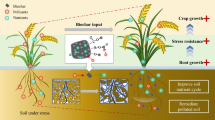
Abstract
Biochar has been applied widely as an amendment in the remediation of contaminated soil to immobilize the heavy metals. However, the role of ultraviolet (UV) irradiation modified biochar derived from the residues of phytoremediation plants in the contaminated soil not investigated yet. In this study, the UV-modified biochars were obtained from Brassica napus L. and Lolium perenne L. by pyrolysis at 600 °C. They were applied in a pot experiment to investigate their effect on Cd bioavailability and uptake in Coriandrum sativum L. in a Cd-contaminated soil at four addition rate (0%, 0.2%, 0.4%, and 0.6%). The results showed that the Cd was effectively stabilized in the biochar with environmentally acceptable leaching toxicity. The specific surface area and carboxyl functional group of biochar were greatly increased after UV modification. The application of biochar progressively increased the soil pH and electrical conductivity (EC). Furthermore, the CaCl2-extractable Cd was significantly reduced by 18.4–51.4% with biochar amendments. The concentration of Cd in shoots and roots was significantly reduced by biochars. In conclusion, the UV-modified biochar obtained from phytoremediation residue could effectively deal with hazardous waste and repair Cd-contaminated soil.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abbas Q, Liu G, Yousaf B, Ali MU, Ullah H, Munir MAM, Liu R (2018) Contrasting effects of operating conditions and biomass particle size on bulk characteristics and surface chemistry of rice husk derived-biochars. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 134:281–292
Ahmad M, Rajapaksha AU, Lim JE, Ming Z, Yong SO (2014) Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: a review. Chemosphere 99:19–33
Al-Wabel MI, Usman ARA, El-Naggar AH, Aly AA, Ibrahim HM, Elmaghraby S, Al-Omran A (2014) Conocarpus biochar as a soil amendment for reducing heavy metal availability and uptake by maize plants. Saudi J Biol Sci 95:503–511
Bian R, Li L, Bao D, Zheng J, Pan G (2016) Cd immobilization in a contaminated rice paddy by inorganic stabilizers of calcium hydroxide and silicon slag and by organic stabilizer of biochar. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:10028–10036
Cao X, Ma L, Gao B, Harris W (2009) Dairy-manure derived biochar effectively sorbs lead and atrazine. Environ Sci Technol 43:3285–3291
Chalot M, Blaudez D, Rogaume Y, Provent AS, Pascual C (2012) Fate of trace elements during the combustion of phytoremediation wood. Environ Sci Technol 46:13361–13369
Chen B, Zhou D, Zhu L (2008a) Transitional adsorption and partition of nonpolar and polar aromatic contaminants by biochars of pine needles with different pyrolytic temperatures. Environ Sci Technol 42:5137–5143
Chen H, Yao J, Zhou Y, Chen H, Wang F, Gai N, Zhuang R, Ceccanti B, Maskow T, Zaray G (2008b) Investigation of the toxic effect of cadmium on Candida humicola and Bacillus subtilis using a microcalorimetric method. J Hazard Mater 159:465–470
Cheng CH, Lehmann J, Engelhard MH (2008) Natural oxidation of black carbon in soils: changes in molecular form and surface charge along a climosequence. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 72:1598–1610
Derek S, Nabila Y, Gordon J, McDougall K, Myton C (1997) Fourier-transform infrared and Raman spectroscopic evidence for the incorporation of cinnamaldehydes into the lignin of transgenic tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) plants with reduced expression of cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase. Planta 201:311–318
Du J, Zhang L, Liu T, Xiao R, Li R, Guo D, Qiu L, Yang X, Zhang Z (2019) Thermal conversion of a promising phytoremediation plant (Symphytum officinale L.) into biochar: dynamic of potentially toxic elements and environmental acceptability assessment of the biochar. Bioresour Technol 274:73–82
Faix O (1991) Classification of lignins from different botanical origins by FT-IR spectroscopy. Holzforschung 45:21–27
Fang S, Tsang D, Zhou F, Zhang W, Qiu R (2016) Stabilization of cationic and anionic metal species in contaminated soils using sludge-derived biochar. Chemosphere 149:263–271
