Abstract
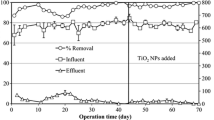
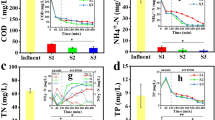
The imminent arrival of nanoparticles (NPs) to the wastewater treatment plants (WWTP) brings concern about their effects, which can be related to the wastewater composition. In this work, the effects of titanium dioxide (TiO2) NPs in the removal of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus by activated sludge bioreactors during the treatment of synthetic, raw, and filtered wastewaters were evaluated. Floc size, compaction of sludge, and morphological interactions between sludge and NPs were also determined. The main effect of TiO2 NPs was the inhibition of up to 22% in the removal of ammonia nitrogen for all types of wastewaters. This effect is strong dependent on combined factors of TiO2 NPs concentration and content of organic matter and ammonia in wastewater. The removal of dissolved organic carbon was affected by TiO2 NPs in lower level (up to 6%) than nitrogen removal for all types of wastewaters. Conversely to adverse effects, the removals of orthophosphate in the presence of TiO2 NPs were improved by 34%, 16%, and 55% for synthetic, raw, and filtered wastewater, respectively. Compaction of the sludge was also enhanced as the concentrations of NPs increased without alterations in the floc size for all types of wastewaters. Based on TEM and STEM imaging, the main interaction between TiO2 NPs and the activated sludge flocs was the adsorption of NPs on cell membrane. This means that NPs can be attached to cell membrane during aerobic wastewater treatment, and potentially disrupt this membrane. The effects of TiO2 NPs on macronutrient removal clearly depended on wastewater characteristics; hence, the use of realistic media is highly encouraged for ecotoxicological experiments involving NPs.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Change history
08 November 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17260-5
References
Adam V, Caballero-Guzman A, Nowack B (2018) Considering the forms of released engineered nanomaterials in probabilistic material flow analysis. Environ Pollut 243:17–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.07.108
Ahmed F, Rodrigues DF (2013) Investigation of acute effects of graphene oxide on wastewater microbial community: a case study. J Hazard Mater 256–257:33–39
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. Stand Methods 541. ISBN 9780875532356
Borcard D, Gillet F, Legendre P (2011) Numerical ecology with R. Springer New York, New York
Brar SK, Verma M, Tyagi RD, Surampalli RY (2010) Engineered nanoparticles in wastewater and wastewater sludge – evidence and impacts. Waste Manag 30:504–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2009.10.012
Cervantes-Avilés P, Keller AA (2021) Incidence of metal-based nanoparticles in the conventional wastewater treatment process. Water Res 189:116603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116603
Cervantes-Avilés P, Brito EMS, Duran R, Martínez AB, Cuevas-Rodríguez G (2016) Effect of ZnO nanoparticles in the oxygen uptake during aerobic wastewater treatment. J Nanopart Res 18:173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-016-3481-3
Cervantes-Avilés P, Camarillo Piñas N, Ida J, Cuevas-Rodríguez G (2017) Influence of wastewater type on the impact generated by TiO2nanoparticles on the oxygen uptake rate in activated sludge process. J Environ Manag 190:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.12.054
Cervantes-Avilés P, Ida J, Toda T, Cuevas-rodríguez G (2018) Effects and fate of TiO 2 nanoparticles in the anaerobic treatment of wastewater and waste sludge. J Environ Manag 222:227–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.05.074
Dale AL, Lowry GV, Casman EA (2015) Stream dynamics and chemical transformations control the environmental fate of silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles in a watershed-scale model. Environ Sci Technol 49:7285–7293. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b01205
García A, Delgado L, Torà JA, Casals E, González E, Puntes V, Font X, Carrera J, Sánchez A (2012) Effect of cerium dioxide, titanium dioxide, silver, and gold nanoparticles on the activity of microbial communities intended in wastewater treatment. J Hazard Mater 199–200:64–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.10.057
Gartiser S, Flach F, Nickel C, Stintz M, Damme S, Schaeffer A, Erdinger L, Kuhlbusch TAJ (2014) Behavior of nanoscale titanium dioxide in laboratory wastewater treatment plants according to OECD 303 A. Chemosphere 104:197–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.11.015
