Abstract
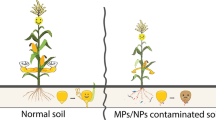
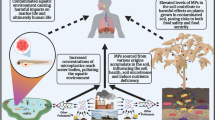
Pesticides and nanoparticles may coexist in soil; however, influences of nanoparticles on accumulation of pesticides in terrestrial organisms are still unclear. This study aims to investigate the influences and mechanisms of metal oxide nanoparticles (nano ZnO and nano CuO) on accumulation of pentachloronitrobenzene (PCNB) in earthworms and their combined toxicity. The earthworms were cultivated in the soil spiked with nanoparticles (10, 50, 250 mg/kg) and PCNB (100 μg/kg) for 21 days. The concentrations of PCNB in earthworms in binary exposure treatments (PCNB + ZnO and PCNB + CuO) reached 2.47 and 3.13 times of that in individual PCNB exposure treatment, indicating that nanoparticles facilitated the accumulation of PCNB in earthworms. The contents of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in earthworms in treatments PCNB + ZnO 250 and PCNB + CuO 250 reached 379 and 316 fluorescence intensity/mg Protein, respectively, which were significantly higher than that in control group (183 fluorescence intensity/mg protein), indicating that nanoparticles would cause oxidative stress to earthworms. Earthworm coelomocytes were extracted from healthy earthworms and cultivated in culture media in cytotoxicity tests. Changes of intracellular ROS contents and cell viability suggested that PCNB and nanoparticles caused serious oxidative damage to earthworm coelomocytes, thus leading to the damage of cell membrane and cell death. In in vivo tests, changes of biomarkers (ROS and malondialdehyde) demonstrated that these pollutants injured the earthworms. Increased accumulation of PCNB in binary exposure treatments was due to the damage of body cavity caused by nanoparticles. This study provides a novel hypothesis for nanoparticles facilitating organic pollutants entering terrestrial organisms and determines whether nanoparticles would bring about greater environmental risks of other pollutants.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abdel-Halim KY, Osman SR, Abdou GY (2020) In vivo evaluation of oxidative stress and biochemical alteration as biomarkers in glass clover snail, Monacha cartusiana exposed to zinc oxide nanoparticles. Environ Pollut 257:113120
Ahmadian K, Jalilian J, Pirzad A (2021) Nano-fertilizers improved drought tolerance in wheat under deficit irrigation. Agric Water Manag 244:106544
Cao F, Souders CL, Li P, Pang S, Liang X, Qiu L, Martyniuk CJ (2019) Developmental neurotoxicity of maneb: notochord defects, mitochondrial dysfunction and hypoactivity in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos and larvae. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 170:227–237
Cui JH, Liu TX, Li FB, Yi JC, Liu CP, Yu HY (2017) Silica nanoparticles alleviate cadmium toxicity in rice cells: mechanisms and size effects. Environ Pollut 228:363–369
Cui JH, Li YD, Jin Q, Li FB (2020) Silica nanoparticles inhibit arsenic uptake into rice suspension cells via improving pectin synthesis and the mechanical force of the cell wall. Environ Sci Nano 7:162–171
Curieses PS, García-Velasco N, Urionabarrenetxea E, Sáenz EM, Bilbao E, Di Marzio DW, Soto M (2017) Responses to silver nanoparticles and silver nitrate in a battery of biomarkers measured in coelomocytes and in target tissues of Eisenia fetida earthworms. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 141:57–63
Farzana S, Cheung SG, Zhou HC, Tam NFY (2019) Growth and antioxidative response of two mangrove plants to interaction between aquaculture effluent and BDE-99. Sci Total Environ 662:796–804
Feng L-J, Shi Y, Li X-Y, Sun X-D, Xiao F, Sun J-W, Wang Y, Liu X-Y, Wang S-G, Yuan X-Z (2020) Behavior of tetracycline and polystyrene nanoparticles in estuaries and their joint toxicity on marine microalgae Skeletonema costatum. Environ Pollut 263:114453
García-Gómez C, Babín M, García S, Almendros P, Pérez RA, Fernández MD (2019) Joint effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles and chlorpyrifos on the reproduction and cellular stress responses of the earthworm Eisenia andrei. Sci Total Environ 688:199–207
