Abstract
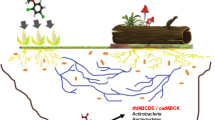
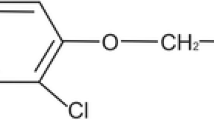
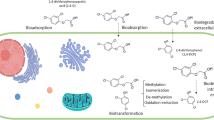
One of the main herbicides used in the agricultural environments is 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D). It is a synthetic plant hormone auxin employed in many crops including rice, wheat, sorghum, sugar cane, and corn to control wide leaf weeds. The indiscriminate use of pesticides can produce numerous damages to the environment. Therefore, this review has the objective to provide an overview on the main characteristics of the herbicides based on 2,4-D, mostly on the role of microorganisms in its degradation and its main degradation metabolite, 2,4- dichlorophenol (2,4-DCP). The remediation processes carried out by microorganisms are advantageous to avoid the pollution of the environment as well as to safeguard the population health.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarry SE, Oghenejoboh KM, Oghenejoboh EO et al (2020) Adsorptive remediation of crude oil contaminated marine water using chemically and thermally modified coconut (Cocos nucifera) husks. J Environ Treat Tech 8:694–707
APVMA (2006) The reconsideration of approvals of the active constituent 2,4-D, registrations of products containing 2,4-D and their associated labels
Arévalo Hernández A, Reynoso SIlva M, Álvarez Moya C (2011) Compuestos organo-persistentes y daño genético en núcleos hepáticos de <i>Goodea atripinnis<i/> del Lago de Chapala. Sci-CUCBA 13:1–8
Bending GD, Turner MK, Jones JE (2002) Interactions between crop residue and soil organic matter quality and the functional diversity of soil microbial communities. Soil Biol Biochem 34:1073–1082. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(02)00040-8
Benli ÇK, Şahin D, Sarikaya R, et al (2016) The sublethal effects of (2,4-dichlorophenoxy) acetic acid (2,4-D) on narrow-clawed crayfish ( Astacus leptodactylus Eschscholtz, 1823). Arch Ind Hyg Toxicol 64
Benndorf D, Thiersch M, Loffhagen N, Kunath C, Harms H (2006) Pseudomonas putida KT2440 responds specifically to chlorophenoxy herbicides and their initial metabolites. Proteomics 6:3319–3329. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.200500781
Bernat P, Nykiel-Szymańska J, Stolarek P, Słaba M, Szewczyk R, Różalska S (2018) 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid-induced oxidative stress: Metabolome and membrane modifications in Umbelopsis isabellina, a herbicide degrader. PLoS One 13:e0199677. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0199677
Bharadwaj A (2018) Bioremediation of xenobiotics: an eco-friendly cleanup approach. In: Green chemistry in environmental sustainability and chemical education. Springer Singapore, Singapore, pp. 1–13
Bhosle NP, Thore AS (2016) Biodegradation of the herbicide 2 , 4-D by some fungi. Am J Agric Enviro Sci 16:1666–1671. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.aejaes.2016.1666.1671
Boivin A, Amellal S, Schiavon M, van Genuchten MT (2005) 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) sorption and degradation dynamics in three agricultural soils. Environ Pollut 138:92–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2005.02.016
Bortolozzi A, Duffard R, de Duffard AME (2003) Asymmetrical development of the monoamine systems in 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid treated rats. Neurotoxicology 24:149–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0161-813X(02)00156-0
Botero LR, Mougin C, Peñuela G, Barriuso E (2017) Formation of 2,4-D bound residues in soils: new insights into microbial metabolism. Sci Total Environ 584–585:715–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.01.105
Carboneras B, Villaseñor J, Fernandez-Morales FJ (2017) Modelling aerobic biodegradation of atrazine and 2,4-dichlorophenoxy acetic acid by mixed-cultures. Bioresour Technol 243:1044–1050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.07.089
Castillo M d P, Torstensson L, Stenström J (2008) Biobeds for environmental protection from pesticide use: a review. J Agric Food Chem 56:6206–6219. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf800844x