Hotze EM, Phenrat T, Lowry GV (2010) Nanoparticle aggregation: challenges to understanding transport and reactivity in the environment. J Environ Qual 39:1909–1924. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2009.0462
Hou J, Miao L, Wang C, Wang P, Ao Y, Lv B (2015) Effect of CuO nanoparticles on the production and composition of extracellular polymeric substances and physicochemical stability of activated sludge flocs. Bioresour Technol 176:65–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.11.020
Huang Y, Keller AA, Cervantes-Avilés P, Nelson J (2020) Fast multielement quantification of nanoparticles in wastewater and sludge using single-particle ICP-MS. ACS ES&T Water 1:205–213. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsestwater.0c00083
Keller AA, Lazareva A (2013) Predicted releases of engineered nanomaterials: from global to regional to local. Environ Sci Technol Lett 1:65–70. https://doi.org/10.1021/ez400106t
Keller AA, Cherr G, Cardinale BJ et al (2010) Stability and aggregation of metal oxide nanoparticles in natural aqueous matrices. J Environ Sci Technol 44:1962–1967. https://doi.org/10.1021/es902987d
Kiser MA, Westerhoff P, Benn T, Wang Y, Pérez-Rivera J, Hristovski K (2009) Titanium nanomaterial removal and release from wastewater treatment plants. Environ Sci Technol 43:6757–6763. https://doi.org/10.1021/es901102n
Kunhikrishnan A, Shon HK, Bolan NS, el Saliby I, Vigneswaran S (2015) Sources, distribution, environmental fate, and ecological effects of nanomaterials in wastewater streams. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 45:277–318. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2013.852407
Li Z, Wang X, Ma B, Wang S, Zheng D, She Z, Guo L, Zhao Y, Xu Q, Jin C, Li S, Gao M (2017) Long-term impacts of titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) on performance and microbial community of activated sludge. Bioresour Technol 238:361–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.04.069
Li K, Qian J, Wang P, Wang C, Lu B, Tian X, Jin W, He X, Chen H, Zhang Y, Liu Y (2020) Differential responses of encoding-amoA nitrifiers and nir denitrifiers in activated sludge to anatase and rutile TiO2 nanoparticles: what is active functional guild in rate limiting step of nitrogen cycle? J Hazard Mater 384:121388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121388
Ma S, Lin D (2013) The biophysicochemical interactions at the interfaces between nanoparticles and aquatic organisms: adsorption and internalization. Environ Sci Process Impacts 15:145–160. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2em30637a
Ma Y, Metch JW, Vejerano EP, Miller IJ, Leon EC, Marr LC, Vikesland PJ, Pruden A (2015) Microbial community response of nitrifying sequencing batch reactors to silver, zero-valent iron, titanium dioxide and cerium dioxide nanomaterials. Water Res 68:87–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.09.008
Neale PA, Jämting AK, O’Malley E et al (2015) Behaviour of titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles in the presence of wastewater-derived organic matter and implications for algal toxicity. Environ Sci Nano 2:86–93. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4en00161c
Perreault F, Oukarroum A, Melegari SP, Matias WG, Popovic R (2012) Polymer coating of copper oxide nanoparticles increases nanoparticles uptake and toxicity in the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Chemosphere 87:1388–1394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.02.046
Polesel F, Farkas J, Kjos M, Almeida Carvalho P, Flores-Alsina X, Gernaey KV, Hansen SF, Plósz BG, Booth AM (2018) Occurrence, characterisation and fate of (nano)particulate Ti and Ag in two Norwegian wastewater treatment plants. Water Res 141:19–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.04.065
Qiu G, Au MJ, Ting YP (2016) Impacts of Nano-TiO2 on system performance and bacterial community and their removal during biological treatment of wastewater. Water Air Soil Pollut 227:386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3081-y
Rathnayake S, Unrine JM, Judy J, Miller AF, Rao W, Bertsch PM (2014) Multitechnique investigation of the ph dependence of phosphate induced transformations of ZnO nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 48:4757–4764. https://doi.org/10.1021/es404544w
