Abstract
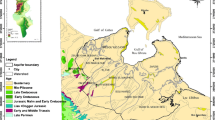
An appraisal of seawater intrusion into the coastal aquifers is one of the major issues for groundwater resource management. The GALDIT model applies to the analysis of multiple parameters using systematic GIS techniques for mapping and assessment of seawater intrusion vulnerability. It demarcates the mapping of potential vulnerability that shows a higher vulnerability to seawater intrusion in various parts of the coast and the estimated vulnerability index value of 7.50 and 9.64. An area of 33.0 km2 spread in the low-lying coastal area comprising estuaries, salt marshes, and saltpans shows the high vulnerability condition with an estimated vulnerability value of 6.42–7.50. An area of 73.20 km2 spread over coastal and alluvial plains experiences moderate vulnerability (temporal salinity in the groundwater sources) with an estimated vulnerability index value of 5.46–6.42. Aquifers underlying coastal uplands (hard rock formations) and some parts of accretionary beaches (2.05 km2) are relatively protected fresh groundwater sources, wherein the estimated vulnerability index is 4.55–5.46. The vulnerability mapping of the GALDIT model using hydrochemical analysis of primary groundwater parameters such as TDS, Cl−, HCO3, and Cl−/HCO3 ratio is validated. Higher concentration of TDS (2637–4162 mg/l) and Cl− (1268–2347 mg/l) is taken for the areas falling under higher vulnerability to seawater intrusion, especially in the placer mining sites and coastal areas facing erosion. Similarly, the groundwater sources of the low-lying areas including estuaries, salt marshes, saltpans, and backwater were noted to have higher values of Cl−/HCO3 with a rationality of 9.87–12.18. Hydrological facies shows the highest concentration of NaCl in the groundwater sources within the proximity of eroded beaches, saltwater bodies, and sand mining areas. A hydrochemical facies evolution (HFE) diagram represents the hydrochemical facies of groundwater elements that shows an intrusion of seawater into the coastal aquifers underlying the very high vulnerable zones. Higher bicarbonate concentration (233–318 mg/l) is noticed in the upland areas and some parts of dunes and accreted beaches, sandy coasts, and uplands. Vulnerability analysis reveals that those areas near saltwater bodies and eroding coasts are prone to lateral and vertical diffusion of saltwater. The geodatabase developed through such modeling studies can help in planning and developing activities for sustainable groundwater resource management in coastal areas.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adepelumi AA, Ako BD, Ajayi TR, Afolabi O, Omotoso EJ (2009) Delineation of saltwater intrusion into the freshwater aquifer of Lekki Peninsula, Lagos, Nigeria. Environ Geol 56(5):927–933
Agoubi B, Kharroubi A, Abida H (2013) Hydrochemistry of groundwater and its assessment for irrigation purpose in coastal Jeffara aquifer, southeastern Tunisia. Arab J Geosci 6(4):1163–1172
Ahmadi SH, Sedghamiz A (2007) Geostatistical analysis of spatial and temporal variations of groundwater level. Environ Monit Assess 129:277–294
Al-Adamat RAN, Foster IDL, Baban SMJ (2003) Groundwater vulnerability and risk mapping for the basaltic aquifer of the Azraq Basin of Jordan using GIS, remote sensing and DRASTIC. Appl Geogr 23:303–324
Alam F (2010) Aquifer system and groundwater resource evaluation in parts of Hindon–Yamuna watershed in parts of western Uttar Pradesh. Unpublished PhD thesis, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh. pp. 227–240
Albinet M, Margat J (1970) Groundwater pollution vulnerability mapping. Bull. Bur. rech. géol. min. Sect. 2 Géol. gîtes minér 3(4):13–22
Alfarrah N, Walraevens K (2018) Groundwater overexploitation and seawater intrusion in coastal areas of arid and semi-arid regions. Water 10(2):143
Aller L, Bennett T, Lehr JH, Petty RJ, Hackett G (1987) DRASTIC: a standardized system for evaluating groundwater pollution potential using hydrogeologic settings. US EPA/600/2-87/035. pp. 622
Allouche N, Brahim FB, Gontara M, Khanfir H, Bouri S (2015) Validation of two applied methods of groundwater vulnerability mapping: application to the coastal aquifer system of southern Sfax (Tunisia). Aqua 64(6):719–737
