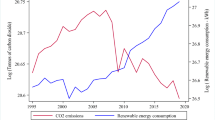
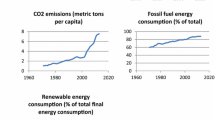
Abstract
A bulk of literature has examined the asymmetric impact of renewable energy consumption on CO2 emissions by using the advanced econometric approach. While the asymmetric role of renewable energy production in the CO2 equation is largely unknown, our present study quantifies the asymmetric relationship between renewable energy production, natural resources, economic progress, and CO2 emission for Pakistan by using the NARDL approach. It is found that positive change in renewable energy production has a positive effect on CO2 emissions, while a negative change in renewable energy production has a negative effect on CO2 emissions in the long run. Furthermore, a positive and negative change in natural resources contributes negatively to CO2 emissions in the long run. The results reveal that a positive change in economic progress significantly increases CO2 emissions in the long run. Based on findings, Pakistan’s government should encourage local and international investors to increase their investment in the production of renewable energy by reducing environmental degradation.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adedoyin FF, Ozturk I, Bekun FV, Agboola PO, Agboola MO (2021) Renewable and non-renewable energy policy simulations for abating emissions in a complex economy: evidence from the novel dynamic ARDL. Renew Energy 177:1408–1420
Ahmad M, Ahmed N, Jabeen M, Jabeen G, Qamar S, Chandio AA, Rehman A, Rauf A (2020) Empirics on heterogeneous links among urbanization, the intensity of electric power consumption, water-based emissions, and economic progress in regional China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(31):38937–38950
Ahmad M, Işık C, Jabeen G, Ali T, Ozturk I, Atchike DW (2021a) Heterogeneous links among urban concentration, non-renewable energy use intensity, economic development, and environmental emissions across regional development levels. Sci Total Environ 765:144527
Ahmad M, Jabeen G, Irfan M, Işık C, Rehman A (2021b) Do inward foreign direct investment and economic development improve local environmental quality: aggregation bias puzzle. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 1–21
Ahmad M, Khan Z, Anser MK, Jabeen G (2021c) Do rural-urban migration and industrial agglomeration mitigate the environmental degradation across China's regional development levels? Sustain Product Consump 27:679–697
Ahmad M, Zhao ZY, Rehman A, Shahzad M, Li H (2019) Revealing long-and short-run empirical interactions among foreign direct investment, renewable power generation, and CO2 emissions in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(22):22220–22245
Ahmadov AK, van der Borg C (2019) Do natural resources impede renewable energy production in the EU? A mixed-methods analysis. Energy Policy 126:361–369
Al-Mulali U, Solarin SA, Ozturk I (2016) Investigating the presence of the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis in Kenya: an autoregressive distributed lag (ARDL) approach. Nat Hazards 80(3):1729–1747
Alola AA, Bekun FV, Sarkodie SA (2019) Dynamic impact of trade policy, economic growth, fertility rate, renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on ecological footprint in Europe. Sci Total Environ 685:702–709
Alsagr N, van Hemmen S (2021a) The impact of financial development and geopolitical risk on renewable energy consumption: evidence from emerging markets. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(20):25906–25919
Alsagr N, van Hemmen S (2021b) The asymmetric influence of corruption on financial development: fresh evidence from BRICS economies. J Financ Crime ahead-of-print
Alvarado R, Deng Q, Tillaguango B, Méndez P, Bravo D, Chamba J, Alvarado-Lopez M, Ahmad M (2021) Do economic development and human capital decrease non-renewable energy consumption? Evidence for OECD countries. Energy 215:119147
Anser MK, Shabbir MS, Tabash MI, Shah SHA, Ahmad M, Peng MYP, Lopez LB (2021) Do renewable energy sources improve clean environmental-economic growth? Empirical investigation from South Asian economies. Energy Explor Exploit 01445987211002278
Apergis N, Ozturk I (2015) Testing environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in Asian countries. Ecol Indic 52:16–22
Arezki, R., & van der Ploeg, R. (2007). Can the natural resource curse be turned into a blessing? The role of trade policies and institutions.
Aslam B, Hu J, Majeed MT, Andlib Z, Ullah S (2021) Asymmetric macroeconomic determinants of CO2 emission in China and policy approaches. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–14
Auty RM (2000) How natural resources affect economic development. Dev Policy Rev 18(4):347–364
Aye GC, Edoja PE (2017) Effect of economic growth on CO2 emission in developing countries: evidence from a dynamic panel threshold model. Cogent Econ Financ 5(1):1379239
Balsalobre-Lorente D, Shahbaz M, Roubaud D, Farhani S (2018) How economic growth, renewable electricity and natural resources contribute to CO2 emissions? Energy Policy 113:356–367
Bento JPC, Moutinho V (2016) CO2 emissions, non-renewable and renewable electricity production, economic growth, and international trade in Italy. Renew Sust Energ Rev 55:142–155
Bhat, A. A., & Mishra, P. P. (2018). The Kyoto Protocol and CO2 emission: is India still hibernating?. Indian Growth and Development Review.
