Abstract
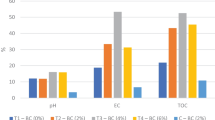
In this work, earthworm effect on the efficiency of biobeds for glyphosate degradation was studied. Three biomixtures with and without the addition of earthworms (Eisenia fetida species) were evaluated. The initial concentration of glyphosate was 1000 mg/kg biomixture. Glyphosate and biological parameters were measured as a function of time. Earthworm survival, biomass, and reproduction were evaluated as well. All biomixtures that contain earthworms reached 90% of glyphosate degradation at 90 days in comparison with the biomixtures without earthworms that reached 80% approximately at the same time. Also, within the biomixtures that contained earthworms, glyphosate degradation rate was significantly higher in the one made up with soil and wheat stubble (Ws-E) showing excellent capacity for aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) degradation, the main metabolite of glyphosate degradation. In addition, a study performed after the vermiremediation process showed that E. fetida can tolerate high glyphosate concentration without modifications in its life traits. It can be concluded that the use of E. fetida within the biobeds is an excellent combination to improve glyphosate and AMPA removal.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aira M, Domínguez J (2008) Optimizing vermicomposting of animal wastes: effects of rate of manure application on carbon loss and microbial stabilization. J Environ Manag 88:1525–1529
Al-Maliki S, Scullion J (2013) Interactions between earthworms and residues of differing quality affecting aggregate stability and microbial dynamics. Appl Soil Ecol 64:56–62
Baier CJ, Gallegos CE, Raisman-Vozari R, Minetti A (2017) Behavioral impairments following repeated intranasal glyphosate-based herbicide administration in mice. Neurotoxicol Teratol 64:63–72
Bergsveinson J, Perry BJ, Sheedy C, Braul L, Reedyk S, Gossen BD, Yost CK (2018) Identifying the core bacterial and fungal communities within four agricultural biobeds used for the treatment of pesticide rinsates. J Appl Microbiol 125:1333–1342
Binet F, Kersanté A, Munier-Lamy C, Le Bayon RC, Belgy MJ, Shipitalo MJ (2006) Lumbricid macrofauna alter atrazine mineralization and sorption in a siltloam soil. Soil Biol Biochem 38:1255–1263
Borggaard O, Gimsing A (2008) Review: Fate of glyphosate in soil and the possibility of leaching to ground and surface waters: a review. Pest Manag Sci 64:441–456
Bórtoli P, Verdeneli R, Conforto C, Vargas S, Meriles J (2012) Efectos del herbicida glifosato sobre la estructura y el funcionamiento de comunidades microbianas de dos suelos de plantaciones de olivo. Ecol Austral 22:33–42
Brown GG, Barois I, Lavelle P (2000) Regulation of soil organic matter dynamics and microbial activity in the drilosphere and the role of interactions with other edaphic functional domains. Eur J Soil Biol 36:177–198
Castillo MP, Torstensson L, Stenström J (2008) Biobeds for environmental protection form pesticide use. A review. J Agric Food Chem 56:6206–6219
Contreras-Ramos SM, Álvarez-Bernal D, Dendooven L (2008) Removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from soil amended with biosolid or vermicompost in the presence of earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Soil Biol Biochem 40:1954–1959
Cooper RJ, Fitt P, Hiscock KM, Lovett AA, Gumm L, Dugdale SJ, Rambohul J, Williamson A, Noble L, Beamish J, Hovesen P (2016) Assessing the effectiveness of a three-stage on-farm biobed in treating pesticide contaminated wastewater. J Environ Manag 181:874–882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.06.047
Correia FV, Moreira JC (2010) Effects of glyphosate and 2,4-D on earthworms (Eisenia foetida) in laboratory tests. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 85:264–268
De Wilde T, Spanoghe P, Debaer C, Ryckeboer J, Springael D, Jaeken P (2007) Overview of on-farm bioremediation systems to reduce the occurrence of point source contamination. Pest Manag Sci 63:111–128
Devliegher W, Verstraete W (1995) Lumbricus terrestris in a soil core experiment: nutrient-enrichment processes (NEP) and gut-associated processes (GAP) and their effect on microbial biomass and microbial activity. Soil Biol Biochem 27(12):1573–1580
Dias L, Gebler L, Niemeyer J, Itako A (2020) Destination of pesticide residues on biobeds: state of the art and future perspectives in Latin America. Chemosphere 248:126038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126038
Domínguez A, Brown GG, Sautter KD, Ribas de Oliveira CM, Carvalho de Vasconcelos E, Niva CC, Bartz MLC, Bedano JC (2016) Toxicity of AMPA to the earthworm Eisenia andrei, Bouchè, 1972 in tropical artificial soil. Sci Rep 6:1–9
Gong X, Cai L, Li S, Chang S, Sun X, An Z (2018) Bamboo biochar amendment improves the growth and reproduction of Eisenia fetida and the quality of green waste vermicompost. Ecotox Environ Saf 156:197–204
Grandcoin A, Piel S, Baurés E (2017) Amino methyl phosphonic acid (AMPA) in natural waters: its sources, behavior and environmental fate. Water Res 117:187–197
Gupta R, Garg VK (2009) Vermiremediation and nutrient recovery of non-recyclable paper waste employing Eisenia fetida. J Hazard Mater 162:430–439
Hickman ZA, Reid BJ (2008) Increased microbial catabolic activity in diesel contaminated soil following addition of earthworms (Dendrobaena veneta) and compost. Soil Biol Biochem 40:2970–2976
