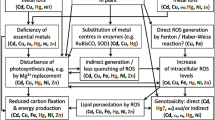
Abstract
Cadmium (Cd) and zinc (Zn) toxicity causes physiological disorders and harms plants, interfering with the rehabilitation of areas affected by mining activities. This study evaluated how the exposure to Zn and/or Cd affects the growth of native andropogon grass (Andropogon gayanus Kunth) plants originally found in areas contaminated with Cd and/or Zn due to zinc mining activities. Plants were cultivated for 7 weeks in a nutrient solution treated with Zn (142.3–854.0 μM) or Cd (0.9–13.3 μM) separately or combined with a molar ratio of 64:1 (Zn:Cd). A control treatment was grown in a complete Hoagland and Arnon solution (without Cd). Plant height, stem diameter, internode length, dry weight, Cd and Zn concentration, and accumulation in shoots/roots, as well as ultrastructure of roots and leaves were analyzed at the end of the experiment. The root dry weight was not significantly affected by the addition of the metals. Moreover, Zn provided higher shoot dry weight (up to 160%) relative to control. Andropogon grass tolerated both metals better separately than when applied together. Transmission electron microscopy analyses showed modifications such as vesiculation and vacuolation in the ultrastructure of andropogon tissues by Cd and/or Zn. The andropogon grass was tolerant to the doses tested, evidencing that it has potential for recovering areas contaminated with Zn and/or Cd.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åkesson A, Barregard L, Bergdahl IA, Nordberg GF, Nordberg M, Skerfving S (2014) Non-renal effects and the risk assessment of environmental cadmium exposure. Environ Health Perspect 122:431–438. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1307110
Ali H, Khan E (2019) Trophic transfer, bioaccumulation, and biomagnification of non-essential hazardous heavy metals and metalloids in food chains/webs—concepts and implications for wildlife and human health. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25(6):1353–1376. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1469398
Ali H, Khan E, Sajad MA (2013) Phytoremediation of heavy metals—concepts and applications. Chemosphere 91:869–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.075
Alloway BJ (2008) Zinc in soils and crop nutrition. International Fertilizer Industry Association, and International Zinc Association, Paris
Amaral DC (2013) Estudos ultraestruturais e da capacidade bioacumuladora de Zn, Cd e Pb por plantas em área de mineração de zinco. Thesis, Federal University of Lavras
Anju M, Banerjee DK (2011) Associations of cadmium, zinc, and lead in soils from a lead and zinc mining area as studied by single and sequential extractions. Environ Monit Assess 176:67–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1567-4
Aravind P, Prasad MNV (2003) Zinc alleviates cadmium-induced oxidative stress in Ceratophyllum demersum L. a free floating freshwater macrophyte. Plant Physiol Biochem 41:391–397
Arena C, Figlioli F, Sorrentino MC, Izzo LG, Capozzi F, Giordano S, Spagnuolo V (2017) Ultrastructural, protein and photosynthetic alterations induced by Pb and Cd in Cynara cardunculus L., and its potential for phytoremediation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 145:83–89
Asad SA, Farooq M, Afzal A, West H (2019) Integrated phytobial heavy metal remediation strategies for a sustainable clean environment - a review. Chemosphere 217:925–941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.021
Asgher M, Khan MIR, Anjum NA, Khan NA (2015) Minimising toxicity of cadmium in plants—role of plant growth regulators. Protoplasma 252:399–413. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-014-0710-4
Azzarello E, Pandolfi C, Giordano C, Rossi M, Mugnai S, Mancuso S (2012) Ultramorphological and physiological modifications induced by high zinc levels in Paulownia tomentosa. Environ Exp Bot 81:11–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2012.02.008
Baker AJM (1981) Accumulators and excluders-strategies in the response of plants to heavy metals. J Plant Nutr 3:643–654
Baker AJM, McGrath SP, Sidoli CMD, Reeves RD (1994) The Possibility of in situ heavy metal decontamination of polluted soils using crops of metal-accumulating plants. Resour Conserv Recycl 11:41–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/0921-3449(94)90077-9