Bilgili F, Koçak E, Bulut Ü (2016) The dynamic impact of renewable energy consumption on CO2 emissions: a revisited Environmental Kuznets Curve approach. Renew Sust Energ Rev 54:838–845
Bird R, Hall AD, Momentè F, Reggiani F (2007) What corporate social responsibility activities are valued by the market?. J Bus Ethics 76(2):189–206
Borucke M, Moore D, Cranston G, Gracey K, Iha K, Larson J, Lazarus E, Morales JC, Wackernagel M, Galli A (2013) Accounting for demand and supply of the biosphere's regenerative capacity: The National Footprint Accounts’ underlying methodology and framework. Ecol Indic 24:518–533
Boyle G (2004) Renewable energy, p 456
Brock W, Dechert W, Scheinkman J (1996) A test for independence based on the correlation dimension. Econ Rev 15:197–235
Charfeddine L, Mrabet Z (2017) The impact of economic development and social-political factors on ecological footprint: a panel data analysis for 15 MENA countries. Renew Sust Energ Rev 76:138–154
Chen Y, He L, Li J, Zhang S (2018) Multi-criteria design of shale-gas-water supply chains and production systems towards optimal life cycle economics and greenhouse gas emissions under uncertainty. Comput Chem Eng 109:216–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2017.11.014
Chishti MZ, Ullah S, Ozturk I, Usman A (2020) Examining the asymmetric effects of globalization and tourism on pollution emissions in South Asia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(22):27721–27737
Danish, Wang Z, Wang B (2018) Energy production, economic growth and CO2 emission: evidence from Pakistan. Nat Hazards 90(1):27–50
Deng R, Li M, Linghu S (2021a) Research on calculation method of steam absorption in steam injection thermal recovery technology. Fresenius Environ Bull 30(05):5362–5369
Deng R, Li M, Linghu S (2021b) Sensitivity analysis of steam injection parameters of steam injection thermal recovery technology. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 30(05):5385–5394
Dogan E, Ozturk I (2017) The influence of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption and real income on CO2 emissions in the USA: evidence from structural break tests. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(11):10846–10854
Fatima N, Li Y, Ahmad M, Jabeen G, Li X (2019) Analyzing long-term empirical interactions between renewable energy generation, energy use, human capital, and economic performance in Pakistan. Energy Sustain Soc 9(1):1–14
Fatima N, Li Y, Ahmad M, Jabeen G, Li X (2021) Renewable and nonrenewable energy consumption, trade and CO2 emissions in high emitter countries: does the income level matter?. J Environ Plan Manag 64(7):1227–1251
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1995) Economic growth and the environment. The Quarterly Journal of Economics 110(2):353–377
Gylfason T (2001) Natural resources, education, and economic development. Eur Econ Rev 45(4-6):847–859
Hafeez M, Yuan C, Khelfaoui I, Sultan Musaad OA, Waqas Akbar M, Jie L (2019a) Evaluating the energy consumption inequalities in the one belt and one road region: implications for the environment. Energies 12(7):1358
Hafeez M, Yuan C, Yuan Q, Zhuo Z, Stromaier D (2019b) A global prospective of environmental degradations: economy and finance. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(25):25898–25915
Hafeez M, Yuan C, Shah WUH, Mahmood MT, Li X, Iqbal K (2020) Evaluating the relationship among agriculture, energy demand, finance and environmental degradation in one belt and one road economies. Carbon Manag 11(2):139–154
Hailu D, Kipgen C (2017) The extractives dependence index (EDI). Res Policy 51:251–264
Halkos GE, Tzeremes NG (2009) Exploring the existence of Kuznets curve in countries’ environmental efficiency using DEA window analysis. Ecol Econ 68(7):2168–2176
Hassan ST, Xia E, Khan NH, Shah SMA (2019) Economic growth, natural resources, and ecological footprints: evidence from Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(3):2929–2938
He L, Chen Y, Li J (2018) A three-level framework for balancing the tradeoffs among the energy, water, and air-emission implications within the life-cycle shale gas supply chains. Resour Conserv Recycl 133:206–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.02.015
Irfan M, Zhao ZY, Panjwani MK, Mangi FH, Li H, Jan A, Ahmad M, Rehman A (2020) Assessing the energy dynamics of Pakistan: prospects of biomass energy. Energy Rep 6:80–93
Jabeen G, Ahmad M, Zhang Q (2021) Perceived critical factors affecting consumers’ intention to purchase renewable generation technologies: rural-urban heterogeneity. Energy 218:119494
Jabeen G, Yan Q, Ahmad M, Fatima N, Jabeen M, Li H, Qamar S (2020) Household-based critical influence factors of biogas generation technology utilization: a case of Punjab province of Pakistan. Renew Energy 154:650–660