Holmsgaard PN, Dealtry S, Dunon V, Heuer H, Hansen LH, Springael D, Smalla K, Riber L, Sørensen SJ (2017) Response of the bacterial community in an on-farm biopurification system, to which diverse pesticides are introduced over an agricultural season. Environ Pollut 229:854–862
Kawai S, Uno B, Tomita M (1991) Determination of glyphosate and its major metabolite aminomethylphosphonic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography after derivatization with p-toluenesulphonyl chloride. J Chromatogr A 540:411–415
Lescano M, Pizzul L, Castillo M, Zalazar C (2018) Glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid degradation in biomixtures based on alfalfa straw, wheat stubble and river waste. J Environ Manag 228:451–457
Mac Loughlin TM, Peluso ML, Aparicio VC, Marino DJG (2020) Contribution of soluble and particulate-matter fractions to the total glyphosate and AMPA load in water bodies associated with horticulture. Sci Total Environ 703:134717
Mamy L, Benoît G, Barriuso E (2010) Comparative environmental impacts of glyphosate and conventional herbicides when used with glyphosate-tolerant and nontolerant crops. Environ Pollut 158:3172–3178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2010.06.036
Marinozzi M, Coppola L, Monaci E, Karpouzas DG, Papadopoulou E, Menkissoglu-Spiroudi U, Vischetti C (2013) The dissipation of three fungicides in a biobed organic substrate and their impact on the structure and activity of the microbial community. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:2546–2555
Masin CE, Rodríguez AR (2012) Evaluación preliminar de dos tipos de dieta en la especie endogea Aporrectodea trapezoides (Dugés, 1828) (Oligochaeta: Lumbricidae). Megadrilogica. 15(10):219–226
Masin CE, Lescano MR, Rodríguez AR, Godoy JL, Zalazar CS (2018) Earthworms to assess the innocuousness of spent biomixtures employed for glyphosate degradation. J Environ Sci Health B:1–7
Myers JP, Antoniou MN, Blumberg B, Carroll L, Colborn T, Everett LG, Hansen M, Landrigan PJ, Lanphear BP, Mesnage R, Vandenberg LN, Vom Saal FS, Welshons WV, Benbrook CM (2016) Concerns over use of glyphosate-based herbicides and risks associated with exposures: a consensus statement. Environ Health:15–19
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) (2004) Guideline for the testing of chemicals. Earthworm reproduction test (Eisenia fetida/Eisenia andrei). OECD, París, No. 222, p 18
Owagboriaye F, Dedeke G, Bamidele J, Aladesida A, Isibor P, Feyisola R, Adeleke M (2020) Biochemical response and vermiremediation assessment of three earthworm species (Alma millsoni, Eudrilus eugeniae and Libyodrilus violaceus) in soil contaminated with a glyphosate-based herbicide. Ecol Indic 108:105678
Piola L, Fuchs J, Oneto ML, Basack S, Kesten E, Casabé N (2013) Comparative toxicity of two glyphosate-based formulations to Eisenia andrei under laboratory conditions. Chemosphere 91:545–551
Ratcliff A, Busse M, Shestak C (2006) Changes in microbial community structure following herbicide (glyphosate) additions to forest soils. Appl Soil Ecol 34:114–124
Rodríguez-Campos J, Dendooven L, Álvarez-Bernal D, Contreras-Ramos SM (2014) Potential of earthworms to accelerate removal of organic contaminants from soil: a review. Appl Soil Ecol 79:10–25
Rorat A, Wloka D, Grobelak A, Grosser A, Sosnecka A, Milczarek M, Jelonek P, Vandenbulcke F, Kacprzak M (2017) Vermiremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and heavy metals in sewage sludge composting process. J Environ Manag 187:347–353
Schnürer J, Rosswall T (1982) Fluorescein diacetate hydrolysis as a measure of total microbial activity in soil and litter. Appl Environ Microb 6:256–1261
Sharma K, Garg VK (2018) Comparative analysis of vermicompost quality produced from rice straw and paper waste employing earthworm Eisenia fetida (Sav.). Bioresour Technol 250:708–715
Souza TA, Matta MHR, Montagner E, Abreu ABG (2006) Estudo de recuperaçao de glifosato e AMPA derivados em solo usando resinas nacionais. Quim Nova 29:1372–1376
Tejada M, Masciandaro G (2011) Application of organic wastes on a benzo(a) pyrene polluted soil. Response of soil biochemical properties and role of Eisenia fetida. Ecotox Environ Safe 74:668–674
Torstensson L, del Castillo MP (1997) Use of biobeds in Sweden to minimize environmental spillages from agricultural spray equipment. Pestic Outlook 8:24–27
Tortella G, Rubilar O, Castillo M, Cea M, Mella-Herrera R, Diez M (2012) Chlorpyrifos degradation in a biomixture of biobed at different maturity stages. Chemosphere 88:224–228
Urrutia C, Rubilar O, Tortella GR, Diez MC (2013) Degradation of pesticide mixture on modified matrix of a biopurification system with alternatives lignocellulosic wastes. Chemosphere 92:1361–1366
Acknowledgments
We thank Ing. Matías Caillat from the Cooperativa Mixta Ltda (Margarita, Santa Fe, Argentina) for providing the materials used in this work.
Funding
This work was financed by CONICET, ANPCyT, SECTeI, and UNL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Chris Lowe
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lescano, M.R., Masin, C.E., Rodríguez, A.R. et al. Earthworms to improve glyphosate degradation in biobeds. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 27023–27031 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09002-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09002-w