Fellet G, Marmiroli M, Marchiol L (2014) Elements uptake by metal accumulator species grown on mine tailings amended with three types of biochar. Sci Total Environ 468-469:598–608
Gallego SM, Pena LB, Barcia RA, Azpilicueta CE, Iannone MF, Rosales EP, Zawoznik MS, Groppa MD, Benavides MP (2012) Unravelling cadmium toxicity and tolerance in plants: insight into regulatory mechanisms. Environ Exp Bot 83:33–46
Gaskin JW, Steiner C, Harris K, Das KC, Bibens B (2008) Effect of low-temperature pyrolysis conditions on biochar for agricultural use. Trans ASABE 51:2061–2069
Ghosh M, Singh SP (2005) A review on phytoremediation of heavy metals and utilization of its byproducts. Appl Ecol Environ Res 3:1–18
Harvey OR, Herbert BE, Rhue RD, Kuo LJ (2011) Metal interactions at the biochar-water interface: energetics and structure-sorption relationships elucidated by flow adsorption microcalorimetry. Environ Sci Technol 45:5550–5556
Hossain MK, Strezov V, Yin Chan K, Nelson PF (2010) Agronomic properties of wastewater sludge biochar and bioavailability of metals in production of cherry tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum). Chemosphere 78:1167–1171
Huang H, Yao W, Li R, Ali A, Awasthi MK (2017) Effect of pyrolysis temperature on chemical form, behavior and environmental risk of Zn, Pb and Cd in biochar produced from phytoremediation residue. Bioresour Technol 249:487–493
Jin HP, Choppala GK, Bolan NS, Chung JW, Chuasavathi T (2011) Biochar reduces the bioavailability and phytotoxicity of heavy metals. Plant Soil 348:439–451
Karami N, Clemente R, Moreno-Jiménez E, Lepp NW, Beesley L (2011) Efficiency of green waste compost and biochar soil amendments for reducing lead and copper mobility and uptake to ryegrass. J Hazard Mater 191:41–48
Laird D, Fleming P, Wang B, Horton R, Karlen D (2010) Biochar impact on nutrient leaching from a Midwestern agricultural soil. Geoderma 158:436–442
Lehmann J, Rillig MC, Thies J, Masiello CA, Hockaday WC, Crowley D (2011) Biochar effects on soil biota—a review. Soil Biol Biochem 43:1812–1836
Liu X, Tian G, Jiang D, Zhang C, Kong L (2016) Cadmium (Cd) distribution and contamination in Chinese paddy soils on national scale. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:1–12
Lu K, Yang X, Shen J, Robinson B, Huang H, Liu D, Bolan N, Pei J, Wang H (2014) Effect of bamboo and rice straw biochars on the bioavailability of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn to Sedum plumbizincicola. Agric Ecosyst Environ 191:124–132
Mahar A, Wang P, Ali A, Awasthi MK (2016) Challenges and opportunities in the phytoremediation of heavy metals contaminated soils: a review. Ecotox Environ Safe 126:111–121
McBride MB, SAUVE S, Hendershot WH (2005) Solubility control of Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb in contaminated soils. Eur J Soil Sci 48:337–346
Mimmo T, Panzacchi P, Baratieri M, Davies CA, Tonon G (2014) Effect of pyrolysis temperature on miscanthus (Miscanthus × giganteus) biochar physical, chemical and functional properties. Biomass Bioenergy 62:149–157
Mohamed I (2015) Ecological restoration of an acidic Cd contaminated soil using bamboo biochar application. Ecol Eng 84:67–76
Namgay T, Singh B, Singh BP (2010) Influence of biochar application to soil on the availability of As, Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn to maize (Zea mays L.). Aust J Soil Res 48:638–647
Nemati K, Bakar NKA, Abas MR, Sobhanzadeh E (2011) Speciation of heavy metals by modified BCR sequential extraction procedure in different depths of sediments from Sungai Buloh, Selangor, Malaysia. J Hazard Mater 192:402–410
Novak JM, Cantrell KB, Watts DW (2013) Compositional and thermal evaluation of lignocellulosic and poultry litter chars via high and low temperature pyrolysis. BioEnergy Res 6:114–130
Paz-Ferreiro J, Lu H, Fu S, Méndez A (2014) Use of phytoremediation and biochar to remediate heavy metal polluted soils: a review. Solid Earth 5:65–75
Peng X, Ye L, Wang C, Zhou H, Sun B (2011) Temperatureand duration-dependent rice straw-derived biochar: characteristics and its effects on soil properties of an Ultisol in southern, China. Soil Tillage Res 112:159–166
Peng Z, Zhao H, Lyu H, Wang L, Huang H, Nan Q, Tang J (2018) UV modification of biochar for enhanced hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous solution. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:1–12