Gong X, Jiang Y, Zheng Y, Chen X, Li H, Hu F, Liu M, Scheu S (2018) Earthworms differentially modify the microbiome of arable soils varying in residue management. Soil Biol Biochem 121:120–129
Gottschalk F, Sun T, Nowack B (2013) Environmental concentrations of engineered nanomaterials: review of modeling and analytical studies. Environ Pollut 181:287–300
Guan G, Zhang L, Zhu J, Wu H, Li W, Sun Q (2021) Antibacterial properties and mechanism of biopolymer-based films functionalized by CuO/ZnO nanoparticles against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J Hazard Mater 402:123542
Guo Y, Chen L, Wu J, Hua J, Yang L, Wang Q, Zhang W, Lee J-S, Zhou B (2019) Parental co-exposure to bisphenol A and nano-TiO2 causes thyroid endocrine disruption and developmental neurotoxicity in zebrafish offspring. Sci Total Environ 650:557–565
Hou J, Liu H, Zhang S, Liu X, Hayat T, Alsaedi A, Wang X (2019) Mechanism of toxic effects of Nano-ZnO on cell cycle of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 229:206–213
Hu CW, Li M, Cui YB, Li DS, Chen J, Yang LY (2010) Toxicological effects of TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles in soil on earthworm Eisenia fetida. Soil Biol Biochem 42:586–591
Huang L, Wang W, Zhang S, Tang S, Zhao P, Ye Q (2017) Bioaccumulation and bound-residue formation of 14C-decabromodiphenyl ether in an earthworm-soil system. J Hazard Mater 321:591–599
Jing M, Han G, Wan J, Zhang S, Yang J, Zong W, Niu Q, Liu R (2020) Catalase and superoxide dismutase response and the underlying molecular mechanism for naphthalene. Sci Total Environ 736:139567
Jośko I, Dobrzyńska J, Dobrowolski R, Kusiak M, Terpiłowski K (2020) The effect of pH and ageing on the fate of CuO and ZnO nanoparticles in soils. Sci Total Environ 721:137771
Keller AA, Lazareva A (2014) Predicted releases of engineered nanomaterials: from global to regional to local. Environ Sci Technol Lett 1:65–70
Li M, Xu G, Yu R, Wang Y, Yu Y (2020) Uptake and accumulation of pentachloronitrobenzene in pak choi and the human health risk. Environ Geochem Health 42:109–120
Liu X, Rodeheaver DP, White JC, Wright AM, Walker LM, Zhang F, Shannon S (2018a) A comparison of in vitro cytotoxicity assays in medical device regulatory studies. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 97:24–32
Liu X, Tang J, Wang L, Giesy JP (2018b) Mechanisms of oxidative stress caused by CuO nanoparticles to membranes of the bacterium Streptomyces coelicolor M145. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 158:123–130
Liu Y, Nie Y, Wang J, Wang J, Wang X, Chen S, Zhao G, Wu L, Xu A (2018c) Mechanisms involved in the impact of engineered nanomaterials on the joint toxicity with environmental pollutants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 162:92–102
Ma HB, Williams PL, Diamond SA (2013) Ecotoxicity of manufactured ZnO nanoparticles - a review. Environ Pollut 172:76–85
Ma J, Cheng C, Du Z, Li B, Wang J, Wang J, Wang Z, Zhu L (2019) Toxicological effects of pyraclostrobin on the antioxidant defense system and DNA damage in earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Ecol Indic 101:111–116
Miao JJ, Chen XL, Xu T, Yin DQ, Hu XL, Sheng GD (2018) Bioaccumulation, distribution and elimination of lindane in Eisenia foetida: the aging effect. Chemosphere 190:350–357
Pikula KS, Zakharenko AM, Aruoja V, Golokhvast KS, Tsatsakis AM (2019) Oxidative stress and its biomarkers in microalgal ecotoxicology. Curr Opin Toxicol 13:8–15
Pu S, Yan C, Huang H, Liu S, Deng D (2019) Toxicity of nano-CuO particles to maize and microbial community largely depends on its bioavailable fractions. Environ Pollut 255:113248
Pullagurala VLR, Adisa IO, Rawat S, Kim B, Barrios AC, Medina-Velo IA, Hernandez-Viezcas JA, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2018) Finding the conditions for the beneficial use of ZnO nanoparticles towards plants-a review. Environ Pollut 241:1175–1181
