 1990 to 2018. The data was analyzed by second- and third-generation economic techniques such as slope heterogeneity and cross-section independence test, unit root test, structural break unit root test, panel cointegration with structural breaks cointegration tests, cross-section autoregressive distributed lags technique, augmented mean group, and Dumitrescu-Hurlin panel causality test. First, the results validated a long-run cointegration among variables. Second, the results showed that renewable energy consumption and positive shocks to green and sustainable technology research are proper to mitigate carbon dioxide emissions (short- and long-run). Third, gross domestic product, foreign direct investment, exports, and negative shocks to green and sustainable technology research increase carbon dioxide emissions. Fourth, the nexus between green and sustainable technology research and carbon dioxide emissions was counter-cyclical during economic expansion and contraction periods. Fifth, the impact of positive shocks to green and sustainable technology research on carbon dioxide emissions was more than the impact of negative shocks to green and sustainable technology research on carbon dioxide emissions.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are variability from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Acheampong AO, Adams S, Boateng E (2019) Do globalization and renewable energy contribute to carbon emissions mitigation in Sub-Saharan Africa? Sci Total Environ 677:436–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2019.04.353
Aghion P, Askenazy P, Berman N, Cette G, Eymard L (2012) credit constraints and the cyclicality of r&d investment: evidence from France. J Eur Econ Assoc 10(5):1001–1024. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1542-4774.2012.01093.x
Ahmad M (2021) Non-linear dynamics of innovation activities over the business cycles: Empirical evidence from OECD economies. Technol Soc 67:101721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2021.101721
Ahmad M, Khattak SI (2020) Is aggregate domestic consumption spending (ADCS) per capita determining CO2 emissions in South Africa? A new perspective. Environ Resource Econ 75(3):529–552. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10640-019-00398-9
Ahmad M, Zheng J (2021) Do innovation in environmental-related technologies cyclically and asymmetrically affect environmental sustainability in BRICS nations? Technol Soc 67:101746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2021.101746
Ahmad M, Hangyi H, Rahman ZU, Khan ZU, Khan S, Khan Z (2018) Carbon emissions, energy use, gross domestic product. Ekonomia I Środowisko 65(2):32–44
Ahmad M, Ur Rahman Z, Hong L, Khan S, Khan Z, Naeem Khan M (2018) Impact of environmental quality variables and socio-economic factors on human health: empirical evidence from China. Pollution 4(4):571–579. https://doi.org/10.22059/POLL.2018.252214.391
Ahmad M, Khan Z, Rahman ZU, Khan S (2019a) Does financial development asymmetrically affect CO 2 emissions in China? An application of the nonlinear autoregressive distributed lag ( NARDL ) model. Carbon Management 9(6):631–644. https://doi.org/10.1080/17583004.2018.1529998
Ahmad Manzoor, Khan Z, Rahman ZU, Khattak SI, Khan ZU (2019) Can innovation shocks determine CO2 emissions (CO2e) in the OECD economies? A new perspective. Econ Innov New Technol 30(1):89–107. https://doi.org/10.1080/10438599.2019.1684643
Ahmad M, Khattak SI, Khan A, Rahman ZU (2020) Innovation, foreign direct investment (FDI), and the energy–pollution–growth nexus in OECD region: a simultaneous equation modeling approach. Environ Ecol Stat 27(2):203–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10651-020-00442-8
Ahmad F, Draz MU, Chandio AA, Su L, Ahmad M, Irfan M (2021) Investigating the myth of smokeless industry: environmental sustainability in the ASEAN countries and the role of service sector and renewable energy. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14641-8
Alola AA, Bekun FV, Sarkodie SA (2019) Dynamic impact of trade policy, economic growth, fertility rate, renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on ecological footprint in Europe. Sci Total Environ 685:702–709
Apergis N (2016) Environmental Kuznets curves: new evidence on both panel and country-level CO2 emissions. Energy Economics 54:263–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2015.12.007
Apergis N, Ozturk I (2015) Testing environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in Asian countries. Ecol Ind 52:16–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.11.026
Apergis N, Christou C, Gupta R (2017) Are there environmental Kuznets curves for US state-level CO2 emissions? Renew Sustain Energy Rev 69:551–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2016.11.219