Kahia M, Jebli MB (2021) Industrial growth, clean energy generation, and pollution: evidence from top ten industrial countries. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 1–10
Kaltschmitt M, Streicher W, Wiese A (eds) (2007) Renewable energy: technology, economics and environment. Springer Science & Business Media
Kathuria V (2001) Pollution: prevention vs control: is EOP treatment the solution? Econ and Polit Wkly pp 2745-2748. https://geneva.usmission.gov/2014/03/28/eop-on-resolution-human-rights-and-the-environment/
Lederman D, Maloney WF (2007) Trade structure and growth. Natural resources: Neither curse nor destiny 15–39
Li J, Hu Z, Shi V, Wang Q (2021a) Manufacturer’s encroachment strategy with substitutable green products. Int J Prod Econ 235:108102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2021.108102
Li X, Li Z, Jia T, Yan P, Wang D et al (2021b) The sense of community revisited in Hankow, China: combining the impacts of perceptual factors and built environment attributes. Cities 111:103108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2021.103108
Li X, Yu Z, Salman A, Ali Q, Hafeez M, Aslam MS (2021c) The role of financial development indicators in sustainable development-environmental degradation nexus. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 1–12
Liu JL, Ma CQ, Ren YS, Zhao XW (2020) Do real output and renewable energy consumption affect CO2 emissions? Evidence for selected BRICS countries. Energies 13(4):960
Mahmood MT, Shahab S, Hafeez M (2020) Energy capacity, industrial production, and the environment: an empirical analysis from Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(5):4830–4839
Mehlum H, Moene K, Torvik R (2006) Institutions and the resource curse. Econ J 116(508):1–20
Menyah K, Wolde-Rufael Y (2010) Energy consumption, pollutant emissions and economic growth in South Africa. Energy Econ 32(6):1374–1382
Miao R, Ma J, Liu Y, Liu Y, Yang Z et al (2019) Variability of aboveground litter inputs alters soil carbon and nitrogen in a coniferous–broadleaf mixed forest of Central China. Forests 10(2):188. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10020188
Moutinho V, Costa C, Bento JPC (2015) The impact of energy efficiency and economic productivity on CO2 emission intensity in Portuguese tourism industries. Tourism Management Perspectives 16:217–227
Namahoro JP, Wu Q, Zhou N, Xue S (2021) Impact of energy intensity, renewable energy, and economic growth on CO2 emissions: evidence from Africa across regions and income levels. Renew Sust Energ Rev 147:111233
Nasir M, Rehman FU (2011) Environmental Kuznets curve for carbon emissions in Pakistan: an empirical investigation. Energy Policy 39(3):1857–1864
Omri A, Daly S, Rault C, Chaibi A (2015) Financial development, environmental quality, trade and economic growth: what causes what in MENA countries. Energy Econ 48:242–252
Ozcan B, Ozturk I (2019) Renewable energy consumption-economic growth nexus in emerging countries: a bootstrap panel causality test. Renew Sust Energ Rev 104:30–37
Ozturk I, Acaravci A (2010) CO2 emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in Turkey. Renew Sust Energ Rev 14(9):3220–3225
Ozturk I, Acaravci A (2013) The long-run and causal analysis of energy, growth, openness and financial development on carbon emissions in Turkey. Energy Econ 36:262–267
Peng X, Liu Z, Jiang D (2021) A review of multiphase energy conversion in wind power generation. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 147:111172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.111172
Pesaran MH, Shin Y, Smith RJ (2001) Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. J Appl Econ 16(3):289–326
Qi T, Zhang X, Karplus VJ (2014) The energy and CO2 emissions impact of renewable energy development in China. Energy Policy 68:60–69
Quan Q, Gao S, Shang Y, Wang B (2021) Assessment of the sustainability of Gymnocypris eckloni habitat under river damming in the source region of the Yellow River. Sci Total Environ 778:146312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146312
Robinson J (2006) Navigating social and institutional barriers to markets: how social entrepreneurs identify and evaluate opportunities. In: Social entrepreneurship. Palgrave Macmillan, London, pp 95–120
Sachs JD, Warner AM (2001) The curse of natural resources. Eur Econ Rev 45(4-6):827–838
Sachs JD, Warner A, Åslund A, Fischer S (1995) Economic reform and the process of global integration. Brook Pap Econ Act 1995(1):1–118
Sadorsky P (2009) Renewable energy consumption and income in emerging economies. Energy Policy 37(10):4021–4028
Sala-i-Martin X, Subramanian A (2013) Addressing the natural resource curse: an illustration from Nigeria. J Afr Econ 22(4):570–615
Salim R, Rafiq S, Shafiei S, Yao Y (2019) Does urbanization increase pollutant emission and energy intensity? Evidence from some Asian developing economies. Appl Econ 51(36):4008–4024
