Abstract
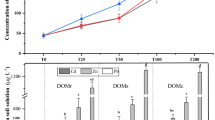
Dissolved organic matter (DOM) extracted from wheat straw (SDOM) and cow manure (MDOM) were used to investigate their effects on the solubilization, uptake, and translocation of 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-47). Partition coefficients (KDOC) of BDE 47 between water and the two types of DOM were measured by the solubility enhancement method. The uptake and translocation of BDE 47 by wheat plants were explored by hydroponic exposure experiments. In the range of 0 to 100 mg/L of DOM, the solubility of BDE 47 increased with increasing concentrations of DOM. The log [KDOC] values of BDE 47 in SDOM and MDOM solutions were 5.77 and 5.31, respectively. The log [KDOC] values of BDE 47 in SDOM solutions were higher than those in MDOM solutions, which might be ascribed to the higher content of aliphatic carbon and lower molecular weight of SDOM. The addition of DOM (50 mg/L) significantly increased the accumulation of BDE 47 in the shoots of wheat plants. Wheat straw DOM had greater effect than MDOM in enhancing the accumulation of BDE 47. This study demonstrated the potential risk of BDE 47 to plants resulting from DOM-facilitated transport or the changes in metabolic properties.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiken GR, Hsu-Kim H, Ryan JN (2011) Influence of dissolved organic matter on the environmental fate of metals, nanoparticles, and colloids. Environ Sci Technol 45:3196–3201
Akkanen J, Vogt RD, Kukkonen JVK (2004) Essential characteristics of natural dissolved organic matter affecting the sorption of hydrophobic organic contaminants. Aquatic Sci 66:171–177
Chen G, Lin C, Chen L, Yang H (2010) Effect of size-fractionation dissolved organic matter on the mobility of prometryne in soil. Chemosphere 79:1046–1055
Chen XF, Chen CG, Wang X, Zhao RS (2012) Sensitive determination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in environmental water samples with etched stainless steel wire based on solid-phase microextraction prior to gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Anal Methods 4:2908–2913
Cheng KY, Wong JWC (2006) Combined effect of nonionic surfactant Tween 80 and DOM on the behaviors of PAHs in soil–water system. Chemosphere 62:1907–1916
Chin YP, Aiken GR, Danielsen KM (1997) Binding of pyrene to aquatic and commercial humic substances: the role of molecular weight and aromaticity. Environ Sci Technol 31:1630–1635
de Wit CA (2002) An overview of brominated flame retardants in the environment. Chemosphere 46:583–624
Gallé T, Grégoire C, Wagner M, Bierl R (2005) Bioavailability of HOC depending on the colloidal state of humic substances: a case study with PCB-77 and Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 61:282–292
Gao Y, Xiong W, Ling W, Wang X, Li Q (2007) Impact of exotic and inherent dissolved organic matter on sorption of phenanthrene by soils. J Hazard Mater 140:138–144
Haitzer M, Höss S, Traunspurger W, Steinberg C (1998) Effects of dissolved organic matter (DOM) on the bioconcentration of organic chemicals in aquatic organisms – a review. Chemosphere 37:1335–1362
Huang H, Zhang S, Christie P, Wang S, Xie M (2010) Behavior of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) in the soil–plant system: uptake, translocation, and metabolism in plants and dissipation in soil. Environ Sci Technol 44:663–667
Jin J, Wang Y, Liu W, Yang C, Hu J, Cui J (2011) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in atmosphere and soil of a production area in China: levels and partitioning. J Environ Sci 23:427–433
Johnson WP, Amy GL (1995) Facilitated transport and enhanced desorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by natural organic matter in aquifer sediments. Environ Sci Technol 29:807–817
Kim YJ, Osako M, Sakai SI (2006) Leaching characteristics of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) from flame-retardant plastics. Chemosphere 65:506–513
Kuivikko M, Sorsa K, Kukkonen JVK, Akkanen J, Kotiaho T, Vähätalo AV (2010) Partitioning of tetra- and pentabromo diphenyl ether and benzo[a]pyrene among water and dissolved and particulate organic carbon along a salinity gradient in coastal waters. Environ Toxicol Chem 29:2443–2449
Kukkonen J, Oikari A (1991) Bioavailability of organic pollutants in boreal waters with varying levels of dissolved organic material. Water Res 25:455–463
Kukkonen J, Pellinen J (1994) Binding of organic xenobiotics to dissolved organic macromolecules: comparison of analytical methods. Sci Total Environ 152:19–29