Arvanitis S, Woerter M (2014) Firm characteristics and the cyclicality of R&D investments. Ind Corp Chang 23(5):1141–1169. https://doi.org/10.1093/icc/dtt013
Asif M, Sharma RB, Adow AHE (2015) An empirical investigation of the relationship between economic growth, urbanization, energy consumption, and CO2 emission in GCC countries: a panel data analysis. Asian Soc Sci 11(21):270
Baek J (2015) Environmental Kuznets curve for CO2 emissions: the case of Arctic countries. Energy Economics 50:13–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENECO.2015.04.010
Bai J, Carrion-I-Silvestre JL (2009) Structural changes, common stochastic trends, and unit roots in panel data. Rev Econ Stud 76(2):471–501. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-937X.2008.00530.x
Bakirtas I, Cetin MA (2017) Revisiting the environmental Kuznets curve and pollution haven hypotheses: MIKTA sample. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(22):18273–18283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9462-y
Banerjee A, Carrion-i-Silvestre JL (2017) Testing for panel cointegration using common correlated effects estimators. J Time Ser Anal 38(4):610–636. https://doi.org/10.1111/jtsa.12234
Behera SR, Dash DP (2017) The effect of urbanization, energy consumption, and foreign direct investment on the carbon dioxide emission in the SSEA (South and Southeast Asian) region. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 70:96–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2016.11.201
Bloom N (2014) Fluctuations in uncertainty. Journal of Economic Perspectives 28(2):153–176. https://doi.org/10.1257/jep.28.2.153
Bölük G, Mert M (2015) The renewable energy, growth and environmental Kuznets curve in Turkey: An ARDL approach. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 52:587–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2015.07.138
Chen Y, Wang Z, Zhong Z (2019) CO2 emissions, economic growth, renewable and non-renewable energy production and foreign trade in China. Renewable Energy 131:208–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RENENE.2018.07.047
Chengde Y, Khattak SI, Ahmad M (2021) Do international collaborations in environmental-related technology development in the U.S. pay off in combating carbon dioxide emissions? Role of domestic environmental innovation renewable energy consumption and trade openness. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17146-6
Chishti MZ, Ahmad M, Rehman A, Khan MK (2021) Mitigations pathways towards sustainable development: Assessing the influence of fiscal and monetary policies on carbon emissions in BRICS economies. J Clean Prod 292:126035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126035
Choi I (2001) Unit root tests for panel data. J Int Money Financ 20(2):249–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0261-5606(00)00048-6
Choi I (2006) Combination unit root tests for cross-sectionally correlated panels. In: Corbae D, Durlauf SN, Hansen BEE (eds) Econometric Theory and Practice: Frontiers of Analysis and Applied Research. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 311–333. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781139164863.014
Chudik A, Pesaran MH (2015) Common correlated effects estimation of heterogeneous dynamic panel data models with weakly exogenous regressors. Journal of Econometrics 188(2):393–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeconom.2015.03.007
Çoban S, Topcu M (2013) The nexus between financial development and energy consumption in the EU: A dynamic panel data analysis. Energy Economics 39:81–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2013.04.001
Danish, Baloch MA, Mahmood N, Zhang JW (2019) Effect of natural resources, renewable energy and economic development on CO2 emissions in BRICS countries. Sci Total Environ 678:632–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2019.05.028
Dechezleprêtre A, Sato M (2017) The impacts of environmental regulations on competitiveness. Rev Environ Econ Polic 11(2):183–206
Dinda S (2004) Environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: a survey. Ecol Econ 49(4):431–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2004.02.011
Dong K, Sun R, Hochman G, Zeng X, Li H (2017) Impact of natural gas consumption on CO2 emissions: Panel data evidence from China’s provinces. J Clean Prod 162:400–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.06.100
Eberhardt M, Teal F (2010) Productivity analysis in global manufacturing production
Fethi S, Rahuma A (2020) The impact of eco-innovation on CO2 emission reductions: Evidence from selected petroleum companies. Struct Chang Econ Dyn 53:108–115
Fodha M, Zaghdoud O (2010) Economic growth and pollutant emissions in Tunisia : An empirical analysis of the environmental Kuznets curve. Energy Policy 38(2):1150–1156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2009.11.002