Sarkodie SA, Strezov V (2018a) Assessment of contribution of Australia's energy production to CO2 emissions and environmental degradation using statistical dynamic approach. Sci Total Environ 639:888–899
Sarkodie SA, Strezov V (2018b) Empirical study of the environmental Kuznets curve and environmental sustainability curve hypothesis for Australia, China, Ghana and USA. J Clean Prod 201:98–110
Shafiei S, Salim RA (2014) Non-renewable and renewable energy consumption and CO2 emissions in OECD countries: a comparative analysis. Energy Policy 66:547–556
Shafik N (1994) Economic development and environmental quality: an econometric analysis. Oxf Econ Pap 757–773
Shaheen A, Sheng J, Arshad S, Muhammad H, Salam S (2020) Forecasting the determinants of environmental degradation: a gray modeling approach. Energy Sourc A Recov Utiliz Environ Effects:1–21
Sharif A, Baris-Tuzemen O, Uzuner G, Ozturk I, Sinha A (2020) Revisiting the role of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on Turkey’s ecological footprint: Evidence from Quantile ARDL approach. Sustain Cities Soc 57:102138
Shin Y, Yu B, Greenwood-Nimmo M (2014) Modelling asymmetric cointegration and dynamic multipliers in a nonlinear ARDL framework. In: Festschrift in honor of Peter Schmidt. Springer, New York, pp 281–314
Sohail MT, Ullah S, Majeed MT, Usman A (2021) Pakistan management of green transportation and environmental pollution: a nonlinear ARDL analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:1–10
Solarin SA, Al-Mulali U (2018) Influence of foreign direct investment on indicators of environmental degradation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(25):24845–24859
Solarin SA, Bello MO (2018) Persistence of policy shocks to an environmental degradation index: the case of ecological footprint in 128 developed and developing countries. Ecol Indic 89:35–44
Thomakos DD, Alexopoulos TA (2016) Carbon intensity as a proxy for environmental performance and the informational content of the EPI. Energy Policy 94:179–190
Ullah S, Ozturk I, Majeed MT, Ahmad W (2021) Do technological innovations have symmetric or asymmetric effects on environmental quality? Evidence from Pakistan. J Clean Prod 316:128239
Ullah S, Ozturk I, Usman A, Majeed MT, Akhtar P (2020) On the asymmetric effects of premature deindustrialization on CO2 emissions: evidence from Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(12):13692–13702
Ulucak R, Apergis N (2018) Does convergence really matter for the environment? An application based on club convergence and on the ecological footprint concept for the EU countries. Environ Sci Pol 80:21–27
Usman A, Bahmani-Oskoee M, Anwar S, Ullah S (2021a) Is there j-curve effect in the trade between Pakistan and United Kingdom? Asymmetric evidence from industry level data. Sing Econ Rev:1–21
Usman A, Ozturk I, Ullah S, Hassan A (2021b) Does ICT have symmetric or asymmetric effects on CO2 emissions? Evidence from selected Asian economies. Technol Soc 67:101692
Yu B (2021) Urban spatial structure and total-factor energy efficiency in Chinese provinces. Ecol Indic 126:107662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107662
Zafar MW, Zaidi SAH, Sinha A, Gedikli A, Hou F (2019) The role of stock market and banking sector development, and renewable energy consumption in carbon emissions: Insights from G-7 and N-11 countries. Res Policy 62:427–436
Zhang Z, Liu S, Niu B (2020) Coordination mechanism of dual-channel closed-loop supply chains considering product quality and return. J Clean Prod 248:119273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119273
Zhao X, Gu B, Gao F, Chen S (2020) Matching model of energy supply and demand of the integrated energy system in coastal areas. J Coast Res 103(sp1):983. https://doi.org/10.2112/SI103-205.1
Zuo X, Dong M, Gao F, Tian S (2020) The modeling of the electric heating and cooling system of the integrated energy system in the coastal area. J Coast Res 103(sp1):1022. https://doi.org/10.2112/SI103-213.1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This idea was given by Shahid Iqbal. Shahid Iqbal, Ying Wang, Parvez Ahmed Shaikh, Adnan Maqbool analyzed the data and wrote the complete paper, while Khizar Hayat and Adnan Maqbool read and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
I am free to contact any of the people involved in the research to seek further clarification and information.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ilhan Ozturk
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iqbal, ., Wang, Y., Shaikh, P.A. et al. Exploring the asymmetric effects of renewable energy production, natural resources, and economic progress on CO2 emissions: fresh evidence from Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 7067–7078 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16138-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16138-w