Chang Y-C, Reddy MV, Umemoto H et al (2015) Bio-augmentation of Cupriavidus sp. CY-1 into 2,4-D contaminated soil: microbial community analysis by culture dependent and independent techniques. PLoS One 10:e0145057. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0145057
Charles JM, Hanley TR, Wilson RD, van Ravenzwaay B, Bus JS (2001) Developmental toxicity studies in rats and rabbits on 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and its forms. Toxicol Sci 60:121–131. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/60.1.121
Cho Y-S, Park S-H, Kim C-K, Oh K-H (2000) Induction of stress shock proteins DnaK and GroEL by phenoxyherbicide 2,4-D in Burkholderia sp. YK-2 isolated from rice field. Curr Microbiol 41:33–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002840010087
Colosio C, Moretto A (2008) Pesticides. In: Heggenhougen K, Quah S (eds) . International encyclopedia of public health, San Diego, pp 59–66
Correia FV, Moreira JC (2010) Effects of glyphosate and 2,4-D on earthworms (Eisenia foetida) in laboratory tests. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 85:264–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-010-0089-7
Czaplicka M (2004) Sources and transformations of chlorophenols in the natural environment. Sci Total Environ 322:21–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2003.09.015
Devault DA, Karolak S (2020) Wastewater-based epidemiology approach to assess population exposure to pesticides: a review of a pesticide pharmacokinetic dataset. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:4695–4702
Ensminger MP, Budd R, Kelley KC, Goh KS (2013) Pesticide occurrence and aquatic benchmark exceedances in urban surface waters and sediments in three urban areas of California, USA, 2008–2011. Environ Monit Assess 185:3697–3710. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2821-8
EPA U, Risk Information System Division I (2008) 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) (CASRN 94–75-7) | IRIS | US EPA
Faulkner JK, Woodcock D (1965) Fungal detoxication. Part VII. Metabolism of 2,4-dichloro-phenoxyacetic and 4-chloro-2-methylphenoxyacetic acids by Aspergillus niger. J Chem Soc 1187–1191. https://doi.org/10.1039/jr9650001187
Fent K (2003) Ecotoxicological problems associated with contaminated sites. Toxicol Lett 140–141:353–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4274(03)00032-8
Ferreira-Guedes S, Mendes B, Leitão AL (2012) Degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by a halotolerant strain of Penicillium chrysogenum: antibiotic production. Environ Technol 33:677–686. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2011.588251
Forti JC, Loretti GH, Tadayozzi YS, de Andrade AR (2020) A phytotoxicity assessment of the efficiency 2,4-D degradation by different oxidative processes. J Environ Manag 266:110588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110588
Ganguli A, Choudhury D, Chakrabarti G (2014) 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid induced toxicity in lung cells by disruption of the tubulin-microtubule network. Toxicol Res (Camb) 3:118. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3tx50082a
Geed SR, Prasad S, Kureel MK, Singh RS, Rai BN (2018) Biodegradation of wastewater in alternating aerobic-anoxic lab scale pilot plant by Alcaligenes sp. S 3 isolated from agricultural field. J Environ Manag 214:408–415
Gonod LV, Chenu C, Soulas G (2003) Spatial variability of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) mineralisation potential at a millimetre scale in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 35:373–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(02)00287-0
González AJ, Gallego A, Gemini VL, Papalia M, Radice M, Gutkind G, Planes E, Korol SE (2012) Degradation and detoxification of the herbicide 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) by an indigenous Delftia sp. strain in batch and continuous systems. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 66:8–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2011.09.010
Grossmann K (2003) Mediation of herbicide effects by hormone interactions. J Plant Growth Regul 22:109–122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-003-0020-0