Fragkos P, Paroussos L (2018) Employment creation in EU related to renewables expansion. Appl Energy 230:935–945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.09.032
Gielen D, Boshell F, Saygin D, Bazilian MD, Wagner N, Gorini R (2019) The role of renewable energy in the global energy transformation. Energ Strat Rev 24:38–50
Goel RK, Ram R (1994) Research and development expenditures and economic growth: a cross-country study. Econ Dev Cult Change 42(2):403–411. https://doi.org/10.1086/452087
Gorus MS, Aslan M (2019) Impacts of economic indicators on environmental degradation: Evidence from MENA countries. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 103:259–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2018.12.042
Grossman G, Krueger A (1991) Environmental Impacts of a North American Free Trade Agreement. https://doi.org/10.3386/w3914
Guzel AE, Okumus İ (2020) Revisiting the pollution haven hypothesis in ASEAN-5 countries: new insights from panel data analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(15):18157–18167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08317-y
Hao Y, Wu Y, Wu H, Ren S (2020) How do FDI and technical innovation affect environmental quality? Evidence from China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:7835–7850
Harbaugh WT, Levinson A, Wilson DM (2002) Reexamining the empirical evidence for an environmental Kuznets curve. Rev Econ Stat 84(3):541–551. https://doi.org/10.1162/003465302320259538
Hashmi R, Alam K (2019) Dynamic relationship among environmental regulation, innovation, CO2 emissions, population, and economic growth in OECD countries: A panel investigation. J Clean Prod 231:1100–1109
Himmelberg CP, Petersen BC (1994) R&D and internal finance: A panel study of small firms in high-tech industries. Rev Econ Stat 76:38–51
Hussain I, Rehman A (2021) Exploring the dynamic interaction of CO2 emission on population growth, foreign investment, and renewable energy by employing ARDL bounds testing approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13502-8
Im KS, Pesaran M, Shin Y (2003) Testing for unit roots in heterogeneous panels. J Econometr 115(1):53–74
InCites Database. (2020). Clarivate analytics web of science. https://incites.clarivate.com/#/explore/0/region
Inglesi-Lotz R, Dogan E (2018) The role of renewable versus non-renewable energy to the level of CO2 emissions a panel analysis of sub- Saharan Africa’s Βig 10 electricity generators. Renewable Energy 123:36–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RENENE.2018.02.041
Itkonen JVA (2012) Problems estimating the carbon Kuznets curve. Energy 39(1):274–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2012.01.018
Jaforullah M, King A (2017) The econometric consequences of an energy consumption variable in a model of CO2 emissions. Energy Economics 63:84–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENECO.2017.01.025
Jalil A (2014) Energy–growth conundrum in energy exporting and importing countries: Evidence from heterogeneous panel methods robust to cross-sectional dependence. Energy Economics 44:314–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2014.04.015
Jebli MB, Youssef SB, Ozturk I (2016) Testing environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: The role of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption and trade in OECD countries. Ecol Ind 60:824–831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.08.031
Jiang Q, Khattak SI, Ahmad M, Lin P (2021) Mitigation pathways to sustainable production and consumption: examining the impact of commercial policy on carbon dioxide emissions in Australia. Sustain Prod Consump 25:390–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2020.11.016
Kaika D, Zervas E (2013) The environmental Kuznets curve ( EKC ) theory. Part B : Critical issues. Energy Policy 62:1403–1411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2013.07.130
Kao C, Chiang M-H, Chen B (1999) International R&D spillovers: an application of estimation and inference in panel cointegration. Oxford Bull Econ Stat 61(S1):691–709. https://doi.org/10.1111/1468-0084.0610s1691
Khan MA, Ozturk I (2020) Examining foreign direct investment and environmental pollution linkage in Asia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(7):7244–7255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07387-x
Khan MK, Teng J-Z, Khan MI (2019) Effect of energy consumption and economic growth on carbon dioxide emissions in Pakistan with dynamic ARDL simulations approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(23):23480–23490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05640-x
Khan Z, Ali M, Jinyu L, Shahbaz M, Siqun Y (2020a) Consumption-based carbon emissions and trade nexus: Evidence from nine oil exporting countries. Energy Economics 89:104806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2020.104806
