Abstract
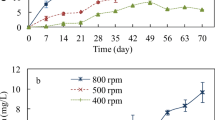
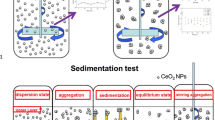
Environmental waters cover a range of water quality characteristics which could greatly affect the behavior and fate of C60 in the aquatic environment. In this study, the dispersion and stability of C60 in several environmental water matrices during a 70-day extended mixing period were investigated to better understand its environmental behavior and fate in environmental waters. Relatively stable nanoscale aggregates in water (aqu/nC60) could be formed in wastewater influent, while unstable suspensions were obtained in river water, wastewater effluent, seawater, and estuarine water. During the extended mixing under sunlight, oxygen-containing moieties were produced on the surface of the C60 aggregates, independent of the kind of environmental water matrices. Once the mixed system went under quiescent condition, aggregation and sedimentation of aqu/nC60 occurred. However, an extremely short-time disturbance could easily resuspend the C60 aggregates deposited and increase the concentration of aqu/nC60 in the overlying water column. Therefore, the effects of resuspension should be considered when investigating the environmental behavior and fate of C60.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baun A, Sørensen SN, Rasmussen RF, Hartmann NB, Koch CB (2008) Toxicity and bioaccumulation of xenobiotic organic compounds in the presence of aqueous suspensions of aggregates of nano-C60. Aquat Toxicol 86(3):379–387
Bijarbooneh FH, Zhao Y, Kim JH, Sun Z, Malgras V, Aboutalebi SH, Heo YU, Ikegami M, Dou SX (2013) Aqueous colloidal stability evaluated by zeta potential measurement and resultant TiO2 for superior photovoltaic performance. J Am Ceram Soc 96(8):2636–2643
Bouchard D, Ma X, Isaacson C (2009) Colloidal properties of aqueous fullerenes: isoelectric points and aggregation kinetics of C60 and C60 derivatives. Environ Sci Technol 43(17):6597–6603
Brant J, Lecoanet H, Wiesner MR (2005) Aggregation and deposition characteristics of fullerene nanoparticles in aqueous systems. J Nanopart Res 7(4–5):545–553
Brunelli A, Pojana G, Callegaro S, Marcomini A (2013) Agglomeration and sedimentation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles (n-TiO2) in synthetic and real waters. J Nanopart Res 15(6):1–10
Chang XJ, Vikesland PJ (2011) UV-vis spectroscopic properties of nC60 produced via extended mixing. Environ Sci Technol 45(23):9967–9974
Chen KL, Elimelech M (2006) Aggregation and deposition kinetics of fullerene (C60) nanoparticles. Langmuir 22(26):10994–11001
Chen KL, Elimelech M (2007) Influence of humic acid on the aggregation kinetics of fullerene (C60) nanoparticles in monovalent and divalent electrolyte solutions. J Colloid Interface Sci 309(1):126–134
Chen KL, Elimelech M (2009) Relating colloidal stability of fullerene (C60) nanoparticles to nanoparticle charge and electrokinetic properties. Environ Sci Technol 43(19):7270–7276
Cho M, Snow SD, Hughes JB, Kim JH (2011) Escherichia coli inactivation by UVC-irradiated C60: kinetics and mechanisms. Environ Sci Technol 45(22):9627–9633
Costa CLA, Chaves IS, Ventura-Lima J, Ferreira JLR, Ferraz L, Carvalho LMD, Monserrat JM (2012) In vitro evaluation of co-exposure of arsenium and an organic nanomaterial (fullerene, C60) in zebrafish hepatocytes. Comput Biol Chem 155(2):206–212
Deguchi S, Alargova RG, Tsujii K (2001) Stable dispersion of fullerenes, C60, and C70, in water preparation and characterization. Langmuir 17(19):6013–6017
Duncan LK, Jinschek JR, Vikesland PJ (2008) C60 colloid formation in aqueous systems: effects of preparation method on size, structure, and surface, charge. Environ Sci Technol 42(1):173–178
Ferreira JLR, Lonné MN, França TA, Maximilla NR, Lugokenski TH, Costa PG, Fillmann G, Soares FAA, Torre FR, Monserrat JM (2014) Co-exposure of the organic nanomaterial fullerene C60 with benzo[a]pyrene in danio rerio (zebrafish) hepatocytes: evidence of toxicological interactions. Aquat Toxicol 147:76–83
Fortner JD, Kim DI, Boyd AM, Falkner JC, Moran S, Colvin VL, Hughes JB, Kim JH (2007) Reaction of water-stable C60 aggregates with ozone. Environ Sci Technol 41(21):7497–7502
