Abstract
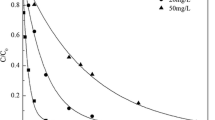
The occurrence of anticancer drugs in the environment has attracted wide attention due to its potential environmental risks. The aim of this study was to investigate degradation characteristics and mechanism of anticancer drug capecitabine (CPC) by electron beam (EB) irradiation. The results showed that EB was an efficient water treatment process for CPC. The degradation followed pseudo-first-order kinetics with dose constants ranged from 1.27 to 3.94 kGy−1. Removal efficiencies in natural water filtered or unfiltered were lower than pure water due to the effect of water matrix components. The degradation was restrained by the presence of NO2−, NO3− and CO32−, and fulvic acid due to competition of reactive radical •OH. It demonstrated that oxidizing radical played important role in irradiation process. The appropriate addition of H2O2 and K2S2O8 providing with oxidizing agents •OH and •SO4− was favorable to improve degradation efficiency of CPC. The possible transformation pathways of CPC including cleavage of the ribofuranose sugar and defluorination were proposed based on intermediate products and were consistent with the theoretical calculation of charge and electron density distribution. Toxicity of CPC and intermediate products were estimated by ECOSAR program. It was found that CPC was transformed to low toxicity products with EB.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel daiem MM, Rivera-Utrilla J, Ocampo-Pérez R, Sánchez-Polo M, López-Peñalver JJ (2013) Treatment of water contaminated with diphenolic acid by gamma radiation in the presence of different compounds. Chem Eng J 219:371–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.12.069
Alkhuraiji TS (2019) Effect of Co60 irradiation on the degradation and mineralization of sulfonated aromatic compounds in aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 228:769–777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.04.087
Atinault E, De Waele V, Schmidhammer U, Fattahi M, Mostafavi M (2008) Scavenging of e(s)(−) and OH(center dot) radicals in concentrated HCl and NaCl aqueous solutions. Chem Phys Lett 460:461–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2008.06.048
Azuma T, Ishiuchi H, Inoyama T, Teranishi Y, Yamaoka M, Sato T, Mino Y (2015) Occurrence and fate of selected anticancer, antimicrobial, and psychotropic pharmaceuticals in an urban river in a subcatchment of the Yodo River basin, Japan. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22:18676–18686. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5013-6
Azuma T et al (2016) Detection of pharmaceuticals and phytochemicals together with their metabolites in hospital effluents in Japan, and their contribution to sewage treatment plant influents. Sci Total Environ 548-549:189–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.12.157
Barışçı S, Turkay O, Ulusoy E, Şeker MG, Yüksel E, Dimoglo A (2018) Electro-oxidation of cytostatic drugs: experimental and theoretical identification of by-products and evaluation of ecotoxicological effects. Chem Eng J 334:1820–1827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.11.105
Besse JP, Latour JF, Garric J (2012) Anticancer drugs in surface waters: what can we say about the occurrence and environmental significance of cytotoxic, cytostatic and endocrine therapy drugs? Environ Int 39:73–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2011.10.002
Booker V, Halsall C, Llewellyn N, Johnson A, Williams R (2014) Prioritising anticancer drugs for environmental monitoring and risk assessment purposes. Sci Total Environ 473-474:159–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.11.145
Calza P, Medana C, Sarro M, Rosato V, Aigotti R, Baiocchi C, Minero C (2014) Photocatalytic degradation of selected anticancer drugs and identification of their transformation products in water by liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1362:135–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.08.035
Chen J, Qu RJ, Pan XX, Wang ZY (2016) Oxidative degradation of triclosan by potassium permanganate: kinetics, degradation products, reaction mechanism, and toxicity evaluation. Water Res 103:215–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.07.041
Claeys L, Iaccino F, Janssen CR, Van Sprang P, Verdonck F (2013) Development and validation of a quantitative structure–activity relationship for chronic narcosis to fish. Environ Toxicol Chem 32:2217–2225. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.2301