Khan ZU, Ahmad M, Khan A (2020b) On the remittances-environment led hypothesis: empirical evidence from BRICS economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(14):16460–16471. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07999-8
Khan MK, Babar SF, Oryani B, Dagar V, Rehman A, Zakari A, Khan MO (2021) Role of financial development, environmental-related technologies, research and development, energy intensity, natural resource depletion, and temperature in sustainable environment in Canada. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15421-0
Khattak SI, Ahmad M, Khan ZU, Khan A (2020) Exploring the impact of innovation, renewable energy consumption, and income on CO2 emissions: new evidence from the BRICS economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07876-4
Khattak SI, Ahmad M, Haq Z, Shaofu G, Hang J (2022) On the goals of sustainable production and the conditions of environmental sustainability: Does cyclical innovation in green and sustainable technologies determine carbon dioxide emissions in G-7 economies. Sustain Prod Consum 29:406–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2021.10.022
Koçak E, Aykut Ş (2018) The impact of foreign direct investment on CO 2 emissions in Turkey: new evidence from cointegration and bootstrap causality analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:790–804
Koçak E, Ulucak ZŞ (2019) The effect of energy R&D expenditures on CO2 emission reduction: estimation of the STIRPAT model for OECD countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(14):14328–14338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04712-2
Kotabe M (1992) The impact of foreign patents on national economy: a case of the United States, Japan, Germany, and Britain. Appl Econ 24(12):1335–1343. https://doi.org/10.1080/00036849200000094
Kouretas GP, and Papadopoulos AP (2014) Macroeconomic analysis and international finance. Emerald Group Publishing Limited. https://books.google.com/books?id=CXUGAwAAQBAJ
Kraft J, Kraft A (1978) On the relationship between energy and GNP. J Energy Dev 1:401–403
Kuznets S (1955) Economic growth and income inequality. Am Econ Rev 45(1):1–28
Lee K-H, Min B (2015) Green R&D for eco-innovation and its impact on carbon emissions and firm performance. J Clean Prod 108:534–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2015.05.114
Levin A, Lin C-F, James Chu C-S (2002) Unit root tests in panel data: asymptotic and finite-sample properties. J Econometr 108(1):1–24
Li H, Khattak SI, Ahmad M (2021) Measuring the impact of higher education on environmental pollution: new evidence from thirty provinces in China. Environ Ecol Stat 28(1):187–217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10651-020-00480-2
Liddle B (2011) Consumption-driven environmental impact and age structure change in OECD countries: A cointegration-STIRPAT analysis. Demogr Res 24:749–770
Liddle B (2018) Consumption-based accounting and the trade-carbon emissions nexus. Energy Econ 69:71–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2017.11.004
Lluís Carrion-i-Silvestre J, Del Barrio-Castro T, López-Bazo E (2005) Breaking the panels: an application to the GDP per capita. Economet J 8(2):159–175. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1368-423X.2005.00158.x
Lv Z, Xu T (2019) Trade openness, urbanization and CO2 emissions: dynamic panel data analysis of middle-income countries. J Int Trade Econ Dev 28(3):317–330. https://doi.org/10.1080/09638199.2018.1534878
Maddala GS, Wu S (1999) A comparative study of unit root tests with panel data and a new simple test. Oxford Bull Econ Stat 61(s1):631–652. https://doi.org/10.1111/1468-0084.0610s1631
Mccoskey S, Kao C (1998) A residual-based test of the null of cointegration in panel data COINTEGRATION IN PANEL DATA. Economet Rev 17:57–84. https://doi.org/10.1080/07474939808800403
Mert M, Bölük G (2016) Do foreign direct investment and renewable energy consumption affect the CO2 emissions? New evidence from a panel ARDL approach to Kyoto Annex countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(21):21669–21681. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7413-7
Mert M, Caglar AE (2020) Testing pollution haven and pollution halo hypotheses for Turkey: a new perspective. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(26):32933–32943. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09469-7
Michieka NM, Fletcher J, Burnett W (2013) An empirical analysis of the role of China’s exports on CO2 emissions. Appl Energy 104:258–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APENERGY.2012.10.044
Moutinho V, Madaleno M, Bento JP (2020) Cointegration and causality: considering Iberian economic activity sectors to test the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis. Environ Ecol Stat 27(2):363–413. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10651-020-00449-1