Fortner JD, Lyon DY, Sayes CM, Boyd AM, Falkner JC, Hotze EM, Alemany LB, Tao YJ, Guo W, Ausman KD, Colvin VL, Hughes JB (2005) C60 in water: nanocrystal formation and microbial response. Environ Sci Technol 39(11):4307–4316
Gauthier TD, Seitz WR, Grant CL (1987) Effects of structural and compositional variations of dissolved humic materials on pyrene koc values. Environ Sci Technol 21(3):243–248
Hong S, Elimelech M (1997) Chemical and physical aspects of natural organic matter (NOM) fouling of nanofiltration membranes. J Membr Sci 132(2):159–181
Hou W, Jafvert C (2009) Photochemistry of aqueous C60 clusters: evidence of 1O2 formation and its role in mediating C60 phototransformation. Environ Sci Technol 43(14):5257–5262
Hwang YS, Li QL (2010) Characterizing photochemical transformation of aqueous nC60 under environmentally relevant conditions. Environ Sci Technol 44(8):3008–3013
Indeglia PA, Krishna VB, Georgieva A, Bonzongo JJ (2013) Mechanical transformation of fullerene (C60) to aqueous nano-C60 (aqu-nC60) in the presence and absence of light. J Nanopart Res 15(11):2069
Isaacson CW, Bouchard DC (2010) Effects of humic acid and sunlight on the generation and aggregation state of aqu/C60 nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 44(23):8971–8976
Jafvert CT, Kulkarni PP (2008) Buckminsterfullerene’s (C60) octanol-water partition coefficient (Kow) and aqueous solubility. Environ Sci Technol 42(16):5945–5950
Ji KH, Kim JK, Choi KH (2014) Sunlight enhances toxicity of fullerene (C60) to freshwater invertebrates Daphnia magna and Moina macrocopa. Korean J Public Health 51(1):35–45
Kamanina NV (2004) Photoinduced phenomena in fullerene-doped PDLC. Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Opt Eng 5565:377–382
Keller AA, Wang HT, Zhou DX, Lenihan HS, Cherr G, Cardinale BJ, Miller R, Ji ZX (2010) Stability and aggregation of metal oxide nanoparticles in natural aqueous matrices. Environ Sci Technol 44(6):1962–1967
Kim K, Jang M, Kim J, Kim SD (2010) Effect of preparation methods on toxicity of fullerene water suspensions to Japanese medaka embryos. Sci Total Environ 408(22):5606–5612
Kong L, Zepp RG (2012) Production and consumption of reactive oxygen species by fullerenes. Environ Toxicol Chem 31(1):136–143
Lee J, Min C, Fortner JD, Hughes JB, Kim JH (2009) Transformation of aggregated C60 in the aqueous phase by UV irradiation. Environ Sci Technol 43(13):4878–4883
Li QL, Xie B, Hwang YS, Xu YJ (2009) Kinetics of C60 fullerene dispersion in water enhanced by natural organic matter and sunlight. Environ Sci Technol 43(10):3574–3579
Lv XH, Huang BM, Zhu XS, Jiang YL, Chen BY, Tao Y, Zhou J, Cai ZH (2017) Mechanisms underlying the acute toxicity of fullerene to Daphnia magna: energy acquisition restriction and oxidative stress. Water Res 123:696–703
Lyon DY, Adams LK, Falkner JC, Alvarezt PJ (2006) Antibacterial activity of fullerene water suspensions: effects of preparation method and particle size. Environ Sci Technol 40(14):4360–4366
Ma X, Bouchard D (2009) Formation of aqueous suspensions of fullerenes. Environ Sci Technol 43(2):330–336
Markus AA, Parsons JR, Roex EWM, de Voogt P, Laane RWPM (2015) Modeling aggregation and sedimentation of nanoparticles in the aquatic environment. Sci Total Environ 506–507:323–329
Mashayekhi H, Ghosh S, Du P, Xing B (2012) Effect of natural organic matter on aggregation behavior of C60 fullerene in water. J Colloid Interface Sci 374(1):111–117
Mousavi SZ, Nafisi S, Maibach HI (2017) Fullerene nanoparticle in dermatological and cosmetic applications. Nanomedicine 13(3):1071–1087
Nakanishi I, Fukuzumi S, Konishi T, Ohkubo K, Fujitsuka M, Ito O, Miyata N (2002) DNA cleavage via superoxide anion formed in photoinduced electron transfer from NADH to γ-cyclodextrin-bicapped C60 in an oxygen-saturated aqueous solution. J Phys Chem B 106(9):2372–2380
Oberdörster E, Zhu S, Blickley TM, McClellan-Green P, Haasch ML (2006) Ecotoxicology of carbon-based engineered nanoparticles: effects of fullerenes (C60) on aquatic organisms. Carbon 44(6):1112–1120
Olsen CF, Cutshall N, Larsen I (1982) Pollutant-particle associations and dynamics in coastal marine environments: a review. Mar Chem 11(6):501–533