Allouche N, Maanan M, Gontara M, Rollo N, Jmal I, Bouri S (2017) A global risk approach to assessing groundwater vulnerability. Environ Model Softw 88:168–182
Almasri M (2008) Assessment of intrinsic vulnerability to contamination for Gaza coastal aquifer, Palestine. J Environ Manag 88:577–593
Al-Zabet T (2002) Evaluation of aquifer vulnerability to contamination potential using the DRASTIC method. Environ Geol 43:203–208
Antonakos AK, Lambrakis NJ (2007) Development and testing of three hybrid methods for the assessment of aquifer vulnerability to nitrates, based on the DRASTIC model, an example from NE Korinthia, Greece. J Hydrol 333:288–304
Antonellini M, Mollema P, Giambastiani B, Bishop K, Caruso L, Minchio A, Pellegrini L, Sabia M, Ulazzi E, Gabbianelli G (2008) Saltwater intrusion in the coastal aquifer of the southern Po Plain, Italy. Hydrogeol J 16:1541–1556
Aris AZ, Abdullah MH, Ahmed A, Woong KK (2007) Controlling factors of groundwater hydrochemistry in a small island’s aquifer. Int J Environ Sci Technol 4(1735–1472):441–450
Aris A, Abdullah M, Kim KPS (2009) Hydrochemical changes in small tropical island’s aquifer: Manukan Island, Sabah, Malaysia. Environ Geol 56(8):1721–1732
Awawdeh MM, Jaradat RA (2010) Evaluation of aquifers vulnerability to contamination in the Yarmouk River basin, Jordan, based on DRASTIC method. Arab J Geosci 3:273–282
Baalousha H (2010) Assessment of a groundwater quality monitoring network using vulnerability mapping and geostatistics: a case study from Heretaunga Plains, New Zealand. Agric Water Manag 97(2):240–246
Babiker I, Mohamed M, Hiyama T, Kato K (2005a) A GIS-based DRASTIC model for assessing aquifer vulnerability in Kakamigahara Heights, Gifu Prefecture, central Japan. Sci Total Environ 345(1–3):127–140
Babiker IS, Mohamed MAA, Hiyama T, Kato K (2005b) A GIS-based DRASTIC model for assessing aquifer vulnerability in Kakamigahara Heights, Gifu Prefecture, central Japan. Sci Total Environ 345(1–3):127–140
Baharuddin MFT, Taib S, Hashim R, Abidin MHZ, Rahman NI (2013) Assessment of seawater intrusion to the agricultural sustainability at the coastal area of Carey Island, Selangor, Malaysia. Arab J Geosci 6(10):3909–3928
Bahir M, Ouazar D, Ouhamdouch S (2018) Characterization of mechanisms and processes controlling groundwater salinization in coastal semi-arid area using hydrochemical and isotopic investigations (Essaouira basin, Morocco). Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:24992–25004. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2543-8
Bear J, Zhou Q (2007) Seawater intrusion into coastal aquifer. In: Delleur WJ (ed) The handbook of groundwater engineering, 2nd ed. Taylor and Francis, London
Bear J, Cheng AHD, Sorek S, Ouazar D, Herrera I (1999) Seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers: concepts, methods and practices. Kluwer Academic, London
Beaujean J, Lemieux JM, Dassargues A, Therrien R, Brouyère S (2013) Physically based groundwater vulnerability assessment using sensitivity analysis methods. Groundwater 52(6):864–874
Bolster DT, Tartakovsky DM, Dentz M (2007) Analytical models of contaminant transport in coastal aquifers. Adv Water Resour 30:1962–1972
Bouzourra H, Bouhlila R, Elango L, Slama F, Ouslati N (2015) Characterization of mechanisms and processes of groundwater salinization in irrigated coastal area using statistics, GIS, and hydrogeochemical investigations. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:2643–2660. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3428-0
Bureau of Indian Standards (2012) Indian standard specification for drinking water (2nd revision). Government of India, New Delhi
Central Ground Water Board (2014) Report on status of ground water quality in coastal aquifers of India, Technical Report Series pp 120–130
Chachadi AG, Lobo-Ferreira JP (2001) Seawater intrusion vulnerability mapping of aquifers using GALDIT method. COASTIN: a coastal policy research newsletter, TERI, New Delhi. http://www.teriin.org/teri-wr/coastin/newslett/coastin4.pdf