Mrabet Z, AlSamara M, Hezam Jarallah S (2017) The impact of economic development on environmental degradation in Qatar. Environ Ecol Stat 24(1):7–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10651-016-0359-6
Muhammad B, Khan MK (2021) Foreign direct investment inflow, economic growth, energy consumption, globalization, and carbon dioxide emission around the world. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14857-8
Murshed M, Ahmed Z, Alam MS, Mahmood H, Rehman A, Dagar V (2021) Reinvigorating the role of clean energy transition for achieving a low-carbon economy: evidence from Bangladesh. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15352-w
Nurgazina Z, Ullah A, Ali U, Koondhar MA, Lu Q (2021) The impact of economic growth, energy consumption, trade openness, and financial development on carbon emissions: empirical evidence from Malaysia. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14930-2
OECD (2018) Growth: rationale for an innovation strategy. 2007. Availabe from https://www.oecd.org/Site/Innovationstrategy/Readingmaterial.htm
OECD (2020) Green growth indicators. OECD Statistics. https://stats.oecd.org/Index.Aspx?DataSetCode=GREEN_GROWTH#. https://stats.oecd.org/Index.aspx?DataSetCode=GREEN_GROWTH#
OECD (2021) Patents - environmental-related technologies. https://stats.oecd.org/Index.aspx?DataSetCode=GREEN_GROWTH#
Ouyang M (2011) Cyclical Persistence and the Cyclicality of R&D
Ouyan Y, Yi X, and Tang L (2019) Growth and transformation of emerging powers: research on BRICS economies. Springer Singapore. https://books.google.com/books?id=uhC9DwAAQBAJ
Özokcu S, Özdemir Ö (2017) Economic growth, energy, and environmental Kuznets curve. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 72:639–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.01.059
Pata UK (2018) Renewable energy consumption, urbanization, financial development, income and CO2 emissions in Turkey: testing EKC hypothesis with structural breaks. J Clean Prod 187:770–779. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2018.03.236
Pedroni P (2001) Purchasing Power Parity Tests in Cointegrated Panels. Rev Econ Stat 83(4):727–731
Pedroni P (2004) Panel cointegration: asymptotic and finite sample properties of pooled time series tests with an application to the PPP hypothesis. Economet Theor 20(03):597–625. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0266466604203073
Pedroni P (2000) Fully modified OLS for heterogeneous cointegrated panels. Department of Economics Working Papers
Pesaran MH (2007) A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross-section dependence. J Appl Economet 22(2):265–312. https://doi.org/10.1002/jae.951
Pesaran MH (2015) Testing weak cross-sectional dependence in large panels testing weak cross-sectional dependence in large panels. Economet Rev 34:1089–1117. https://doi.org/10.1080/07474938.2014.956623
Pesaran MH, Yamagata T (2008) Testing slope homogeneity in large panels. J Econometr 142(1):50–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JECONOM.2007.05.010
Qingquan J, Khattak SI, Ahmad M, Ping L (2020) A new approach to environmental sustainability: Assessing the impact of monetary policy on CO 2 emissions in Asian economies. Sustain Dev. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2087
Rafique MZ, Li Y, Larik AR, Monaheng MP (2020) The effects of FDI, technological innovation, and financial development on CO2 emissions: evidence from the BRICS countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(19):23899–23913
Rahman ZU, Ahmad M (2019) Modeling the relationship between gross capital formation and CO2 (a)symmetrically in the case of Pakistan: an empirical analysis through NARDL approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(8):8111–8124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04254-7
Rahman ZU, Cai H, Khattak SI, Hasan MM (2019) Energy production-income-carbon emissions nexus in the perspective of N.A.F.T.A. and B.R.I.C. nations: a dynamic panel data approach. Econ Res Ekon Istraživanja 32(1):3378–3391. https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677X.2019.1660201
Regmi K, Rehman A (2021) Do carbon emissions impact Nepal’s population growth, energy utilization, and economic progress? Evidence from long- and short-run analyses. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(39):55465–55475. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14546-6
Rehman A, Ma H, Ahmad M, Ozturk I, Chishti MZ (2021a) How do climatic change, cereal crops and livestock production interact with carbon emissions? Updated evidence from China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(24):30702–30713. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12948-0
Rehman A, Ma H, Ahmad M, Ozturk I, Işık C (2021b) An asymmetrical analysis to explore the dynamic impacts of CO2 emission to renewable energy, expenditures, foreign direct investment, and trade in Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(38):53520–53532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14537-7