Bert V, Meerts P, Salis P, Gruber W, Verbruggen N (2003) Genetic basis of Cd tolerance and hyperaccumulation in Arabidopsis halleri. Plant Soil 249:9–18
Bešter PK, Lobnik F, Eržen I, Kastelec D, Zupan M (2013) Prediction of cadmium concentration in selected home-produced vegetables. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 96:182–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.06.011
Bishak YK, Payahoo L, Osatdrahimi A, Nourazarian A (2015) Mechanisms of cadmium carcinogenicity in the gastrointestinal tract. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 16:9–21. https://doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2015.16.1.9
Bolan NS, Park JH, Robinson B, Naidu R, Huh KY (2011) Phytostabilization: a green approach to contaminant containment. In: Advances in Agronomy. Elsevier, pp 145-204
Bolan N, Kunhikrishnan A, Thangarajan R, Kumpiene J, Park J, Makino T, Kirkham MB, Scheckel K (2014) Remediation of heavy metal(loid)s contaminated soils – to mobilize or to immobilize? J Hazard Mater 266:141–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.12.018
Broadley MR, White PJ, Hammond JP, Zelko I, Lux A (2007) Zinc in plants. New Phytol 173:677–702. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.01996.x
Broadley M, Brown P, Cakmak I, Rengel Z, Zhao F (2012) Function of nutrients: micronutrients. In: Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants. Elsevier, pp 191–248
Cakmak I (2000) Possible roles of zinc in protecting plant cells from damage by reactive oxygen species. New Phytol 146:185–205
Carvalho MTV (2010) Fitoextração de Cd e Zn e atividade de enzimas antioxidantes em ecótipos de Gomphrena elegans. Thesis, Federal University of Lavras
Carvalho MTV, Amaral DC, Guilherme LRG, Aarts MGM (2013) Gomphrena claussenii, the first South-American metallophyte species with indicator-like Zn and Cd accumulation and extreme metal tolerance. Front Plant Sci 4:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2013.00180
Chang X, Song Z, Xu Y, Gao M (2020) Effects of carbon nanotubes on growth of wheat seedlings and Cd uptake. Chemosphere 240:124931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124931
Chi K, Zou R, Wang L, Huo W, Fan H (2019) Cellular distribution of cadmium in two amaranth (Amaranthus mangostanus L.) cultivars differing in cadmium accumulation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:22147–22158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05390-w
Cleasby IR, Nakagawa S (2011) Neglected biological patterns in the residuals. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 65:2361–2372
Cui W, Gao C, Fang P, Lin G, Shen W (2013) Alleviation of cadmium toxicity in Medicago sativa by hydrogen-rich water. J Hazard Mater 260:715–724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.06.032
Cundy AB, Bardos RP, Puschenreiter M, Mench M, Bert V, Friesl-Hanl W, Müller I, Li XN, Weyens N, Witters N, Vangronsveld J (2016) Brownfields to green fields: realising wider benefits from practical contaminant phytomanagement strategies. J Environ Manag 184:67–77
da Cunha KPV, do Nascimento CWA, Pimentel RMM, Accioly AMA, da Silva AJ (2008) Disponibilidade, acúmulo e toxidez de cádmio e zinco em milho cultivado em solo contaminado. Rev Bras Ciênc Solo 32:1319–1328. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-06832008000300039
Dias MC, Monteiro C, Moutinho-Pereira J, Correia C, Gonçalves B, Santos C (2013) Cadmium toxicity affects photosynthesis and plant growth at different levels. Acta Physiol Plant 35:1281–1289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-012-1167-8
Djebali W, Zarrouk M, Brouquisse R, El Kahoui S, Limam F, Ghorbel MH, Chïbi W (2005) Ultrastructure and lipid alterations induced by cadmium in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) chloroplast membranes. Plant Biol 7:358–368
Favas PJC, Pratas J, Gomes MEP, Cala V (2011) Selective chemical extraction of heavy metals in tailings and soils contaminated by mining activity: environmental implications. J Geochem Explor 111:160–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2011.04.009