Chae G, Kim K, Yun S, Kim K, Kim S, Choi B, Kim H, Rhee CW (2004) Hydrogeochemistry of alluvial groundwater in an agricultural area: an implication for groundwater contamination susceptibility. Chemosphere 55(3):369–378
Chandrasekar N, Cherian A, Rajamanickam M, Rajamanickam GV (2000) Coastal landform mapping between Tuticorin and Vaippar using IRS-IC data. Indian J Geomorp 5(1&2):115–122
Chandrasekar N, Selvakumar S, Srinivas Y, John Wilson JS, Simon Peter T, Magesh NS (2013) Hydrogeochemical assessment of groundwater quality along the coastal aquifers of southern Tamil Nadu, India. Environ Earth Sci 71:4739–4750
Chen H, Zhang Y, Ren Z, Li L (1997) Salt-water intrusion in the lower reaches of the Weihe River, Shandong Province, China. Hydrogeol J 5(3):82–88
Chidambaram S, Senthil Kumar G, Prasanna MV, Peter AJ, Ramanthan AL, Srinivasamoorthy K (2009) A study on the hydrogeology and hydrogeochemistry of groundwater from different depths in a coastal aquifer: Annamalai Nagar, Tamilnadu India. Environ Geol 57(1):59–73
Civita M, De Maio M (2004) Assessing and mapping groundwater vulnerability to contamination: the Italian “combined” approach. Geofis Int 43(4):513–532
Cooper HH Jr, Kohout FA, Henry HR, Glover RE (1964) Seawater in coastal aquifers—relation of saltwater to freshwater groundwater. Geologicl Survey Water Supply Paper, pp. 1613–1622
Dash JP, Sarangi A, Singh DK (2010) Spatial variability of groundwater depth and quality parameters in the national capital territory of Delhi. Environ Manag 45:640–650
Ding H, Zhang J (2002) The problem of environmental caused by groundwater level continuous decline in the inland basins of arid area, Northwest China—an example in middle reaches of Heihe river basin. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 3:71–75
Doerfliger N, Jeannin PY, Zwahlen F (1999) Water vulnerability assessment in karst environments: a new method of defining protection areas using a multi-attribute approach and GIS tools (EPIK method). Environ Geol 39:165–176
Elango L, Kannan R, Senthilkumar M (2003) Major ion chemistry and identification of hydrogeochemical processes of groundwater in a part of Kancheepuram District, Tamil Nadu, India. J Environ Geosci 10(4):157–166
Elena GF, Javier SSR (2015) An Excel Macro to plot the HFE-diagram to identify seawater intrusion phases. Groundwater 53(5):819–824
El-Fadel M, Tomaszkiewicz M, AbouNajm M (2013) Sustainable coastal aquifer management in urban areas: the role of groundwater quality indices proceedings of the resilient cities 2013 congress. 4th Global Forum on Urban Resilience and Adaptation, Bonn
Elumalai V, Brindh K, Sithole B et al (2017) Spatial interpolation methods and geostatistics for mapping groundwater contamination in a coastal area. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:11601–11617. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8681-6
Essaid E (1986) A comparison of the coupled fresh water-salt water flow and the Ghyben–Herzberg sharp interface approaches to modeling of transient behavior in coastal aquifer systems. J Hydrol 86:169–193
Fass T, Cook PG, Stieglitz T, Herczeg AL (2007) Development of saline groundwater through transpiration of seawater. Ground Water 45(6):703–710
Faye S, Maloszewski P, Stichler W, Trimborn P, Faye SC, Gaye CB (2005) Groundwater salinization in the Saloum (Senegal) delta aquifer: minor elements and isotopic indicators. Sci Total Environ 343:243–259
Ferguson G, Gleeson T (2012) Vulnerability of coastal aquifers to groundwater use and climate change. Nat Clim Chang 2:342–345
Foster SSD (1987) Fundamental concepts in aquifer vulnerability, pollution risk and protection strategy. In: van Duijvanbooden W, van Waegeningh HG (eds) Vulnerability of soil and groundwater to pollution. TNO Committee on Hydrological Research, Delft, The Netherlands
Ghyben BW (1889) Nota in Verband met de Voorgenomen Putboring Nabij Amsterdam [Memorandum related to planned well drilling near Amsterdam]. Tijdschr Koninhitk Inst Ing 9:8–22
Giambastiani BMS, Antonellini M, Oude Essink GHP, Stuurman RJ (2007) Saltwater intrusion in the unconfined coastal aquifer of Ravenna (Italy): a numerical model. J Hydrol 340:91–104