Rehman A, Ma H, Ozturk I, Ahmad MI (2021c) Examining the carbon emissions and climate impacts on main agricultural crops production and land use: updated evidence from Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15481-2
Rehman A, Ulucak R, Murshed M, Ma H, Işık C (2021d) Carbonization and atmospheric pollution in China: the asymmetric impacts of forests, livestock production, and economic progress on CO2 emissions. J Environ Manage 294:113059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113059
Salahuddin M, Alam K, Ozturk I, Sohag K (2018) The effects of electricity consumption, economic growth, financial development and foreign direct investment on CO2emissions in Kuwait. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 81(June):2002–2010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.06.009
Salim R, Yao Y, Chen GS (2017) Does human capital matter for energy consumption in China? Energy Economics 67:49–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2017.05.016
Sarkodie SA, Strezov V (2019) Effect of foreign direct investments, economic development and energy consumption on greenhouse gas emissions in developing countries. Sci Total Environ 646:862–871. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2018.07.365
Schorderet Y, Schorderet, and Yann. (2003). Asymmetric cointegration. https://econpapers.repec.org/paper/gengeneem/2003.01.htm
Schwab WTWJSK, Woo WT, Sachs J, and Schwab K (2000) The Asian financial crisis: lessons for a resilient Asia. MIT Press. https://books.google.com/books?id=1xXqWQ6u2S8C
Sebri M, Ben-Salha O (2014) On the causal dynamics between economic growth, renewable energy consumption, CO2 emissions and trade openness: Fresh evidence from BRICS countries. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 39:14–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2014.07.033
Shin Y, Yu B, Greenwood-Nimmo M (2014) Modelling asymmetric cointegration and dynamic multipliers in a nonlinear ARDL framework. Festschrift in Honor of Peter Schmidt. Springer, New York, pp 281–314. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4899-8008-3_9
Sinha A, Shahbaz M (2018) Estimation of environmental Kuznets curve for CO2 emission: role of renewable energy generation in India. Renew Energy 119:703–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.12.058
Stiglitz J (1993) Endogenous Growth and Cycles. https://doi.org/10.3386/w4286
Su Y, Jiang Q, Khattak SI, Ahmad M, Li H (2021) Do higher education research and development expenditures affect environmental sustainability? New evidence from Chinese provinces. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14685-w
Sung B, Song W-Y, Park S-D (2018) How foreign direct investment affects CO2 emission levels in the Chinese manufacturing industry: Evidence from panel data. Econ Syst 42(2):320–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOSYS.2017.06.002
Swamy PA (1970) Efficient inference in a random coefficient regression model. Econometr: J Econometr Soc 38(2):311–323
Tang CF, Tan BW, Ozturk I (2016) Energy consumption and economic growth in Vietnam. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 54:1506–1514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.10.083
The World Bank. (2017). World Development Report 2018: learning to realize education’s promise. World Bank Publications. https://books.google.com.pk/books?id=uWM9DwAAQBAJ
Töbelmann D, Wendler T (2020) The impact of environmental innovation on carbon dioxide emissions. J Clean Prod 244:118787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118787
Uddin MMM (2021) Revisiting the impacts of economic growth on environmental degradation: new evidence from 115 countries. Environ Ecol Stat 28(1):153–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10651-020-00479-9
Ur Rahman Z, Chongbo W, Ahmad M (2019) An (a)symmetric analysis of the pollution haven hypothesis in the context of Pakistan: a non-linear approach. Carbon Management 10(3):227–239. https://doi.org/10.1080/17583004.2019.1577179
Usman M, Hammar N (2021) Dynamic relationship between technological innovations, financial development, renewable energy, and ecological footprint: fresh insights based on the STIRPAT model for Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(12):15519–15536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11640-z
Usman M, Khalid K, Mehdi MA (2021a) What determines environmental deficit in Asia? Embossing the role of renewable and non-renewable energy utilization. Renewable Energy 168:1165–1176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.01.012
Usman M, Yaseen MR, Kousar R, Makhdum MSA (2021b) Modeling financial development, tourism, energy consumption, and environmental quality: Is there any discrepancy between developing and developed countries? Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14837-y