Criquet J, Karpel vel Leitner N (2011) Electron beam irradiation of aqueous solution of persulfate ions. Chem Eng J 169:258–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.02.025
Deng J, Shao Y, Gao N, Deng Y, Zhou S, Hu X (2013) Thermally activated persulfate (TAP) oxidation of antiepileptic drug carbamazepine in water. Chem Eng J 228:765–771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.05.044
Desmoulin F, Gilard V, Malet-Martino M, Martino R (2002) Metabolism of capecitabine, an oral fluorouracil prodrug: F-19 NMR studies in animal models and human urine. Drug Metab Dispos 30:1221–1229. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.30.11.1221
Devi P, Das U, Dalai AK (2016) In-situ chemical oxidation: principle and applications of peroxide and persulfate treatments in wastewater systems. Sci Total Environ 571:643–657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.07.032
Elersek T et al (2016) Toxicity of the mixture of selected antineoplastic drugs against aquatic primary producers. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23:14780–14790. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-6005-2
Fabiańska A, Ofiarska A, Fiszka-Borzyszkowska A, Stepnowski P, Siedlecka EM (2015) Electrodegradation of ifosfamide and cyclophosphamide at BDD electrode: decomposition pathway and its kinetics. Chem Eng J 276:274–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.04.071
Franquet-Griell H, Gomez-Canela C, Ventura F, Lacorte S (2017a) Anticancer drugs: consumption trends in Spain, prediction of environmental concentrations and potential risks. Environ Pollut 229:505–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.06.011
Franquet-Griell H, Medina A, Sans C, Lacorte S (2017b) Biological and photochemical degradation of cytostatic drugs under laboratory conditions. J Hazard Mater 323:319–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.06.057
Guo R, Zheng F, Chen J (2015) Evaluation of the aquatic toxic effect varied during the degradation of capecitabine under the environmental abiotic and biotic processes. RSC Adv 5:76772–76778. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra17315a
Isidori M, Piscitelli C, Russo C, Smutna M, Blaha L (2016) Teratogenic effects of five anticancer drugs on Xenopus laevis embryos. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 133:90–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.06.044
Kosjek T, Perko S, Zigon D, Heath E (2013) Fluorouracil in the environment: analysis, occurrence, degradation and transformation. J Chromatogr A 1290:62–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2013.03.046
Lai WW, Lin HH, Lin AY (2015) TiO2 photocatalytic degradation and transformation of oxazaphosphorine drugs in an aqueous environment. J Hazard Mater 287:133–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.01.045
Li Y, Yang SG, Sun C, Wang LH, Wang QG (2016) Aqueous photofate of crystal violet under simulated and natural solar irradiation: kinetics, products, and pathways. Water Res 88:173–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.10.007
Lin HH, Lin AY (2014) Photocatalytic oxidation of 5-fluorouracil and cyclophosphamide via UV/TiO2 in an aqueous environment. Water Res 48:559–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.10.011
Liu N et al (2015) Radiation induced degradation of antiepileptic drug primidone in aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 270:66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.01.120
Liu N, Lei Z-D, Wang T, Wang J-J, Zhang X-D, Xu G, Tang L (2016) Radiolysis of carbamazepine aqueous solution using electron beam irradiation combining with hydrogen peroxide: efficiency and mechanism. Chem Eng J 295:484–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.03.040
Liu N, Huang WY, Li ZM, Shao HY, Wu MH, Lei JQ, Tang L (2018) Radiolytic decomposition of sulfonamide antibiotics: implications to the kinetics, mechanisms and toxicity. Sep Purif Technol 202:259–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.03.060
Lutterbeck CA, Wilde ML, Baginska E, Leder C, Machado EL, Kummerer K (2016) Degradation of cyclophosphamide and 5-fluorouracil by UV and simulated sunlight treatments: assessment of the enhancement of the biodegradability and toxicity. Environ Pollut 208:467–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.10.016
Mendoza A et al (2016) Drugs of abuse, cytostatic drugs and iodinated contrast media in tap water from the Madrid region (central Spain):a case study to analyse their occurrence and human health risk characterization. Environ Int 86:107–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2015.11.001