Gill SS, Khan NA, Tuteja N (2012) Cadmium at high dose perturbs growth, photosynthesis and nitrogen metabolism while at low dose it up regulates sulfur assimilation and antioxidant machinery in garden cress (Lepidium sativum L.). Plant Sci 182:112–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2011.04.018
Guimarães MA, Santana TA, Silva EV, Zenzen IL, Loureiro ME (2008) Toxicidade e tolerância ao cádmio em plantas. Revista Trópica – Ciências Agrárias e Biológicas 1:58–68
Gutiérrez M, Mickus K, Camacho LM (2016) Abandoned Pb-Zn mining wastes and their mobility as proxy to toxicity: a review. Sci Total Environ 565:392–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.04.143
Hafeez B, Khanif YM, Saleem M (2013) Role of zinc in plant nutrition- a review. Am J Exp Agric 3:374–391
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. Circ - Calif Agric Exp Stn 347:1–32
Huang Z, Pan X, Wu P, Han J, Chen Q (2014) Heavy metals in vegetables and the health risk to population in Zhejiang, China. Food Control 36:248–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2013.08.036
Hussain T, Murtaza G, Ghafoor A, Cheema MA (2016) The Cd: Zn ratio in a soil affects Cd toxicity in spinach (Spinacea oleracea L). Pak J Agric Sci 53:419–424
Ibigbami OA, Ogundiran MB, Osibanjo O (2014) Lead and cadmiumphytoremediation potentials of plants from four lead smelting slagscontaminated sites. Nat Environ 2:33–88
Jia L, He X, Chen W, Liu Z, Huang Y, Yu S (2013) Hormesis phenomena under Cd stress in a hyperaccumulator—Lonicera japonica Thunb. Ecotoxicology 22:476–485. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-013-1041-5
Jia W, Lv S, Feng J, Li J, Li Y, Li S (2016) Morphophysiological characteristic analysis demonstrated the potential of sweet sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) in the phytoremediation of cadmium-contaminated soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:18823–18831
Jiao YQ, Ge W, Qin R, Sun BL, Jiang WS, Liu DH (2012) Influence of cadmium stress on growth, ultra-structure and antioxidative enzymes in Populus 2025. Fresenius Environ Bull 21:1375–1384
John R, Ahmad P, Gadgil K, Sharma S (2009) Heavy metal toxicity: effect on plant growth, biochemical parameters and metal accumulation by Brassica juncea L. Int J Plant Prod 3:65–76
Kabata-Pendias A, Szteke B (2015) Trace elements in abiotic and biotic environments. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Lagriffoul A, Mocquot B, Mench M, Vangronsveld J (1998) Cadmium toxicity effects on growth, mineral and chlorophyll contents, and activities of stress related enzymes in young maize plants (Zea mays L.). Plant Soil 200:241–250. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004346905592
Li Z, Ma Z, Van der Kuijp TJ, Yuan Z, Huang L (2014) A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: pollution and health risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 468–469:843–853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.090
Lin Y-F, Aarts MGM (2012) The molecular mechanism of zinc and cadmium stress response in plants. Cell Mol Life Sci 69:3187–3206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1089-z
Liu Z, Chen W, He X, Jia L, Yu S, Zhao M (2015) Hormetic responses of Lonicera japonica Thunb. to cadmium stress. Dose-Response 1:1–10. https://doi.org/10.2203/dose-response.14-033.He
Liu L, Li W, Song W, Guo M (2018) Remediation techniques for heavy metal-contaminated soils: principles and applicability. Sci Total Environ 633:206–219
Mahar A, Wang P, Li R, Zhang Z (2015) Immobilization of lead and cadmium in contaminated soil using amendments: a review. Pedosphere 25:555–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(15)30036-9
Mahar A, Wang P, Ali A, Awasthi MK, Lahori AH, Wang Q, Li R, Zhang Z (2016) Challenges and opportunities in the phytoremediation of heavy metals contaminated soils: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 126:111–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.12.023
Martins GC, Penido ES, Alvarenga IFS, Teodoro JC, Bianchi ML, Guilherme LRG (2018) Amending potential of organic and industrial by-products applied to heavy metal-rich mining soils. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 162:581–590
Mingorance MD, Franco I, Rossini-Oliva S (2016) Application of different soil conditioners to restorate mine tailings with native (Cistus ladanifer L.) and non-native species (Medicago sativa L.). J Geochem Explor 174:35–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.02.010