Gibbs RJ (1970) Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 17:1088–1090
Giménez-Forcada E (2010) Dynamic of sea water interface using hydrochemical facies evolution diagram. Groundwater 48(2):212–216
Gogu RC, Dassargues A (2000) Sensitivity analysis for the EPIK method of vulnerability assessment in a small karstic aquifer, southern Belgium. Hydrogeol J 8(3):337–345
Gontara M, Allouche N, Jmal I, Bouri S (2016) Sensitivity analysis for the GALDIT method based on the assessment of vulnerability to pollution in the northern Sfax coastal aquifer. Tunisia Arab J Geosci 9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2437-3
Gounari C, Skordas K, Gounaris A, Kosmidis D, Karyoti A (2014) Seawater intrusion and nitrate pollution in coastal aquifer of Almyros-NeaAnchialos basin, Central Greece. WSEAS Transactions on Environment and Development 10:211–222
Guo H, Wang Y (2004) Specific vulnerability assessment using the MLPI model in Datong City, Shanxi Province, China. Environ Geol 45:401–407
Hamerlinck JD, Arneson CS (1998) Wyoming groundwater vulnerability assessment handbook, vol 1: background, model development and aquifer sensitivity analysis. SDVC 98-01-1, Spatial Data and Visualization Center, Laramie, WY
Hasiniaina F, Zhou J, Guoyi L (2010) Regional assessment of groundwater vulnerability in Tamtsag basin, Mongolia using drastic model. J Am Sci 6(11):65–78
Healy RW (2010) Estimating groundwater recharge. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Henry HR(1964) Effects of dispersion on salt encroachment in coastal aquifers. Sea water in coastal aquifers, U.S. Geol. Surv. Supply Paper, 1613-C, C71–C84
Hentry C (2013) Spatial characterization and coastal change assessment between Kanyakumari and Thengapattanam coast, Kanyakumari district, Tamil Nadu through remote sensing and geographic information system (GIS), Unpublished thesis report, Manonmaniam Sundaranar University, Tirunelveli, pp. 83–110
Hentry C, Chandrasekar N, Saravanan S (2012) Beach dynamics of Colachel open coast, Kanyakumari District (SW India). Z Geomorphol 57(1):75–95
Herzberg B (1901) Die Wasserversorgungeiniger Nordseebäder [The water supply of some resorts on the North Sea]. J Gasbeleuchtung Wasserversorg 44:815–844
Huang G, Sun J, Zhang Y, Chen Z, Liu F (2013) Impact of anthropogenic and natural processes on the evolution of groundwater chemistry in a rapidly urbanized coastal area, South China. Sci Total Environ 463–464:209–221
Huang G, Liu C, Sun J, Zhang M, Jing J, Li L (2018) A regional scale investigation on factors controlling the groundwater chemistry of various aquifers in a rapidly urbanized area: a case study of the Pearl River Delta. Sci Total Environ 625:510–518
Isa NM, Aris AZ, Sulaiman WNAW (2012) Extent and severity of groundwater contamination based on hydrochemistry mechanism of sandy tropical coastal aquifer. Sci Total Environ 438:414–425
Izuka SK, Gingerich SB (1998) Estimation of the depth to the freshwater/salt-water interface from vertical head gradients in wells in coast and island aquifers. Hydrogeol J 6:365–373
Jalali M (2010) Application of multivariate analysis to study water chemistry of groundwater in a semi-arid aquifer, Malayer, Western Iran. Desalin Water Treat 19(1–3):307–317
Jayangondaperumal R, Murari MK, Sivasubramanian P, Chandrasekar N, Singhvi AK (2012) Luminescence dating of fluvial and coastal red sediments in the SE coast, India, and implications for paleoenvironmental changes and dune reddening. Quat Res 77:468–481
Jones BF, Vengosh A, Rosenthal E, Yechieli Y (1999) Geochemical investigations. In: Bear J et al (eds) Seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers concepts, methods and practices. Kluwer Academic, Berlin, pp 51–72
Kaliraj S, Chandrasekar N, Magesh NS (2015a) Evaluation of coastal erosion and accretion processes along the southwest coast of Kanyakumari, Tamil Nadu using geospatial techniques. Arab J Geosci 8(1):239–253
Kaliraj S, Chandrasekar N, Simon Peter T, Selvakumar S, Magesh NS (2015b) Mapping of coastal aquifer vulnerable zone in the south west coast of Kanyakumari, South India, using GIS-based DRASTIC model. Environ Monit Assess 187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-4073-2