Peng Z, Liu X, Chen H, Liu Q, Tang J (2019) Characterization of ultraviolet-modified biochar from different feedstocks for enhanced removal of hexavalent chromium from water. Water Sci Technol 79:1705–1716
Pueyo M, López-Sánchez JF, Rauret G (2004) Assessment of CaCl2, NaNO3 and NH4NO3 extraction procedures for the study of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn extractability in contaminated soils. Anal Chim Acta 504:217–226
Qiao L, Ding W, Yi Y, Zeng X, Gao Y (2016) Effects of ultraviolet modification on physicochemical property and adsorption performance of biochar. Nanosci Nanotechnol Lett 8:978–984
Rajapaksha AU, Chen S, Tsang CW, Zhang MD, Vithanage M, SanchitaMandal BG, Bolan SN, SikOka Y (2016) Engineered/designer biochar for contaminant removal/immobilization from soil and water: potential and implication of biochar modification. Chemosphere 148:276–291
Rizwan M, Ali S, Abbas T, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Hannan F, Keller C, Al-Wabel MI, Ok YS (2016) Cadmium minimization in wheat: a critical review. Ecotox Environ Safe 130:43–53
Sas-Nowosielska A, Kucharski R, Małkowski E, Pogrzeba M, Kuperberg JM, Kryński K (2004) Phytoextraction crop disposal—an unsolved problem. Environ Pollut 128:373–379
Sastre J, Hernández E, Rodrguez R, Alcobé X, Vidal M, Rauret G (2004) Use of sorption and extraction tests to predict the dynamics of the interaction of trace elements in agricultural soils contaminated by a mine tailing accident. Sci Total Environ 329:261–281
Shaheen, Sabry M, Rinklebe J, Frohne T (2016) Amendment of biochar reduces the release of toxic elements under dynamic redox conditions in a contaminated floodplain soil. Chemosphere 142:41–47
Sun Y, Gao B, Yao Y, Fang J, Zhang M, Zhou Y, Chen H, Yang L (2014) Effects of feedstock type, production method, and pyrolysis temperature on biochar and hydrochar properties. Chem Eng J 240:574–578
Tahir A, Muhammad R, Shafaqat A, Muhammad Z-u-R, Muhammad F (2017) Effect of biochar on cadmium bioavailability and uptake in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grown in a soil with aged contamination. Ecotox Environ Safe 140:37–47
Walkley AJ, Black CA (1934) An estimation of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37:29–38
Wang S, Gao B, Zimmerman AR, Li Y, Ma L, Harris WG, Migliaccio KW (2015) Removal of arsenic by magnetic biochar prepared from pinewood and natural hematite. Bioresour Technol 175:391–395
Wang L, Ji B, Hu Y, Liu R, Sun W (2017) A review on in situ phytoremediation of mine tailings. Chemosphere 184:594–600
Xu X, Cao X, Zhao L, Wang H, Yu H, Gao B (2013) Removal of Cu, Zn, and Cd from aqueous solutions by the dairy manure-derived biochar. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:358–368
Zeng G, Li X, Tang L, Yu M, Liang J (2017) Changes in heavy metal mobility and availability from contaminated wetland soil remediated with combined biochar-compost. Chemosphere 181:281–288
Zhang X, Wang H, He L, Lu K, Sarmah A, Li J, Bolan NS, Pei J, Huang H (2013) Using biochar for remediation of soils contaminated with heavy metals and organic pollutants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:8472–8483
Zhang Y, Chen Z, Xu W, Liao Q, Zhang H, Hao S, Chen S (2020) Pyrolysis of various phytoremediation residues for biochars: chemical forms and environmental risk of Cd in biochar. Bioresour Technol 299:122581
Funding
This work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFD0800304).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Yaping Zhang; writing—original draft: Zhenyan Chen; formal analysis: Chunhong Chen; investigation: Fangzhou Li; writing—review and editing: Kai Shen.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Zhihong Xu
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 493 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Chen, Z., Chen, C. et al. Effects of UV-modified biochar derived from phytoremediation residue on Cd bioavailability and uptake in Coriandrum sativum L. in a Cd-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 17395–17404 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11931-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11931-5