Abstract
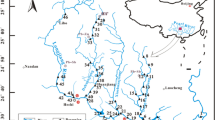
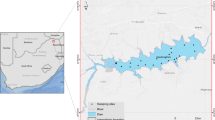
Nansi Lake is the largest lake along the eastern route of China’s South-to-North Water Diversion Project (SNWDP). It is divided into the upper lake and the lower lake by a dam. By using UV-Vis spectroscopy, synchronous fluorescence (SF) spectroscopy, excitation-emission matrix and parallel factor analysis (EEM-PARAFAC), spatial, and temporal differences in the properties of dissolved organic matter (DOM) were found in the 2 areas of Nansi Lake under different hydrological conditions. A total of 5 fluorescence components were obtained by EEM-PARAFAC, which included 3 humic-like components (C1–C3) and 2 protein-like components (C4 and C5). On the spatial scale, the fluorescence intensities (Fmax) of humic-like substances and the ratio of the fluorescence intensity of humic-like components to the total fluorescence intensity (%Fmax) and degree of humification (HIX) in the upper lake were higher than those in the lower lake. This indicated the strong contributions of terrestrial sources to the upper lake, while DOM properties in the lower lake were more endogenous than those in the upper lake. On the temporal scale, protein-like substances played a more important role in DOM properties in April (Fmax=0.72±0.03 in the upper lake and 1.84±0.13 in the lower lake) and July (Fmax=1.10±0.05 in the upper lake and 1.49±0.04 in the lower lake) than in October. This result might be related to the water transfer of the eastern route of the SNWDP and to the death of submerged plants. However, the contents of humic-like substances (ranging from 55.61±1.23% to 66.56±0.58% for the upper lake and 29.98±1.56% to 61.98±0.99% for the lower lake) and degree of humification (from 2.23±0.06 to 3.10±0.05 for the upper lake and 1.06±0.05 to 2.62±0.08 for the lower lake) in Nansi Lake showed an increasing trend from April to October. In addition, significant correlations and good linear relationships between humic-like components, a254, and DOC in the 3 months reflected the continuous contribution of humic-like substances to DOM properties in Nansi Lake. Rapid changes in the fluorescence signal were largely dependent on changes in water quality. The fluorescence signal could be a tool for the management of water quality in Nansi Lake.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
They are all publically available.
References
Almeida RM, Barros N, Cole JJ et al (2020) Emissions from amazonian dams. Nat Clim Chang 3(12):1005
Andrew AA, Vecchio RD, Subramaniam A et al (2013) Chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in the Equatorial Atlantic Ocean: optical properties and their relation to CDOM structure and source. Mar Chem 148:33–43
Bai L, Zhao Z, Wang C, Wang C, Liu X, Jiang H (2017) Multi-spectroscopic investigation on the complexation of tetracycline with dissolved organic matter derived from algae and macrophyte. Chemosphere 187:421–429
Bai L, Zhang Q, Ju Q, Wang C, Zhang H, Jiang H (2020) Priming effect of autochthonous organic matter on enhanced degradation of 17α-ethynylestradiol in water-sediment system of one eutrophic lake. Water Res 184:116153
Baker A (2002) Fluorescence excitation emission matrix characterization of river waters impacted by a tissue mill effluent. Environ Sci Technol 36(7):1377–1382
Carr N, Davis CE, Blackbird S, Daniels LR, Preece C, Woodward M, Mahaffey C (2019) Seasonal and spatial variability in the optical characteristics of DOM in a temperate shelf sea. Prog Oceanogr 177:101929
Cheimonopoulou MT, Bobori DC, Theocharopoulos I, Lazaridou M (2011) Assessing ecological water quality with macroinvertebrates and fish: a case study from a small Mediterranean river. Environ Manag 47(2):279–290
Chen M, Jaffe R (2014) Photo- and bio-reactivity patterns of dissolved organic matter from biomass and soil leachates and surface waters in a subtropical wetland. Water Res 61:181–190
Datry T, Pella H, Leigh C, Bonada N, Hugueny B (2016) A landscape approach to advance intermittent river ecology. Freshw Biol 61:1200–1213
de Zarruk KK, Scholer G, Dudal Y (2007) Fluorescence fingerprints and Cu2+-complexing ability of individual molecular size fractions in soil-and waste-borne DOM. Chemosphere 69:540–548
Deng HG, Zhang J, Chen SY et al (2016) Metal release/accumulation during the decomposition of Potamogeton crispus in a shallow macrophytic lake. Environ Sci 42:71–78
DeVilbiss SE, Zhou ZZ, Klump JV, Guo LD (2016) Spatiotemporal variations in the abundance and composition of bulk and chromophoric dissolved organic matter in seasonally hypoxia-influenced Green Bay, Lake Michigan, USA. Sci Total Environ 565:742–757