Hattab S, Boughattas I, Boussetta H, Viarengo A, Banni M, Sforzini S (2015) Transcriptional expression levels and biochemical markers of oxidative stress in the earthworm Eisenia andrei after exposure to 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 122:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.07.014
Hausinger RP (2015) Biochemical diversity of 2-oxoglutarate-dependent oxygenases. In: Hausinger RP, Schofield CJ (eds) In 2-Oxoglutarate-dependent oxygenases. pp 1–58
Hiran S, Kumar S (2017) 2, 4- dichlorophenoxyacetic acid poisoning; case report and literature review. Mashhad Univ Med Sci 6:29–33. https://doi.org/10.22038/APJMT.2017.8475
Hou J, Liu F, Wu N, Ju J, Yu B (2016) Efficient biodegradation of chlorophenols in aqueous phase by magnetically immobilized aniline-degrading Rhodococcus rhodochrous strain. J Nanobiotechnol 14:5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-016-0158-0
Huang X, He J, Yan X, Hong Q, Chen K, He Q, Zhang L, Liu X, Chuang S, Li S, Jiang J (2017) Microbial catabolism of chemical herbicides: microbial resources, metabolic pathways and catabolic genes. Pestic Biochem Physiol 143:272–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2016.11.010
Hütsch BW (2001) Methane oxidation in non-flooded soils as affected by crop production — invited paper. Eur J Agron 14:237–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1161-0301(01)00110-1
Igbinosa EO, Ajisebutu SO, Okoh AI (2017a) Studies on aerobic biodegradation activities of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by bacteria species isolated from petroleum polluted site. Afr J Biotechnol 6:1426–1431
Igbinosa EO, Ajisebutu SO, Okoh AI (2017b) Aerobic dehalogenation activities of two petroleum degrading bacteria. Afr J Biotechnol 6:897–901
Ikehata K, Nicell JA (2000) Color and toxicity removal following tyrosinase-catalyzed oxidation of phenols. Biotechnol Prog 16:533–540. https://doi.org/10.1021/bp0000510
Islam F, Wang J, Farooq MA, Khan MSS, Xu L, Zhu J, Zhao M, Muños S, Li QX, Zhou W (2018) Potential impact of the herbicide 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid on human and ecosystems. Environ Int 111:332–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2017.10.020
Itoh K, Hayashi S, Sano T et al (2016) 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D)- and 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4,5-T)-degrading gene cluster in the soybean root-nodulating bacterium Bradyrhizobium elkanii USDA94. Microbiol Res 188–189:62–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2016.04.014
Javaid MK, Ashiq M, Tahir M (2016) Potential of biological agents in decontamination of agricultural soil. Scientifica (Cairo) 2016:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/1598325
Joshi N, Gupta D (2008) Soil mycofloral responses following the exposure to 2, 4-D. J Environ Biol 29:211–214
Ju Z, Liu SS, Xu YQ, Li K (2019) Combined toxicity of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and its metabolites 2,4-dichlorophenol (2,4-DCP) on two nontarget organisms. ACS Omega 4:1669–1677. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b02282
Karas PA, Perruchon C, Exarhou K, Ehaliotis C, Karpouzas DG (2011) Potential for bioremediation of agro-industrial effluents with high loads of pesticides by selected fungi. Biodegradation 22:215–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-010-9389-1
Kaštánek F, Topka P, Soukup K, Šolcová O (2020) Chapter 3. Thermal treatment. In: The handbook of environmental remediation. R Soc Chem 53–87
Kelley KB, Riechers DE (2007) Recent developments in auxin biology and new opportunities for auxinic herbicide research. Pestic Biochem Physiol 89:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PESTBP.2007.04.002
Kennepohl E, Munro I. (2001) Phenoxy herbicides (2,4-D). In: Krieger R (ed) Handbook of pesticide toxicology, 2nd Edtion. San Diego, pp 1623–1638
Khalil AB (2003) Isolation and characterization of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid degrading organisms from soil in Jordan Valley. Biotechnology(Faisalabad) 2:73–85. https://doi.org/10.3923/biotech.2003.73.85