Weimin Z, Chishti MZ, Rehman A, Ahmad M (2021) A pathway toward future sustainability: assessing the influence of innovation shocks on CO2 emissions in developing economies. Environ Dev Sustain. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01634-3
Wen L, Shao H (2019) Analysis of influencing factors of the carbon dioxide emissions in China’s commercial department based on the STIRPAT model and ridge regression. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(26):27138–27147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05929-x
Westerlund J (2005) New simple tests for panel cointegration. Economet Rev 24(3):297–316. https://doi.org/10.1080/07474930500243019
Westerlund J (2007) Testing for error correction in panel data. Oxford Bull Econ Stat 69(6):709–748. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-0084.2007.00477.x
Westerlund J, Edgerton DL (2008) A simple test for cointegration in dependent panels with structural breaks*. Oxford Bull Econ Stat 70(5):665–704. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-0084.2008.00513.x
World Bank (2020) World Development Indicators (WDI) | Data Catalog. In: World Bank. https://datacatalog.worldbank.org/dataset/worlddevelopment-indicators. Accessed 25 Feb 2020.
Xiaosan Z, Qingquan J, Shoukat Iqbal K, Manzoor A, Zia Ur R (2021) Achieving sustainability and energy efficiency goals: assessing the impact of hydroelectric and renewable electricity generation on carbon dioxide emission in China. Energy Policy 155:112332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2021.112332
Xin D, Ahmad M, Lei H, Khattak SI (2021) Do innovation in environmental-related technologies asymmetrically affect carbon dioxide emissions in the United States? Technol Soc 67:101761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2021.101761
Yang Z, Zhao Y (2014) Energy consumption, carbon emissions, and economic growth in India: evidence from directed acyclic graphs. Econ Model 38:533–540
Yang B, Jahanger A, Usman M, Khan MA (2021) The dynamic linkage between globalization, financial development, energy utilization, and environmental sustainability in GCC countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(13):16568–16588
Yao Y, Ivanovski K, Inekwe J, Smyth R (2019) Human capital and energy consumption: evidence from OECD countries. Energy Economics 84:104534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2019.104534
Yilanci V, Bozoklu S, Gorus MS (2020) Are BRICS countries pollution havens? Evidence from a bootstrap ARDL bounds testing approach with a Fourier function. Sustainable Cities and Society 55:102035
Yu Y, Du Y (2019) Impact of technological innovation on CO2 emissions and emissions trend prediction on ‘New Normal’ economy in China. Atmos Pollut Res 10(1):152–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APR.2018.07.005
Zheng J, Sheng P, Zheng J, Sheng P (2017) The impact of foreign direct investment (FDI) on the environment: market perspectives and evidence from China. Economies 5(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies5010008
Zheng J, Song J, Zhang Y, Zheng Y, and Jiang Q (2018) The evaluation of conversion of new and old driving force of China’s economic growth. China Industrial Economics, 6. http://www.ciejournal.org/Magazine/Show?id=54276
Zhou WY, Yang WL, Wan WX, Zhang J, Zhou W, Yang HS, Yang H, Xiao H, Deng SH, Shen F, Wang YJ (2018) The influences of industrial gross domestic product, urbanization rate, environmental investment, and coal consumption on industrial air pollutant emission in China. Environ Ecol Stat 25(4):429–442. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10651-018-0412-8
Zoundi Z (2017) CO2 emissions, renewable energy and the environmental Kuznets curve, a panel cointegration approach. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 72:1067–1075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.10.018
Funding
This work is supported by the Fujian Province Social Science Plan Project “Research on the Sustainable Development of the BRICS Cooperation Mechanism under the Context of Low-Carbon Economy” (Grant number: FJ2021B019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SIK: conceptualization; data curation; formal analysis, investigation, methodology. MA: writing—original draft; writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication.
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Ilhan Ozturk.
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Responsible Editor: Ilhan Ozturk
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khattak, S., Ahmad, M. The cyclical impact of green and sustainable technology research on carbon dioxide emissions in BRICS economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 22687–22707 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17368-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17368-8