Feng T, Wang C, Hou J, Wang P, Liu Y, Dai Q, Yang Y, You G (2018) Effect of inter-basin water transfer on water quality in an urban lake: a combined water quality index algorithm and biophysical modelling approach. Ecol Indic 92:61–71
Granados V, Gutierrez-Cánovas C, Arias-Real R et al (2020) The interruption of longitudinal hydrological connectivity causes delayed responses in dissolved organic matter. Sci Total Environ 713:136619
Guo CB, Chen YS, Gozlan RE et al (2020a) Patterns of fish communities and water quality in impounded lakes of China’s south-to-north water diversion project. Sci Total Environ 713:136515
Guo CB, Chen YS, Xia WT et al (2020b) Eutrophication and heavy metal pollution patterns in the water suppling lakes of China’s south-to-north water diversion project. Sci Total Environ 711(1):134543
Huguet A, Vacher L, Relexans S, Saubusse S, Froidefond JM, Parlanti E (2009) Properties of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in the Gironde Estuary. Org Geochem 40(6):706–719
Hur J, Lee B-M (2011) Characterization of binding site heterogeneity for copper within dissolved organic matter fractions using two-dimensional correlation fluorescence spectroscopy. Chemosphere 83(11):1603–1611
Kramer GD, Herndl GJ (2004) Photo- and bioreactivity of chromophoric dissolved organic matter produced by marine bacterioplankton. Aquat Microb Ecol 36(3):239–246
Larned ST, Datry T, Arscott DB et al (2010) Emerging concepts in temporary river ecology. Freshw Biol 55:717–738
Liu D, Du Y, Yu S et al (2020) Human activities determine quantity and composition of dissolved organic matter in lakes along the Yangtze River. Water Res 168:115132
Lv J, Zhang Z, Li S, Liu Y, Sun Y, Dai B (2014) Assessing spatial distribution, sources, and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Nansi Lake, Eastern China. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 299(3):1671–1681
Maavara T, Chen Q et al (2020) River dam impacts on biogeochemical cycling. Nat Rev Earth Environ1, 103–116
McIntyre AM, Guéguen C (2013) Binding interactions of algal-derived dissolved organic matter with metal ions. Chemosphere 90:620–626
Mori T, Onoda Y, Kayaba Y (2018) Geographical patterns of flow-regime alteration by flood-control dams in Japan. Limnology 19(1):53–67
Morling K, Herzsprung P, Kamjunke N (2017) Discharge determines production of, decomposition of and quality changes in dissolved organic carbon in pre-dams of drinking water reservoirs. Sci Total Environ 577(15):329–339
Pal S, Talukdar S (2018) Drivers of vulnerability to wetlands in Punarbhaba river basin of India-Bangladesh. Ecol Indic 93:612–626
Ren HY, Yao X, Ma FY (2020a) The interaction between macrophytes-derived dissolved organic matter and heavy metal under the influence of microbial degradation. China Environ Sci 40(11):4989–4997 (In Chinese)
Ren HY, Ma FY, Yao X et al (2020b) Multi-spectroscopic investigation on the spatial distribution and copper binding ability of sediment dissolved organic matter in Nansi Lake, China. J Hydrol 591:125289
Rodeles AA, Galicia D, Miranda R (2020) A new method to include fish biodiversity in river connectivity indices with applications in dam impact assessments. Ecol Indic 117:106605
Rolls RJ, Bond NR (2017) Environmental and ecological effects of flow alteration in surface water ecosystems. Water for the Environment, 65-82
Santín C, Yamashita Y, Otero XL, Álvarez MÁ, Jaffé R (2009) Characterizing humic substances from estuarine soils and sediments by excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy and parallel factor analysis. Biogeochemistry 96(1):131–147
Shi Y, Zhang L, Li Y et al (2019) Influence of land use and rainfall on the optical properties of dissolved organic matter in a key drinking water reservoir in china. Sci Total Environ 699:134301
Shin Y, Lee E-J, Jeon Y-J, Hur J, Oh NH (2016) Hydrological changes of DOM composition and biodegradability of rivers in temperate monsoon climates. J Hydrol 540:538–548
Song N, Bai L, Xu H et al (2020) The composition difference of macrophyte litter-derived dissolved organic matter by photodegradation and biodegradation: role of reactive oxygen species on refractory component. Chemosphere 242(Mar.):125155.1–125155.10
Talukdar S, Pal S, Chakraborty A, Mahato S (2020) Damming effects on trophic and habitat state of riparian wetlands and their spatial relationship. Ecol Indic 118:106757
Tang J, Li Z, Yu Z, Liu XM, Wang YQ, Wen P, Zhou SG (2019) Insight into complexation of Cu(II) to hyperthermophilic compost-derived humic acids by EEM-PARAFAC combined with heterospectral two dimensional correlation analyses. Sci Total Environ 656:29–38
Tank JL, Rosi-Marshall EJ, Griffiths NA, Entrekin SA, Stephen ML (2010) A review of allochthonous organic matter dynamics and metabolism in streams. North Am Benthol Soc 29:118–146