Kaliraj S, Chandrasekar N, Ramachandran KK (2017a) Mapping of coastal landforms and volumetric change analysis in the south west coast of Kanyakumari, South India using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Egypt J Remote Sens Space Sci 20(2):265–282
Kaliraj S, Chandrasekar N, Ramachandran KK, Srinivas Y, Saravanan S (2017b) Coastal landuse and land cover change and transformations of Kanyakumari coast, India using remote sensing and GIS. Egypt J Remote Sens Space Sci 20(2):169–185
Kanagaraj G, Elango L, Sridhar SGD, Gowrisankar G (2018) Hydrogeochemical processes and influence of seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers south of Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:8989–9011. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0910-5
Kanakoudis V, Tsitsifli S, Papadopoulou A, Cencur Curk B, Karleusa B (2017) Water resources vulnerability assessment in the Adriatic Sea region: the case of Corfu Island. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:20173–20186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9732-8
Karanth KR (1987) Groundwater assessment development and management. Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi
Kennedy GW (2012) Development of a GIS-based approach for the assessment of relative seawater vulnerability in Nova Scotia. IAH Congress, Canada
Kerrou J, Renard P, Lecca G, Tarhouni J (2010) Grid-enabled Monte Carlo analysis of the impacts of uncertain discharge rates on seawater intrusion in the Korba aquifer (Tunisia). Hydrol Sci J 55(8):1325–1336
Khmaj A, Ezlit Y, Elaalem M (2014) The situation of seawater intrusion in Tripoli, Libya. International conference on biological, chemical and environmental sciences (BCES-2014). Penang
Korfali SI, Jurdi M (2010) Deterioration of coastal water aquifers: causes and impacts. Eur Water 29:3–10
Kouzana L, Benassi R, Ben Mammou A, SfarFelfoul M (2010) Geophysical and hydrochemical study of the seawater intrusion in Mediterranean semi arid zones. Case of the Korba coastal aquifer (Cap-Bon, Tunisia). J Afr Earth Sci 58(2):242–254
Kura NU, Ramli MF, Sulaiman WNA, Ibrahim S, Aris AZ, Mustapha A (2013) Evaluation of factors influencing the groundwater chemistry in a small tropical island of Malaysia. Int J Environ Res Public Health 10(5):1861–1881
Kura NU, Ramli MF, Ibrahim S, Sulaiman WNA, Aris AZ (2014) An integrated assessment of seawater intrusion in a small island using geophysical, geochemical and geostatistical techniques. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:7047–7064. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2598-0
Kura NU, Ramli MF, Ibrahim S, Sulaiman WNA, Aris AZ, Tanko AI, Zaudi MA (2015) Assessment of groundwater vulnerability to anthropogenic pollution and seawater intrusion in a small tropical island using index-based methods. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:1512–1533. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3444-0
Kura NU, Ramli MF, Sulaiman WNA, Ibrahim S, Aris AZ (2018) An overview of groundwater chemistry studies in Malaysia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:7231–7249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5957-6
Latha PS, Rao KN (2012) An integrated approach to assess the quality of groundwater in a coastal aquifer of Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Earth Sci 66:2143–2169
Liggett JE, Talwar S (2009) Groundwater vulnerability assessments and integrated water resource management. Watershed Manag Bull 13(1):18–29
Lodwick WA, Monson W, Svoboda L (1990) Attribute error and sensitivity analysis of map operations in geographical information systems: suitability analysis. Int J Geogr Inf Syst 4(4):413–428
Loveson VJ, Rajamanickam GV (1998) Coastal geomorphology of southern Tamil Nadu. In: Bhanu SK, Jha VK (eds) Proc. of national seminar on remote sensing in land transformation and publ. NRSA, Hyderabad, pp 38–46
Loveson VJ, Angusamy N, Rajamanickam GV (1996) Usefulness of identifying different geomorphic blocks along the coast of southern Tamilnadu. Indian J Geomorp 01:97–110