Kiljanek T, Niewiadowska A, Semeniuk S, Gaweł M, Borzęcka M, Posyniak A (2016) Multi-residue method for the determination of pesticides and pesticide metabolites in honeybees by liquid and gas chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry—honeybee poisoning incidents. J Chromatogr A 1435:100–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHROMA.2016.01.045
Kumar A, Trefault N, Olaniran AO (2014) Microbial degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid: insight into the enzymes and catabolic genes involved, their regulation and biotechnological implications. Crit Rev Microbiol:1–15. https://doi.org/10.3109/1040841X.2014.917068
Leahy J, Mendelsohn M, Kough J et al (2014) Biopesticide oversight and registration at the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. ACS Symp Ser 1172:3–18. https://doi.org/10.1021/bk-2014-1172.ch001
Lerro CC, Beane Freeman LE, Portengen L, Kang D, Lee K, Blair A, Lynch CF, Bakke B, de Roos AJ, Vermeulen RCH (2017) A longitudinal study of atrazine and 2,4-D exposure and oxidative stress markers among Iowa corn farmers. Environ Mol Mutagen 58:30–38. https://doi.org/10.1002/em.22069
Magnoli K, Benito N, Aluffi M et al (2019) Micobiota cultivable tolerante a 2,4-D aislada de suelos agrícolas con historial de exposición a plaguicidas organoclorados. III Jornadas de Microbiología sobre Temáticas Específicas del NOA. Microbiología Agrícola y Ambiental. San Miguel de Tucumán, Tucumán, Argentina
Mahmood I, Imadi SR, Shazadi K, Gul A, Hakeem KR (2016) Effects of pesticides on environment. In: Plant, soil and microbes. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 253–269
Menezes C, Ruiz-Jarabo I, Martos-Sitcha JA, Toni C, Salbego J, Becker A, Loro VL, Martínez-Rodríguez G, Mancera JM, Baldisserotto B (2015) The influence of stocking density and food deprivation in silver catfish ( Rhamdia quelen ): a metabolic and endocrine approach. Aquaculture 435:257–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2014.09.044
Merini LJ, Cuadrado V, Flocco CG, Giulietti AM (2007) Dissipation of 2,4-D in soils of the humid Pampa region, Argentina: a microcosm study. Chemosphere 68:259–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2007.01.012
Muller RH, Babel W (2004) Delftia acidovorans MC1 resists high herbicide concentrations — a study of nutristat growth on ( RS )-2-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)propionate and 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetate. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 68:622–630. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.68.622
Nykiel-Szymańska J, Stolarek P, Bernat P (2018) Elimination and detoxification of 2,4-D by Umbelopsis isabellina with the involvement of cytochrome P450. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:2738–2743. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0571-4
Ordaz-Guillén Y, Galíndez-Mayer CJ, Ruiz-Ordaz N, Juárez-Ramírez C, Santoyo-Tepole F, Ramos-Monroy O (2014) Evaluating the degradation of the herbicides picloram and 2,4-D in a compartmentalized reactive biobarrier with internal liquid recirculation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:8765–8773. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2809-8
Ortiz-Hernandez ML, Snchez-Salinas E, Dantn Gonzlez E, Luisa M (2013) Pesticide biodegradation: mechanisms, genetics and strategies to enhance the process. In: Biodegradation - Life of Science. InTech
Osborne PP, Xu Z, Swanson KD, Walker T, Farmer DK (2015) Dicamba and 2,4-D residues following applicator cleanout: a potential point source to the environment and worker exposure. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 65:1153–1158. https://doi.org/10.1080/10962247.2015.1072593
Pandey C, Prabha D, Negi YK (2018) Mycoremediation and environmental sustainability. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-77386-5
Pazmiño DM, Romero-Puertas MC, Sandalio LM (2012) Insights into the toxicity mechanism of and cell response to the herbicide 2,4-D in plants. Plant Signal Behav 7:425–427. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.19124
Peterson MA, McMaster SA, Riechers DE et al (2016) 2,4-D past, present, and future: a review. Weed Technol 30:303–345. https://doi.org/10.1614/wt-d-15-00131.1