Tombolini I, Caneva G, Cancellieri L et al (2014) Damming effects on upstream riparian and aquatic vegetation: the case study of Nazzano (Tiber River, central Italy). Knowl Manag Aquat Ecosyst 412:350–353
Xu HC, Zou L, Guan DX et al (2019) Molecular weight-dependent spectral and metal binding properties of sediment dissolved organic matter from different origins. Sci Total Environ 665:828–835
Xue L, Zhang H, Yang C, Zhang L, Sun C (2017) Quantitative assessment of hydrological alteration caused by irrigation projects in the Tarim River basin. China. Sci Rep 7(1):1–13
Yamashita Y, Jaffé R (2008) Characterizing the interactions between trace metals and dissolved organic matter using excitation-emission matrix and parallel factor analysis. Environ Sci Technol 42(19):7374–7379
Yamashita Y, Boyer JN, Jaffé R (2013) Evaluating the distribution of terrestrial dissolved organic matter in a complex coastal ecosystem using fluorescence spectroscopy. Cont Shelf Res 66:136–144
Yang XF, Meng L, Meng FG (2019) Combination of self-organizing map and parallel factor analysis to characterize the evolution of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in a full-scale landfill leachate treatment plant. Sci Total Environ 654:1187–1195
Yao X, Zhang YL, Zhu GW et al (2014) Different degradation mechanism of dissolved organic matter derived from phytoplankton and macrophytes in Lake Taihu, China. Acta Sci Circumst 34(3):688–694 (In Chinese)
Yao X, Wang S, Ni Z, Jiao L (2015) The response of water quality variation in Poyang Lake (Jiangxi, People’s Republic of China) to hydrological changes using historical data and DOM fluorescence. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(4):3032–3042
Yu M, Wang C, Liu Y, Olsson G, Wang C (2018) Sustainability of mega water diversion projects: Experience and lessons from China. Sci Total Environ 619-620:721–731
Zhang G, Liu X, Lu S, Zhang J, Wang W (2020) Occurrence of typical antibiotics in Nansi Lake’s inflowing rivers and antibiotic source contribution to Nansi Lake based on principal component analysis-multiple linear regression model. Chemosphere 242:125269
Zhang YL, Zhou L, Zhou YQ et al (2021) Chromophoric dissolved organic matter in inland waters: present knowledge and future challenges. Sci Total Environ 759:143550
Zhou Y, Xiao Q, Yao X, Zhang Y, Zhang M, Shi K, Lee X, Podgorski DC, Qin B, Spencer RGM, Jeppesen E (2018) Accumulation of terrestrial dissolved organic matter potentially enhances dissolved methane levels in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Environ Sci Technol 52(18):10297–10306
Zhou Y, Zhou L, Zhang Y, Garcia de Souza J, Podgorski DC, Spencer RGM, Jeppesen E, Davidson TA (2019) Autochthonous dissolved organic matter potentially fuels methane ebullition from experimental lakes. Water Res 166:115048
Zhu M, Zhu G, Nurminen L, Wu T, Deng J, Zhang Y, Qin B, Ventelä AM (2015) The influence of macrophytes on sediment resuspension and the effect of associated nutrients in a shallow and large Lake (Lake Taihu, China). PLoS One 10:e0127915
Zhuang W, Ying SC, Frie AL, Wang Q, Song J, Liu Y, Chen Q, Lai X (2019) Distribution, pollution status, and source apportionment of trace metals in lake sediments under the influence of the south-to-north water transfer project, china. Sci Total Environ 671:108–118
Funding
We gratefully thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41977322, 41901120), Open research Foundation of the State Key Laboratory of Lake Science and Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences (2018SKL004), and Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (ZR2019BD052), for their support on this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Haoyu Ren: writing - original draft, formal analysis, investigation; Xin Yao: writing - review and editing; Feiyang Ma: data curation, formal analysis; Tuantuan Fan: data curation, formal analysis; Huanguang Deng: methodology, software; Yinghao Zhang: methodology, software.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
All of the authors consented to participate in the drafting of this manuscript.
Consent for publication
All of the authors consented to publish this manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Xianliang Yi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, H., Yao, X., Ma, F. et al. Characterizing variations in dissolved organic matter (DOM) properties in Nansi Lake: a typical macrophytes-derived lake in northern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 58730–58741 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14266-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14266-x