Rajkovic S, Bornhöft NA, van der Weijden R, Nowack B, Adam V (2020) Dynamic probabilistic material flow analysis of engineered nanomaterials in European waste treatment systems. Waste Manag 113:118–131
Sinha AK, Romano N, Shrivastava J, Monico J, Bishop WM (2020) Oxidative stress, histopathological alterations and anti-oxidant capacity in different tissues of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) exposed to a newly developed sodium carbonate peroxyhydrate granular algaecide formulated with hydrogen peroxide. Aquat Toxicol 218:105348
Song P, Gao J, Li X, Zhang C, Zhu L, Wang J, Wang J (2019) Phthalate induced oxidative stress and DNA damage in earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Environ Int 129:10–17
Tatsi K, Shaw BJ, Hutchinson TH, Handy RD (2018) Copper accumulation and toxicity in earthworms exposed to CuO nanomaterials: effects of particle coating and soil ageing. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 166:462–473
Teng Y, Wang X, Zhu Y, Chen W, Christie P, Li Z, Luo Y (2017) Biodegradation of pentachloronitrobenzene by Cupriavidus sp. YNS-85 and its potential for remediation of contaminated soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:9538–9547
Wang Z, Zhang C, Huang F, Liu X, Wang Z, Yan B (2021) Breakthrough of ZrO2 nanoparticles into fetal brains depends on developmental stage of maternal placental barrier and fetal blood-brain-barrier. J Hazard Mater 402:123563
Young A, Oldford C, Mailloux RJ (2020) Lactate dehydrogenase supports lactate oxidation in mitochondria isolated from different mouse tissues. Redox Biol 28:101339
Yuan Y, Wu Y, Ge X, Nie D, Wang M, Zhou H, Chen M (2019) In vitro toxicity evaluation of heavy metals in urban air particulate matter on human lung epithelial cells. Sci Total Environ 678:301–308
Zhang C, Zhu LS, Wang J, Wang JH, Du ZK, Li B, Zhou TT, Cheng C, Wang ZB (2018) Evaluating subchronic toxicity of fluoxastrobin using earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Sci Total Environ 642:567–573
Zhang R, Zhang X, Gao S, Liu R (2019) Assessing the in vitro and in vivo toxicity of ultrafine carbon black to mouse liver. Sci Total Environ 655:1334–1341
Zhang N, Guo D, Zhu Y, Wang X, Zhu L, Liu F, Teng Y, Christie P, Li Z, Luo Y (2020) Microbial remediation of a pentachloronitrobenzene-contaminated soil under Panax notoginseng: a field experiment. Pedosphere 30:563–569
Zhou Y, Liu X, Wang J (2020) Ecotoxicological effects of microplastics and cadmium on the earthworm Eisenia foetida. J Hazard Mater 392:122273
Zhu J, Zou Z, Shen Y, Li J, Shi S, Han S, Zhan X (2019) Increased ZnO nanoparticle toxicity to wheat upon co-exposure to phenanthrene. Environ Pollut 247:108–117
Zou X, Xiao X, Zhou H, Chen F, Zeng J, Wang W, Feng G, Huang X (2018) Effects of soil acidification on the toxicity of organophosphorus pesticide on Eisenia fetida and its mechanism. J Hazard Mater 359:365–372
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the grants from Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA23070502), Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province (20200201043JC), National Natural Science Foundation of China (41977336, 31670527), and China Scholarship Council (CSC).
Funding
This study was funded by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province, National Natural Science Foundation of China, and China Scholarship Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ming Li: Investigation and writing—original draft preparation
Guanghui Xu: Validation
Na Guo: Formal analysis
Na Zheng: Resources
Weihua Dong: Resources
Xiao Li: Methodology
Yong Yu: Supervision, conceptualization, reviewing, and editing
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Chris Lowe
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOC 9322 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Xu, G., Guo, N. et al. Influences and mechanisms of nanoparticles on pentachloronitrobenzene accumulation by earthworms. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 51471–51479 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14368-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14368-6