Pimviriyakul P, Wongnate T, Tinikul R, Chaiyen P (2020) Microbial degradation of halogenated aromatics: molecular mechanisms and enzymatic reactions. Microb Biotechnol 13:67–86. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.13488
Pretto A, Loro VL, Menezes C, Silveira Moraes B, Boschmann Reimche G, Zanella R, de Ávila LA (2011) Commercial formulation containing quinclorac and metsulfuron-methyl herbicides inhibit acetylcholinesterase and induce biochemical alterations in tissues of Leporinus obtusidens. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:336–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2010.10.003
Quan X, Ma J, Xiong W, Wang X (2015) Bioaugmentation of half-matured granular sludge with special microbial culture promoted establishment of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid degrading aerobic granules. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 38:1081–1090. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-014-1350-y
Qurratu A, Reehan A (2016) A review of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) derivatives: 2,4-D dimethylamine salt and 2,4-D butyl ester. Int J Appl Eng Res 11:9946–9955
Raghavendra K., Gundappagol R., Santhosh G. (2017) Impact of herbicide application on beneficial soil microbial community, nodulation and yield parameters of chickpea ( Cicer arietinum L. )
Rivas L, Fegan N, Dykes GA (2008) Expression and putative roles in attachment of outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli O157 from planktonic and sessile culture. Foodborne Pathog Dis 5:155–164. https://doi.org/10.1089/fpd.2007.0052
Rodil R, Quintana JB, Concha-Graña E, López-Mahía P, Muniategui-Lorenzo S, Prada-Rodríguez D (2012) Emerging pollutants in sewage, surface and drinking water in Galicia (NW Spain). Chemosphere 86:1040–1049. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2011.11.053
Rose MT, Cavagnaro TR, Scanlan CA et al (2016) Impact of herbicides on soil biology and function. Adv Agron 136:133–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/BS.AGRON.2015.11.005
Ryan T, Bumpus J (1989) Biodegradation of 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid in liquid culture and in soil by the white rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 31:302–307. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00258414
Santín-Montanyá I, Zambrana-Quesada E, Tenorio-Pasamón JL (2013) Weed management in cereals in semi-arid environments: a review. In: Herbicides - Current Research and Case Studies in Use. InTech 133–152
Sharma A, Kumar V, Shahzad B, Tanveer M, Sidhu GPS, Handa N, Kohli SK, Yadav P, Bali AS, Parihar RD, Dar OI, Singh K, Jasrotia S, Bakshi P, Ramakrishnan M, Kumar S, Bhardwaj R, Thukral AK (2019) Worldwide pesticide usage and its impacts on ecosystem. SN Appl Sci 1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-1485-1
Silva TM, Stets MI, Mazzetto AM, Andrade FD, Pileggi SAV, Fávero PR, Cantú MD, Carrilho E, Carneiro PIB, Pileggi M (2007) Degradation of 2,4-D herbicide by microorganisms isolated from Brazilian contaminated soil. Braz J Microbiol 38:522–525
Silver MK, Shao J, Li M, Ji C, Chen M, Xia Y, Lozoff B, Meeker JD (2019) Prenatal exposure to the herbicide 2,4-D is associated with deficits in auditory processing during infancy. Environ Res 172:486–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.02.046
Singh H (2006) Mycoremediation: fungal bioremediation. Wiley-Interscience, New Jersey
Soloneski S, Nikoloff N, Larramendy ML (2016) Analysis of possible genotoxicity of the herbicide flurochloridone and its commercial formulations: Endo III and Fpg alkaline comet assays in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO-K1) cells. Mutat Res Toxicol Environ Mutagen 797:46–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MRGENTOX.2016.01.004
Song Y (2014) Insight into the mode of action of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) as an herbicide. J Integr Plant Biol 56:106–113. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12131
Soulas G (2003) Pesticide degradation in soils. In: Encyclopedia of Environmental Microbiology. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, NJ, USA
