Abstract
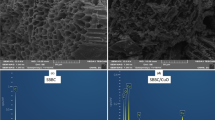
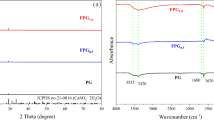
Given the prevalence of nitrate and phosphate in surface and groundwater, it is important to develop technology for the simultaneous removal of nitrate and phosphate. In this study, we prepared the bimetallic nanoparticles of Fe coupled with copper or nickel supported on chelating resin DOW 3N (D-Fe/Ni and D-Fe/Cu) for removing nitrate and phosphate simultaneously. XPS profiles revealed that Cu has better ability than Ni to increase the stability of Fe nanoparticles and prevent nZVI from oxidation. The results showed that nitrate removal efficiencies by D-Fe/Ni and D-Fe/Cu were 98.7% and 95.5%, respectively and the phosphate removal efficiencies of D-Fe/Cu and D-Fe/Ni were 99.0% and 93.0%, respectively. Besides adsorption and coprecipitation as reported in previous studies, the mechanism of phosphate removal also includes the adsorption of the newly formed polymeric ligand exchanger (PLE). Moreover, in previous studies, the presence of phosphate had significant negative effects on the reduction of nitrate. However, in this study, the removal efficiency of nitrate was less affected with the increasing concentration of phosphate for D-Fe/Cu. This was mainly because D-Fe/Cu had higher adsorption capacity of phosphate due to the newly formed PLE according to the XPS depth profile analysis.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acelas NY, Martin BD, López D, Jefferson B (2015) Selective removal of phosphate from wastewater using hydrated metal oxides dispersed within anionic exchange media. Chemosphere 119:1353–1360
Almeelbi T, Bezbaruah A (2012) Aqueous phosphate removal using nanoscale zero-valent iron. J Nanopart Res 14:900–914
An B, Steinwinder TR, Zhao D (2005) Selective removal of arsenate from drinking water using a polymeric ligand exchanger. Water Res 39:4993–5004
An B, Nam J, Choi JW, Hong SW, Lee SH (2013) Enhanced phosphate selectivity from wastewater using copper-loaded chelating resin functionalized with polyethylenimine. J Colloid Interface Sci 409:129–134
Dong L, Lin L, Li Q, Huang Z, Tang X, Wu M, Li C, Cao X, Scholz M (2018) Enhanced nitrate-nitrogen removal by modified attapulgite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron treating simulated groundwater. J Environ Manag 213:151–158
Du HX, Lung CYK, Lau TC (2018) Efficient adsorption, removal and recovery of phosphate and nitrate from water by a novel lanthanum(iii)-Dowex M4195 polymeric ligand exchanger. Environ Sci-Wat Res 4:421–427
Garcia-Segura S, Lanzarini-Lopes M, Hristovski K, Westerhoff P (2018) Electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate: fundamentals to full-scale water treatment applications. Appl Catal B Environ 236:546–568
He Y, Lin H, Dong Y, Li B, Wang L, Chu S, Luo M, Liu J (2018) Zeolite supported Fe/Ni bimetallic nanoparticles for simultaneous removal of nitrate and phosphate: synergistic effect and mechanism. Chem Eng J 347:669–681
Henry WD, Zhao D, SenGupta AK, Lange C (2004) Preparation and characterization of a new class of polymeric ligand exchangers for selective removal of trace contaminants from water. React Funct Polym 60:109–120
Hua M, Xiao L, Pan B, Zhang Q (2013) Validation of polymer-based nano-iron oxide in further phosphorus removal from bioeffluent: laboratory and scaled up study. Front Env Sci Eng 7:435–441
Khalil AME, Eljamal O, Amen TWM, Sugihara Y, Matsunaga N (2017) Optimized nano-scale zero-valent iron supported on treated activated carbon for enhanced nitrate and phosphate removal from water. Chem Eng J 309:349–365
Khalil AME, Eljamal O, Saha BB, Matsunaga N (2018) Performance of nanoscale zero-valent iron in nitrate reduction from water using a laboratory-scale continuous-flow system. Chemosphere 197:502–512
Li N, Tian Y, Zhao J, Zhan W, Du J, Kong L, Zhang J, Zuo W (2018) Ultrafast selective capture of phosphorus from sewage by 3D Fe3O4@ZnO via weak magnetic field enhanced adsorption. Chem Eng J 341:289–297
Liu F, Yang J, Zuo J, Ma D, Gan L, Xie B, Wang P, Yang B (2014) Graphene-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron: removal of phosphorus from aqueous solution and mechanistic study. J Environ Sci 26:1751–1762
Loganathan P, Vigneswaran S, Kandasamy J, Bolan NS (2014) Removal and recovery of phosphate from water using sorption. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 44:847–907
Lundberg JO, Weitzberg E, Cole JA, Benjamin N (2004) Nitrate, bacteria and human health. Nat Rev Microbiol 2:593–602
Shi J, Yi S, He H, Long C, Li A (2013) Preparation of nanoscale zero-valent iron supported on chelating resin with nitrogen donor atoms for simultaneous reduction of Pb2+ and NO3. Chem Eng J 230:166–171
Shi J, Long C, Li A (2016) Selective reduction of nitrate into nitrogen using Fe–Pd bimetallic nanoparticle supported on chelating resin at near-neutral pH. Chem Eng J 286:408–415
Shi J, Ma Y, Shen Z, Liu D, Long C, Zhang X, Shi J, Wang C (2018) Fe-Pd bimetallic composites supported by resins for nitrate reduction: role of surface functional groups in controlling rate and selectivity. Environ Eng Sci 36:295–304. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2018.0204
Sleiman N, Deluchat V, Wazne M, Mallet M, Courtin-Nomade A, Kazpard V, Baudu M (2017) Phosphate removal from aqueous solutions using zero valent iron (ZVI): influence of solution composition and ZVI aging. Colloids Surf A 514:1–10
Wen Z, Zhang Y, Dai C (2014) Removal of phosphate from aqueous solution using nanoscale zerovalent iron (nZVI). Colloids Surf A 457:433–440
Wu X, Lu S, Qiu Z, Sui Q, Lin K, Du X, Luo Q (2014) The reductive degradation of 1,1,1-trichloroethane by Fe(0) in a soil slurry system. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:1401–1410
Zhang Q, Liu H, Chen T, Chen D, Li M, Chen C (2017) The synthesis of NZVI and its application to the removal of phosphate from aqueous solutions. Water Air Soil Pollut 228:321–331
Zhao D, Sengupta AK (1998) Ultimate removal of phosphate from wastewater using a new class of polymeric ion exchangers. Water Res 32:1613–1625
Zheng T, Zhan J, He J, Day C, Lu Y, McPherson GL, Piringer G, John VT (2008) Reactivity characteristics of nanoscale zerovalent iron-silica composites for trichloroethylene remediation. Environ Sci Technol 42:4494–4499
Funding
This research was financially funded by the postdoctoral science foundation of China (No. 2018M642758), the State Key Laboratory of Pollution Control and Resource Reuse Foundation (No. PCRRF 17034), the Education Department of the Henan Science and Technology Fund Project (No. 16A610009), the State Key Program of National Natural Science of China (No. 51438008 and No. 51604099).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Bingcai Pan
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 668 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, Z., Dong, X., Shi, J. et al. Simultaneous removal of nitrate/phosphate with bimetallic nanoparticles of Fe coupled with copper or nickel supported on chelating resin. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 16568–16576 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05050-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05050-z