Pakarinen K, Petersen EJ, Alvila L, Waissi-Leinonen GC, Akkanen J, Leppänen MT, Kukkonen JVK (2013) A screening study on the fate of fullerenes (nC60) and their toxic implications in natural freshwaters. Environ Toxicol Chem 32(6):1224–1232
Palmer NE, von Wandruszka R (2001) Dynamic light scattering measurements of particle size development in aqueous humic materials. Fresenius J Anal Chem 371(7):951–954
Pan B, Ghosh S, Xing B (2008) Dissolved organic matter conformation and its interaction with pyrene as affected by water chemistry and concentration. Environ Sci Technol 42(5):1594–1599
Polewski K, Sławinska D, ławinski JS, Pawlak A (2005) The effect of UV and visible light radiation on natural humic acid: EPR spectral and kinetic studies. Geoderma 126(3):291–299
Qu X, Hwang YS, Alvarez PJ, Bouchard D, Li QL (2010) UV irradiation and humic acid mediate aggregation of aqueous fullerene (nC60) nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 44(20):7821–7826
Quik JTK, Stuart MC, Wouterse M, Peijnenburg W, Hendriks J, Meent DVD (2012) Natural colloids are the dominant factor in the sedimentation of nanoparticles. Environ Toxicol Chem 31(5):1019–1022
Sanchís J, Aminot Y, Abad E, Jha AN, Readman JW, Farré M (2018) Transformation of C60 fullerene aggregates suspended and weathered under realistic environmental conditions. Carbon 128:54–62
Sayes CM, Fortner JD, Guo W, Lyon D, Boyd AM, Ausman KD, Tao YJ, Sitharaman B, Wilson LJ, Hughes JB, West JL, Colvin VL (2004) The differential cytotoxicity of water-soluble fullerenes. Nano Lett 4(10):1881–1188
Sherigara BS, Kutner W, D’Souza F (2003) Electrocatalytic properties and sensor applications of fullerenes and carbon nanotubes. Electroanalysis 15(9):753–772
Socoowski BR, Garcia ML, Martins DRA, Flores JA, Pinheiro MV, Monserrat JM, Ferreira JL (2012) Effects of carbon nanomaterials fullerene C60 and fullerol C60(OH)18–22 on gills of fish Cyprinus carpio (Cyprinidae) exposed to ultraviolet radiation. Aquat Toxicol 114–115:80–87
Sutton R, Sposito G (2005) Molecular structure in soil humic substances: the new view. Environ Sci Technol 39(23):9009–9015
Terashima M, Fukushima M, Tanaka S (2004) Evaluation of solubilizing ability of humic aggregate basing on the phase-separation model. Chemosphere 57(6):439–445
Wharton T, Wilson LJ (2002) Highly-iodinated fullerene as a contrast agent for X-ray imaging. Bioorg Med Chem 10(11):3545–3554
Xie B, Xu Z, Guo W, Li Q (2008) Impact of natural organic matter on the physicochemical properties of aqueous C60 nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 42(8):2853–2859
Yan XM, Zha JM, Shi BY, Wang DS, Wang ZJ, Tang HX (2010) In vivo toxicity of nano-C60 aggregates complex with atrazine to aquatic organisms. Chin Sci Bull 55(4–5):339–345
Yang L, Niu JF, Shang EX, Crittenden J (2015) Synergistic photogeneration of reactive oxygen species by dissolved organic matter and C60 in aqueous phase. Environ Sci Technol 49(2):965–973
Yang YK, Nakada N, Nakajima R, Yasojima M, Wang C, Tanaka H (2013) pH, ionic strength and dissolved organic matter alter aggregation of fullerene C60 nanoparticles suspensions in wastewater. J Hazard Mater 244–245:582–587
Zhang LQ, Zhang YK, Lin XC, Yang K, Lin DH (2014) The role of humic acid in stabilizing fullerene (C60) suspensions. J Zheijang Univ Sci A 15(8):634–642
Zhang Y, Chen Y, Westerhoff P, Crittenden J (2009) Impact of natural organic matter and divalent cations on the stability of aqueous nanoparticles. Water Res 43(17):4249–4257
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51479016 and 51308083), the Startup Foundation for Doctoral Scientific Research of Liaoning Province (20170520368), and the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province of China (20180510004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ester Heath
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1222 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, G., Li, X., Zhang, J. et al. The dispersion, stability, and resuspension of C60 in environmental water matrices. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 25538–25549 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05817-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05817-4