Stibal M, Bælum J, Holben WE, Sørensen SR, Jensen A, Jacobsen CS (2012) Microbial degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid on the Greenland ice sheet. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:5070–5076. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00400-12
Syberg K, Binderup ML, Cedergreen N, Rank J (2015) Mixture genotoxicity of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, acrylamide, and maleic hydrazide on human Caco-2 cells assessed with comet assay. J Toxicol Environ Heal - Part A Curr Issues 78:369–380. https://doi.org/10.1080/15287394.2014.983626
Thiel M, Kaschabek SR, Gruning J et al (2005) Two unusual chlorocatechol catabolic gene clusters in Sphingomonas sp. TFD44. Arch Microbiol 183:80–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-004-0748-3
Tsaboula A, Papadakis E-N, Vryzas Z, Kotopoulou A, Kintzikoglou K, Papadopoulou-Mourkidou E (2016) Environmental and human risk hierarchy of pesticides: a prioritization method, based on monitoring, hazard assessment and environmental fate. Environ Int 91:78–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVINT.2016.02.008
United State Department of Agriculture (USDA) (2017) Foreign agricultural service. In: Circular series. In: World Agricultural Production
Vroumsia T, Steiman R, Seigle-Murandi F, Benoit-Guyod JL (2005) Fungal bioconversion of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) and 2,4-dichlorophenol (2,4-DCP). Chemosphere 60:1471–1480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.11.102
Wágner G, Nádasy E (2006) Effect of pre-emergence herbicides on growth parameters of green pea. Commun Agric Appl Biol Sci 71:809–813
WHO (World Health Organization) (2017) Guidelines for drinking-water quality. Fourth edition incorporating the first addenum
Wijnja H, Doherty JJ, Safie SA (2014) Changes in pesticide occurrence in suburban surface waters in Massachusetts, USA, 1999–2010. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 93:228–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-014-1251-4
Wilson NK, Chuang JC, Lyu C, Menton R, Morgan MK (2003) Aggregate exposures of nine preschool children to persistent organic pollutants at day care and at home. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 13:187–202. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jea.7500270
Wu X, Wang W, Liu J, Pan D, Tu X, Lv P, Wang Y, Cao H, Wang Y, Hua R (2017) Rapid biodegradation of the herbicide 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by Cupriavidus gilardii T-1. J Agric Food Chem 65:3711–3720. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b00544
Xia ZY, Zhang L, Zhao Y, Yan X, Li SP, Gu T, Jiang JD (2017) Biodegradation of the herbicide 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by a new isolated strain of Achromobacter sp. LZ35. Curr Microbiol 74:193–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-016-1173-y
Yamini Y, Saleh A (2013) Ultrasound-assisted emulsification microextraction combined with injection-port derivatization for the determination of some chlorophenoxyacetic acids in water samples. J Sep Sci 36:2330–2338. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201300340
Zabaloy MC, Garland JL, Gómez MA (2008) An integrated approach to evaluate the impacts of the herbicides glyphosate, 2,4-D and metsulfuron-methyl on soil microbial communities in the Pampas region, Argentina. Appl Soil Ecol 40:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APSOIL.2008.02.004
Zhang W (2018) Global pesticide use: profile, trends, cost/benefit and more. Proc Int Acad Ecol Environ Sci 8:1–27
Funding
This work was carried out thanks to grants from the Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONICET PIP), Secretaría de Ciencia y Técnica de la Universidad Nacional de Río Cuarto (SECYT-UNRC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Robert Duran
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Magnoli, K., Carranza, C.S., Aluffi, M.E. et al. Herbicides based on 2,4-D: its behavior in agricultural environments and microbial biodegradation aspects. A review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 38501–38512 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10370-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10370-6