Lowe M, Butler M (2003) Groundwater sensitivity and vulnerability to pesticides, Herber and Round Valleys, Watsach County, Utah. Utah Geological Survey, Salt Lake City, UT
Luoma S, Okkonen J, Korkka-Niemi K (2017) Comparison of the AVI, modified SINTACS and GALDIT vulnerability methods under future climate-change scenarios for a shallow low-lying coastal aquifer in southern Finland. Hydrogeol J 25:203–222
Madl-Szonyi J, Fule L (1998) Groundwater vulnerability assessment of the SW Trans-Danubian central range. Environ Geol 35:9–17
Mahesha A, Vysh A, Lathashri UA, Ramesh H (2011) Parameter estimation and vulnerability assessment of coastal unconfined aquifer to saltwater intrusion. J Hydrol 17:933–943. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000524
Masoud AA, El Bouraie MM, El-Nashar W et al (2017) Spatiotemporal evaluation of the groundwater quality in Gharbiya Governorate, Egypt. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:8256–8278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8445-3
Mazi K, Koussis AD, Destouni G (2014) Intensively exploited Mediterranean aquifers: resilience to seawater intrusion and proximity to critical thresholds. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 18:663–1677
Melloul AJ, Zeitoun DG (1999) A semi-empirical approach to intrusion monitoring in Israeli coastal aquifer. In: Bear J et al (eds) Seawater intrusionin coastal aquifers concepts, methods and practices. Kluwer Academic, Berlin, pp 543–558
Mondal NC, Singh VP, Singh VS (2011) Hydrochemical characteristic of coastal aquifer from Tuticorin, Tamilnadu, India. Environ Monit Assess 175:531–550
Moujabber M, Bou Samra B, Darwish T (2006) Comparison of different indicators for groundwater contamination by seawater intrusion on the Lebanese Coast. Water Resour Manag 20:161–180
Najib S, Grozavu A, Mehd K, Breaban IG, Guessir H, Boutayeb K (2012) Application of the method GALDIT for the cartography of groundwater vulnerability: aquifer of Chaouia coast (Morocco). Scientific Annals of “AlexandruIoanCuza” University of Iasi - Geography series. https://doi.org/10.15551/scigeo.v58i2.163
Napolitano P, Fabbri AG (1996) Single parameter sensitivity analysis for aquifer vulnerability assessment using DRASTIC and SINTACS. In: Proceedings of the 2nd HydroGIS conference, vol 235. IAHS Publication, Wallingford, pp 559–566
Narany TS, Ramli MF, Aris AZ, Sulaiman WNA, Fakharian K (2014) Spatiotemporal variation of groundwater quality using integrated multivariate statistical and geostatistical approaches in Amol-Babol Plain, Iran. Environ Monit Assess 186:5797–5815
Nas B (2009) Geostatistical approach to assessment of spatial distribution of groundwater quality. Polish J Environ Stud 18(6):1073–1082
Özyurt G, Ergin A (2010) Improving coastal vulnerability assessments to sea-level rise: a new indicator based methodology for decision makers. J Coast Res 262:265–273
Perumal SB, Thamarai P, Elango L (2010) Hydrogeological studies along the coastal area of Kanyakumari to Colachel after tsunami, South Tamil Nadu. Indian J Environ Protect 30(10):793–813
Pham VH, Lee SI (2015) Assessment of seawater intrusion potential from sea-level rise and groundwater extraction in a coastal aquifer. Desalin Water Treat 53(9): 2324–2338
Piper AM (1944) A graphic procedure in geochemical interpretation of water analysis. Trans Am Geophys Union 25(6):914–928
Polemio M, Dragone V, Limoni PP (2006) Salt contamination in Apulian aquifer: spatial and time trend. Proceedings of 1st SWIM-SWICA (19th saltwater intrusion meeting- 3rdsalt water intrusion in coastal aquifers), Cagliari, pp. 119–125
Rahman A (2008) A GIS based DRASTIC model for assessing groundwater vulnerability in shallow aquifer in Aligarh, India. Appl Geogr 28(1):32–53
Rao SN (2006) Seasonal variation of groundwater quality in a part of Guntur district Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Geo 49:413–429
Recinos N, Kallioras A, Pliakas F, Schuth C (2015a) Application of GALDIT index to assess the intrinsic vulnerability to seawater intrusion of coastal granular aquifers. Environ Earth Sci 73(3):1017–1032