Mohtadi A, Ghaderian SM, Schat H (2012) Lead, zinc and cadmium accumulation from two metalliferous soils with contrasting calcium contents in heavy metal-hyperaccumulating and non-hyperaccumulating metallophytes: a comparative study. Plant Soil 361:109–118
Ng CC, Law SH, Amru NB, Motior MR, Radzi BM (2016) Phyto-assessment of soil heavy metal accumulation in tropical grasses. J Anim Plant Sci 26:686–696
Ono FB, Penido ES, Tappero R, Sparks D, Guilherme LRG (2016) Bioaccessibility of Cd and Pb in tailings from a zinc smelting in Brazil: implications for human health. Environ Geochem Health 38:1083–1096. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-015-9774-0
R Core Team (2017) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/
Rabêlo FHS, Borgo L (2016) Changes caused by heavy metals in micronutrient content and antioxidant system of forage grasses used for phytoremediation: an overview. Cienc Rural 46:1368–1375. https://doi.org/10.1590/0103-8478cr20151291
Riaz S, Iqbal M, Hussain I, Rasheed R, Ashraf MA, Mahmood S, Younas M, Iqbal MZ (2014) Chronic cadmium induced oxidative stress not the DNA fragmentation modulates growth in spring wheat (Triticum aestivum). Int J Agric Biol 16:789–794
Romeo S, Francini A, Ariani A, Sebastiani L (2014) Phytoremediation of Zn: identify the diverging resistance, uptake and biomass production behaviours of poplar clones under high zinc stress. Water Air Soil Pollut 225:1813. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1813-9
Schaider LA, Senn DB, Estes ER, Brabander DJ, Shine JP (2014) Sources and fates of heavy metals in a mining-impacted stream: temporal variability and the role of iron oxides. Sci Total Environ 490:456–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.04.126
Sindern S, Tremöhlen M, Dsikowitzky L, Gronen L, Schwarzbauer J, Hartati T, Ariyani F, Eko H (2016) Heavy metals in river and coast sediments of the Jakarta Bay region ( Indonesia ) — geogenic versus anthropogenic sources. Mar Pollut Bull 110:624–633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.06.003
Sorrentino MC, Capozzi F, Amitrano C, Giordano S, Arena C, Spagnuolo V (2018) Performance of three cardoon cultivars in an industrial heavy metal contaminated soil: effects on morphology, cytology and photosynthesis. J Hazard Mater 351:131–137
Sousa BMDL, do Nascimento D Jr, da Silva SC, Monteiro HCDF, Rodrigues CS, da Fonseca DM, da Silveira MCT, Sbrissia AF (2010) Morphogenetic and structural characteristics of andropogon grass submitted to different cutting heights. R Bras Zootec 39:2141–2147. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982010001000006
Sun H, Li Y, Ji Y, Yang L, Wang W, Li H (2010) Environmental contamination and health hazard of lead and cadmium around Chatian mercury mining deposit in western Hunan Province, China. Trans Nonferrous Metal Soc 20:308–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(09)60139-4
Tian HZ, Zhu CY, Gao JJ, Cheng K, Hao JM, Wang K, Hua SB, Wang Y, Zhou JR (2015) Quantitative assessment of atmospheric emissions of toxic heavy metals from anthropogenic sources in China: historical trend, spatial distribution, uncertainties, and control policies. Atmos Chem Phys 15:10127–10147. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-15-10127-2015
Tkalec M, Štefanić PP, Cvjetko P, Šikić S, Pavlica M, Balen B (2014) The effects of cadmium-zinc interactions on biochemical responses in tobacco seedlings and adult plants. PLoS ONE 9:e87582. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0087582
Tran TA, Popova LP (2013) Functions and toxicity of cadmium in plants: recent advances and future prospects. Turk J Bot 37:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3906/bot-1112-16
Tsonev T, Lidon FJC (2012) Zinc in plants - an overview. Emir J Food Agric 24:322–333
Umeoguaju UF, Ononamadu CJ, Okonkwo MC, Ezeigwe OC (2016) The survival of four tropical plants on soils artificially polluted with toxic levels of zinc. Int J Environ Sci Technol 5:17–24
United States Environmental Protection Agency – USEPA (2007) Method 3051A (SW-846): microwave assisted acid digestion of sediments, sludges, and oils, revision 1. https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-12/documents/3051a.pdf. Accessed 29 March 2020