Li Y, He W, Liu W, Kong X, Yang B, Yang C, Xu F (2015) Influences of binding to dissolved organic matter on hydrophobic organic compounds in a multi-contaminant system: coefficients, mechanisms and ecological risks. Environ Pollut 206:461–468
Li H, Qiu Y, Wang X, Liu W, Chen G, Ma Y, Xing B (2016) Suspension stability and aggregation of multi-walled carbon nanotubes as affected by dissolved organic matters extracted from agricultural wastes. Environ Pollut 210:323–329
Lin H, Xia X, Bi S, Jiang X, Wang H, Zhai Y, Wen W (2018) Quantifying bioavailability of pyrene associated with dissolved organic matter of various molecular weights to Daphnia magna. Environ Sci Technol 52:644–653
Louie SM, Tilton RD, Lowry GV (2013) Effects of molecular weight distribution and chemical properties of natural organic matter on gold nanoparticle aggregation. Environ Sci Technol 47:4245–4254
Lu M, Zhang Z, Su X, Xu Y, Wu X, Zhang M (2013) Effect of copper on in vivo fate of BDE-209 in pumpkin. J Hazard Mater 262:311–317
Nardi S, Pizzeghello D, Muscolo A, Vianello A (2002) Physiological effects of humic substances on higher plants. Soil Biol Biochem 34:1527–1536
Nuerla A, Qiao X, Li J, Zhao D, Yang X, Xie Q, Chen J (2013) Effects of substituent position on the interactions between PBDEs/PCBs and DOM. Chin Sci Bull 58:884–889
Rahman F, Langford KH, Scrimshaw MD, Lester JN (2001) Polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) flame retardants. Sci Total Environ 275:1–17
Schnitzler F, Lavorenti A, Berns AE, Drewes N, Vereecken H, Burauel P (2007) The influence of maize residues on the mobility and binding of benazolin: investigating physically extracted soil fractions. Environ Pollut 147:4–13
Song M, Chu S, Letcher RJ, Seth R (2006) Fate, partitioning, and mass loading of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) during the treatment processing of municipal sewage. Environ Sci Technol 40:6241–6246
Song NH, Zhang S, Hong M, Yang H (2010) Impact of dissolved organic matter on bioavailability of chlorotoluron to wheat. Environ Pollut 158:906–912
Vrkoslavová J, Demnerová K, Macková M, Zemanová T, Macek T, Hajšlová J, Pulkrabová J, Hrádková P, Stiborová H (2010) Absorption and translocation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) by plants from contaminated sewage sludge. Chemosphere 81:381–386
Wang S, Zhang S, Huang H, Zhao M, Lv J (2011a) Uptake, translocation and metabolism of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in maize (Zea mays L.). Chemosphere 85:379–385
Wang W, Delgado-Moreno L, Ye Q, Gan J (2011b) Improved measurements of partition coefficients for polybrominated diphenyl ethers. Environ Sci Technol 45:1521–1527
Wang X, Shu L, Wang Y, Xu B, Bai Y, Tao S, Xing B (2011c) Sorption of peat humic acids to multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Environ Sci Technol 45:9276–9283
Wang Y, Zhu H, Tam NFY (2014) Effect of a polybrominated diphenyl ether congener (BDE-47) on growth and antioxidative enzymes of two mangrove plant species, Kandelia obovata and Avicennia marina, in South China. Mar Pollut Bull 85:376–384
Wania F, Dugani CB (2003) Assessing the long-range transport potential of polybrominated diphenyl ethers: a comparison of four multimedia models. Environ Toxicol Chem 22(6):1252–1261
Wei-Haas ML, Hageman KJ, Chin Y (2014) Partitioning of polybrominated diphenyl ethers to dissolved organic matter isolated from Arctic surface waters. Environ Sci Technol 48:4852–4859
Xu X, Huang H, Wen B, Wang S, Zhang S (2015) Phytotoxicity of brominated diphenyl ether-47 (BDE-47) and its hydroxylated and methoxylated analogues (6-OH-BDE-47 and 6-MeO-BDE-47) to maize (Zea mays L.). Chem Res Toxicol 28:510–517
Yang C, Chang M, Wu S, Shih Y (2017) Partition uptake of a brominated diphenyl ether by the edible plant root of white radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Environ Pollut 223:178–184
Yue L, Wu F, Liu C, Li W, Wang J, Mei Y (2004) Molecular weight distribution of dissolved organic matter in Lake Hongfeng determined by high performance size exclusion chromatography (HPSEC) with on-line UV-vis absorbance and fluorescence detection. Chin J of Geochem 23:275–283
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21207049).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ester Heath
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 22 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Shao, F., Qiu, Y. et al. Solubility, uptake, and translocation of BDE 47 as affected by DOM extracted from agricultural wastes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 19871–19878 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05393-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05393-7