Recinos N, Kallioras A, Pliakas F, Schuth C (2015b) Application of GALDIT index to assess the intrinsic vulnerability to seawater intrusion of coastal granular aquifers. Environ Earth Sci 73(3):1017–1032
Reddy A, Saibaba B, Sudarshan G (2012) Hydrogeochemical characterization of contaminated groundwater in Patancheru industrial area, southern India. Environ Monit Assess 184:3557–3576
Revelle R (1941) Criteria for recognition of sea water in groundwater. Trans Am Geophys Union 22:593–597
Rey J, Martínez J, Barberá GG, García-Aróstegui JL, García-Pintado J, Martínez-Vicente D (2013) Geophysical characterization of the complex dynamics of groundwater and seawater exchange in a highly stressed aquifer system linked to a coastal lagoon (SE Spain). Environ Earth Sci 70(5):2271–2282
Richter BC, Kreitler WC (1993) Geochemical techniques for identifying sources of groundwater salinization. CRC, New York
Saidi S, Bouri S, Ben Dhia H (2009) Groundwater vulnerability and risk mapping of the Jelma aquifer (central Tunisia) using a GIS-based DRASTIC model. Environ Earth Sci 59:1579–1588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0143-0
Salem ZES, El-horiny MM (2014) Hydrogeochemical evaluation of calcareous eolianite aquifer with saline soil in a semiarid area. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:8294–8314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2735-9
Salem ZES, Osman OM (2017) Use of major ions to evaluate the hydrogeochemistry of groundwater influenced by reclamation and seawater intrusion, West Nile Delta, Egypt. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:3675–3704. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8056-4
Sathish S, Elango L (2011) Groundwater quality and vulnerability mapping of an unconfined coastal aquifer. J Spat Hydrol 11:18–33
Satishkumar V, Sankaran S, Taufiquewarsi, Amarender B, Dhakate R (2016) Mapping of salinity ingress using Galdit model for Sirkali coastal region: a case study. J Geogr Inf Syst 8:526–536 https://doi.org/10.4236/jgis.2016.84044
Selmi A (2013) Water management and modeling of a coastal aquifer case study (Gaza strip). Thesis. Faculty of Mathematics, Physics and Natural Sciences. The University of Milano-Bicocca, Milan (Italy)
Selvakumar S, Chandrasekar N, Magesh NS (2012) Preliminary investigation of groundwater quality along the coastal aquifers of southern Tamil Nadu using GIS techniques. Bonfring International Journal of Industrial Engineering and Management Science 2(1):46–52
Selvakumar S, Chandrasekar N, Srinivas Y, Simon Peter T, Magesh NS (2014) Evaluation of the groundwater quality along coastal stretch between Vembar and Taruvaikulam, Tamil Nadu, India; a statistical approach. Journal of Coastal Sciences 1:22–26. https://sites.google.com/site/journalofcoastalsciences/view-articles/archives
Selvakumar S, Chandrasekar N, Kaliraj S, Magesh NS (2017) Salinization of shallow aquifer in the Karamaniyar river basin, southern India. Environ Dev Sustain 20:1255–1273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-017-9937-5
Shammi M, Rahman MM, Islam MA, Bodrud-Doza M, Zahid A, Akter Y, Quaiyum S, Kurasaki M (2017) Spatio-temporal assessment and trend analysis of surface water salinity in the coastal region of Bangladesh. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:14273–14290. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8976-7
Sherif M, Mohamed M, Kacimo A, Shetty A (2011) Assessment of groundwater quality in the northeastern coastal area of UAE as precursor for desalination. Desalination 273:436–446
Simmons CT, Barry DA (2013) Seawater intrusion processes, investigation and management: recent advances and future challenges. Adv Water Resour 51:3–26
Singh VS, Gupta CP (1986) Hydrogeological parameter estimation from pumping test on large diameter well. J Hydrol 87:223–232
Sophiya MS, Syed TH (2013) Assessment of vulnerability to seawater intrusion and potential remediation measures for coastal aquifers: a case study from eastern India. Environ Earth Sci 70(3):1197–1209
Srinivasamoorthy K, Vasanthavigar M, Chidambaram S, Anandhan P, Sarma VS (2011) Characterisation of groundwater chemistry in an eastern coastal area of Cuddalore district, Tamil Nadu. J Geol Soc India 78(6):549–558