Misik M, Pichler C, Rainer B, Filipic M, Nersesyan A, Knasmueller S (2014) Acute toxic and genotoxic activities of widely used cytostatic drugs in higher plants: possible impact on the environment. Environ Res 135:196–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2014.09.012
Mohamed KA, Basfar AA, Al-Shahrani AA (2009) Gamma-ray induced degradation of diazinon and atrazine in natural groundwaters. J Hazard Mater 166:810–814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.11.081
Negreira N, de Alda ML, Barcelo D (2014a) Cytostatic drugs and metabolites in municipal and hospital wastewaters in Spain: filtration, occurrence, and environmental risk. Sci Total Environ 497-498:68–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.07.101
Negreira N, Lopez de Alda M, Barcelo D (2014b) Study of the stability of 26 cytostatic drugs and metabolites in wastewater under different conditions. Sci Total Environ 482–483:389–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.02.131
Novak M, Zegura B, Modic B, Heath E, Filipic M (2017) Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of anticancer drug residues and their mixtures in experimental model with zebrafish liver cells. Sci Total Environ 601-602:293–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.115
Ocampo-Pérez R, Sánchez-Polo M, Rivera-Utrilla J, Leyva-Ramos R (2010) Degradation of antineoplastic cytarabine in aqueous phase by advanced oxidation processes based on ultraviolet radiation. Chem Eng J 165:581–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.09.076
Ocampo-Pérez R, Rivera-Utrilla J, Sánchez-Polo M, López-Peñalver JJ, Leyva-Ramos R (2011) Degradation of antineoplastic cytarabine in aqueous solution by gamma radiation. Chem Eng J 174:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.07.017
Olalla A, Negreira N, Lopez de Alda M, Barcelo D, Valcarcel Y (2018) A case study to identify priority cytostatic contaminants in hospital effluents. Chemosphere 190:417–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.09.129
Parrella A, Lavorgna M, Criscuolo E, Russo C, Isidori M (2014) Estrogenic activity and cytotoxicity of six anticancer drugs detected in water systems. Sci Total Environ 485-486:216–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.03.050
Rivera-Utrilla J, Daiem MMA, Sanchez-Polo M, Ocampo-Perez R, Lopez-Penalver JJ, Velo-Gala I, Mota AJ (2016) Removal of compounds used as plasticizers and herbicides from water by means of gamma irradiation. Sci Total Environ 569-570:518–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.114
Roshani B, Karpel vel Leitner N (2011) The influence of persulfate addition for the degradation of micropollutants by ionizing radiation. Chem Eng J 168:784–789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.12.023
Santos MSF, Franquet-Griell H, Lacorte S, Madeira LM, Alves A (2017) Anticancer drugs in Portuguese surface waters-estimation of concentrations and identification of potentially priority drugs. Chemosphere 184:1250–1260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.06.102
Secretariat UNECfE (2009) Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS). United Nations Publications
Velo Gala I, Lopez Penalver JJ, Sanchez Polo M, Rivera Utrilla J (2013) Degradation of X-ray contrast media diatrizoate in different water matrices by gamma irradiation. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 88:1336–1343. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.3981
Yin J, Shao B, Zhang J, Li K (2010) A preliminary study on the occurrence of cytostatic drugs in hospital effluents in Beijing, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 84:39–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-009-9884-4
Zhang Z, Yang Q, Wang J (2016) Degradation of trimethoprim by gamma irradiation in the presence of persulfate. Radiat Phys Chem 127:85–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2016.06.019
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 11975147, 11675098, 11875185, and 11775138) and by the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University No. IRT_17R71.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Vítor Pais Vilar
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 37 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huo, Z., Wang, S., Shao, H. et al. Radiolytic degradation of anticancer drug capecitabine in aqueous solution: kinetics, reaction mechanism, and toxicity evaluation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 20807–20816 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08500-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08500-1