Vareda PJ, Valente AJM, Durães L (2019) Assessment of heavy metal pollution from anthropogenic activities and remediation strategies: a review. J Environ Manag 246:101–118
Verbruggen N, Juraniec M, Baliardini C, Meyer C-L (2013) Tolerance to cadmium in plants: the special case of hyperaccumulators. BioMetals 26:633–638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-013-9659-6
Visconti D, Fiorentino N, Caporale AG, Stinca A, Adamo P, Motti R, Fagnano M (2019) Analysis of native vegetation for detailed characterization of a soil contaminated by tannery waste. Environ Pollut 252:1599e1608
Wan X, Lei M, Chen T (2016) Cost–benefit calculation of phytoremediation technology for heavy-metal-contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ 563-564:796–802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.12.080
Wang M, Zhu Y, Cheng L, Andserson B, Zhao X, Wang D, Din A (2018) Review on utilization of biochar for metal-contaminated soil and sediment remediation. J Environ Sci 63:156–173
Watanabe Y, Nogawa K, Nishijo M, Sakurai M, Ishizaki M, Morikawa Y, Kido T, Nakagawa H, Suwazono Y (2020) Relationship between cancer mortality and environmental cadmium exposure in the general Japanese population in cadmium non-polluted areas. Int J Hyg Environ Health 223:65–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2019.10.005
Wiszniewska A, Hanus-Fajerska E, Muszyńska E, Ciarkowska K (2016) Natural organic amendments for improved phytoremediation of polluted soils: a review of recent progress. Pedosphere 26:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(15)60017-0
Wong MH (2003) Ecological restoration of mine degraded soils, with emphasis on metal contaminated soils. Chemosphere 50:775–780
Xiong J, Madejón P, Madejón E, Cabrera F (2015) Assisted natural remediation of a trace element-contaminated acid soil: an eight-year field study. Pedosphere 25:250–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(15)60010-8
Yao Z, Li J, Xie H, Yu C (2012) Review on remediation technologies of soil contaminated by heavy metals. Procedia Environ Sci 16:722–729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2012.10.099
Zhang X, Yang L, Li Y, Li H, Wang W, Ye B (2012) Impacts of lead/zinc mining and smelting on the environment and human health in China. Environ Monit Assess 184:2261–2273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2115-6
Zhang H, Zhang L-L, Li J, Chen M, An R-D (2020) Comparative study on the bioaccumulation of lead, cadmium and nickel and their toxic effects on the growth and enzyme defence strategies of a heavy metal accumulator, Hydrilla verticillata (L.f.) Royle. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:9853–9865
Zuur AF, Ieno EN, Elphick CS (2010) A protocol for data exploration to avoid common statistical problems. Methods Ecol Evol 1:3–14. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2041-210X.2009.00001.x
Funding
This study was given granting scholarships and has financially supported by CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior), (CAPES-PRINT - 88887.371138/2019-00, CAPES 88887.160998/2017-00) CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico) 141228/2018-0, and FAPEMIG (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais). The authors would also like to thank the Laboratory of Electron Microscopy and Analysis of Ultrastructural Federal University of Lavras, (http://www.prp.ufla.br/labs/microscopiaeletronica/) and Finep, Fapemig, CNPq, and Capes for supplying the equipment and technical support for experiments involving electron microscopy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Roberto Terzano
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 530 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ribeiro, P.G., Martins, G.C., Moreira, C.G. et al. Interactions of cadmium and zinc in high zinc tolerant native species Andropogon gayanus cultivated in hydroponics: growth endpoints, metal bioaccumulation, and ultrastructural analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 45513–45526 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10183-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10183-7