Sundaram VLK, Dinesh G, Ravikumar G, Govindarajalu D (2008) Vulnerability assessment of seawater intrusion and effect of artificial recharge in Pondicherry coastal region using GIS. Indian J Sci Technol 1(7):1–7
Teubner MD (2012) Vulnerability indicators of seawater intrusion. Ground Water 50:48–58. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.2008.00535.x
Todd DK (1980) Groundwater hydrology. Wiley, New York
Tomaszkiewicz M, AbouNajm M, El-Fadel M (2014) Development of a groundwater quality index for seawater intrusion coastal aquifers. Environ Model Softw 57:13–26
Trabelsi N, Triki I, Hentati I, Zairi M (2016) Aquifer vulnerability and seawater intrusion risk using GALDIT, GQISWI and GIS: case of a coastal aquifer in Tunisia. Environ Earth Sci 75(669):1–19
Triki I, Trabelsi N, Hentati I, Zairi M (2013) Groundwater levels time series sensitivity to pluviometry and air temperature: a geostatistical approach to Sfax region, Tunisia. Environ Monit Assess 186:1593–1608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3477-8
Van Stempvoort D, Ewert DLE, Wassenaar L (1993) Aquifer vulnerability index: a GIS-compatible method for groundwater vulnerability mapping. Can Water Resour J 18(1):25–37
Vasawa H, Yadav SM, Samtani BK (2010) Sea water intrusion mapping using GALDIT indicator model—a case study of in Surat. Unpublished PhD thesis, SVNIT, Surat, India
Venkatramanan S, Chung SY, Selvam S et al (2017) Factors controlling groundwater quality in the Yeonjegu District of Busan City, Korea, using the hydrogeochemical processes and fuzzy GIS. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:23679. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9990-5
Verruijt A (1987) Modeling groundwater flow and pollution. Reidel Publications, Boston
Wang J, He J, Chen H (2012) Assessment of groundwater contamination risk using hazard quantification, a modified DRASTIC model and groundwater value, Beijing Plain, China. Sci Total Environ 432:216–226
Werner D, Gallagher MR (2006) Characterisation of sea-water intrusion in the Pioneer valley, Australia hydrochemistry and three-dimensional numerical modeling. Hydrogeol J 14(8):1452–1469
Werner AD, Ward JD, Morgan LK, Simmons CT, Robinson NI, Teubner MD (2012) Vulnerability indicators of sea water intrusion. Ground Water 50(1):48–58
Wetzelhuetter C (2015) Groundwater in the coastal zones of Asia-Pacific. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 317–342
Wu X, Li B, Ma C (2018) Assessment of groundwater vulnerability by applying the modified DRASTIC model in Beihai City, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:12713–12727. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1449-9
Xie R, Pang Y, Luo B, Li J, Wu C, Zheng Y, Sun Q, Zhang P, Wang F (2017) Spatiotemporal variability in salinity and hydraulic relationship with salt intrusion in the tidal reaches of the Minjiang River, Fujian Province, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:11847–11855. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8788-9
Zhang X, Miao J, Hu BX et al (2017) Hydrogeochemical characterization and groundwater quality assessment in intruded coastal brine aquifers (Laizhou Bay, China). Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:21073. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9641-x
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Director, National Centre for Earth Science Studies, Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India, for providing support and continuous encouragement. The authors would like to acknowledge the GSI, CGWB, and SOI for providing necessary data sources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Marcus Schulz
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seenipandi, K., Nainarpandian, C., Kandathil, R.K. et al. Seawater intrusion vulnerability in the coastal aquifers of southern India—an appraisal of the GALDIT model, parameters’ sensitivity, and hydrochemical indicators. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 9755–9784 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04401-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04401-0