Sani-Kast N, Scheringer M, Slomberg D, Labille J, Praetorius A, Ollivier P, Hungerbühler K (2015) Addressing the complexity of water chemistry in environmental fate modeling for engineered nanoparticles. Sci Total Environ 535:150–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.12.025
Sirelkhatim A, Mahmud S, Seeni A, Kaus NHM, Ann LC, Bakhori SKM, Hasan H, Mohamad D (2015) Review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: Antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nano-Micro Lett 7:219–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-015-0040-x
Supha C, Boonto Y, Jindakaraked M, Ananpattarachai J, Kajitvichyanukul P (2015) Long-term exposure of bacterial and protozoan communities to TiO<inf>2</inf> nanoparticles in an aerobic-sequencing batch reactor. Sci Technol Adv Mater 16:034609. https://doi.org/10.1088/1468-6996/16/3/034609
Taurozzi JS, Hackley VA, Wiesner MR (2012) Preparation of nanoparticle dispersions from powdered material using ultrasonic disruption. Spec Publ (NIST SP). https://doi.org/10.6028/NIST.SP.1200-2
Tuoriniemi J, Cornelis G, Hassellöv M (2012) Size discrimination and detection capabilities of single-particle ICPMS for environmental analysis of silver nanoparticles. Anal Chem 84:3965–3972. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac203005r
van Loosdrecht MC, Nielsen PH, Lopez-Vazquez, C. M, Brdjanovic D (2016) Experimental methods in wastewater treatment
Wang G, Feng H, Gao A, Hao Q, Jin W, Peng X, Li W, Wu G, Chu PK (2016) Extracellular electron transfer from aerobic bacteria to Au-loaded TiO2 semiconductor without light: a new bacteria-killing mechanism other than localized surface plasmon resonance or microbial fuel cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:24509–24516. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b10052
Weir A, Westerhoff P, Fabricius L, Hristovski K, von Goetz N (2012) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles in food and personal care products. Environ Sci Technol 46:2242–2250. https://doi.org/10.1021/es204168d
You G, Hou J, Wang P, Xu Y, Wang C, Miao L, Lv B, Yang Y, Luo H (2016) Effects of CeO2 nanoparticles on sludge aggregation and the role of extracellular polymeric substances – explanation based on extended DLVO. Environ Res 151:698–705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2016.08.023
Zhang F, Lee MH, Huang Y, Keller AA, Majumdar S, Cervantes-Avilés P, Tang X, Yin S (2019) Effective water disinfection using magnetic barium phosphate nanoflakes loaded with Ag nanoparticles. J Clean Prod 218:173–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.01.232
Zheng X, Chen Y, Wu R (2011) Long-term effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on nitrogen and phosphorus removal from wastewater and bacterial community shift in activated sludge. Environ Sci Technol 45:7284–7290. https://doi.org/10.1021/es2008598
Zhou X, Huang B, Zhou T, Liu YC, Shi HC (2015) Aggregation behavior of engineered nanoparticles and their impact on activated sludge in wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 119:568–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.07.037
Funding
This work was supported by the Research Direction and Support to Postgraduate of the University of Guanajuato. Pabel Cervantes-Avilés received funding from National Council of Science and Technology of Mexico and from Sciences Department of Tecnologico de Monterrey Campus Puebla.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
P. Cervantes-Avilés: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing of original draft; writing review and edition, funding acquisition; A.N. Saber: data curation, formal analysis, writing of original draft, writing review and edition; A. Mora Polanco: formal analysis, writing review and edition; conceptualization; J. Mahlknecht: formal analysis, writing review and edition; G. Cuevas-Rodríguez: data curation, resources, supervision, funding acquisition, project administration, writing review and edition.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: Figures 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8 do not match with its caption.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cervantes-Avilés, P., Saber, A.N., Mora, A. et al. Influence of wastewater type in the effects caused by titanium dioxide nanoparticles in the removal of macronutrients by activated sludge. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 8746–8757 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16221-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16221-2