Abstract
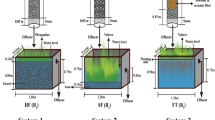
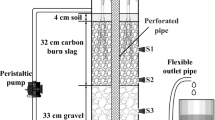
Landfill leachates contain a variety of toxic compounds, which makes them one of the most difficult types of wastewater to be treated. An alternative “green” technology for leachate treatment is the use of constructed wetlands (CWs). The aims of this study were to select macrophytes and substrates to be used in vertical flow wetlands (VFWs) and to evaluate the performance of hybrid systems composed by a VFW and a horizontal subsurface flow (HSSW) or a free water surface flow (FWSW) wetlands for the treatment of a high ammonium concentration landfill leachate. In microcosms scale experiments, Typha domingensis, Scirpus californicus, and Iris pseudacorus were studied to assess their tolerance to raw and diluted leachate. Substrate selection for VFWs was evaluated using different layers of light expanded clay aggregate (LECA), coarse sand, fine sand, and gravel. Contaminant removals were higher in planted than in unplanted wetlands. Plants did not tolerate the raw effluent but showed a positive effect on plant growth when exposed to the diluted leachate. T. domingensis and I. pseudacorus showed higher contaminant removal ability and tolerance to landfill leachate than S. californicus. VFW with LECA + coarse sand showed the best performance in removal efficiencies. Hybrid system composed by VFW-FWSW planted with T. domingensis presented the best performance for the treatment of landfill leachate with high concentrations of ammonium.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
A D, Oka M, Fujii Y, Soda S, Ishigaki T, Machimura T, Ike M (2017) Removal of heavy metals from synthetic landfill leachate in lab-scale vertical flow constructed wetlands. Sci Total Environ 584–585:742–750
Adyel TM, Oldham CE, Hipsey MR (2017) Storm event-scale nutrient attenuation in constructed wetlands experiencing a Mediterranean climate: A comparison of a surface flow and hybrid surface-subsurface flow system. Sci Total Environ 598:1001–1014
Akinbile CO, Yussof MS, Zuki Ahmad AZ (2012) Landfill leachate treatment using sub-surface flow constructed wetlands by Cyperus haspan. Waste Manag 32:1387–1393
APHA (2012) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. Amer. Publ. Health Assoc, New York
Brix H (1997) Do macrophytes play a role in constructed treatment wetlands? Water Sci Technol 35(5):11–17
Bulc T (2006) Long term performance of a constructed wetland for landfill leachate treatment. Ecol Eng 26:365–374
Butterworth E, Dotro G, Jones M, Richards A, Onunkwo P, Narroway Y, Jefferson B (2013) Effect of artificial aeration on tertiary nitrification in a full-scale subsurface horizontal flow constructed wetland. Ecol Eng 54:236–244
Camaño Silvestrini NE, Maine MA, Hadad HR, Nocetti E, Campagnoli MA (2019) Effect of feeding strategy on the performance of a pilot scale vertical flow wetland for the treatment of landfill leachate. Sci Total Environ 648:542–549
Clarke E, Baldwin A (2002) Response of wetlands plants to ammonia and water level. Ecol Eng 18:257–264
Connolly R, Zhao Y, Sun G, Allen S (2004) Removal of ammoniacal-nitrogen from an artificial landfill leachate in downflow reed beds. Process Biochem 39(12):1971–1976
Cooper P (1999) A review of the design and performance of vertical-flow and hybrid reed bed treatment systems. Water Sci Technol 40(3):1–9
Guo L, Lv T, He K, Wu S, Dong X, Dong R (2017) Removal of organic matter, nitrogen and faecal indicators from diluted anaerobically digested slurry using tidal flow constructed wetlands. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:5486–5496
Kadlec RH, Wallace SD (2009) Treatment wetlands, second edition. Boca Raton. CRC Press, Florida
Kadlec RH, Zmarthie LA (2010) Wetland treatment of leachate from a closed landfill. Ecol Eng 36:946–957
Kizito S, Lv T, Wu S, Ajmal Z, Luo H, Dong R (2017) Treatment of anaerobic digested effluent in biochar-packed vertical flow constructed wetland columns: role of media and tidal operation. Sci Total Environ 592:197–205
Kjeldsen P, Barlaz MA, Rooker AP, Baum A, Ledin A, Christensen T (2002) Present and long-term composition of MSW landfill leachate: a review. Environ Sci Technol 32:297–336
Lavrova S (2016) Treatment of landfill leachate in two stage vertical-flow wetland system with/without addition of carbon source. J Chem Technol Metall 51(2):223–228
Lee CG, Fletcher TD, Sun G (2009) Nitrogen removal in constructed wetland systems. Eng Life Sci 9(1):11–22
Liu M, Wu S, Chen L, Dong R (2014) How substrate influences nitrogen transformations in tidal flow constructed wetlands treating high ammonium wastewater? Ecol Eng 73:478–486
Maine MA, Suñé N, Hadad HR, Sanchez G, Bonetto C (2009) Influence of vegetation on the removal of heavy metals and nutrients in a constructed wetland. J Environ Manag 90(1):355–363
Maine MA, Hadad HR, Sánchez GC, Di Luca GA, Mufarrege MM, Caffaratti SE, Pedro MC (2017) Long-term performance of two free-water surface wetlands for metallurgical effluent treatment. Ecol Eng 98:372–377
Milani M, Toscano A (2013) Evapotranspiration from pilot-scale constructed wetlands planted with Phragmites australis in a Mediterranean environment. J Environ Sci Health Part A: Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 48(5):568–580
Molle P, Prost-Boucle S, Lienard A (2008) Potential for total nitrogen removal by combining vertical flow and horizontal flow constructed wetlands: A full-scale experiment study. Ecol Eng 34(1):23–29
Molle P, Lombard Latune R, Riegel C, Lacombe G, Esser D, Mangeot L (2015) French vertical-flow constructed wetland design: adaptations for tropical climates. Water Sci Technol 71(10):1516–1523
Nivala J, Hoos MB, Cross C, Wallace S, Parkin G (2007) Treatment of landfill leachate using an aerated, horizontal subsurface-flow constructed wetland. Sci Total Environ 380(1–3):19–27
Ogata Y, Ishigaki T, Ebie Y, Sutthasil N, Witthayaphirom C, Chiemchaisri C (2018) Design considerations of constructed wetlands to reduce landfill leachate contamination in tropical regions. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 20(4):1961–1968
Politeo M (2013) Performance of hybrid constructed wetland for piggery wastewater treatment. Ecol Eng 51:229–236
Reddy GB, Forbes DA, Phillips R, Cyrus JS, Porter J (2013) Demonstration of technology to treat swine waste using geotextile bag, zeolite bed and constructed wetland. Ecol Eng 57:353–360
Renou S, Givaudan JG, Poulain S, Dirassouyan F, Moulin P (2008) Landfill leachate treatment: review and opportunity. J Hazard Mater 150(3):468–493
Song U, Waldman B, Park JS, Lee K, Park JS, Lee K, Park SJ, Lee EJ (2018) Improving the remediation capacity of a landfill leachate channel by selecting suitable macrophytes. J Hydro Environ Res 20:31–37
Tanner CC (1996) Plants for constructed wetland treatment systems - A comparison of the growth and nutrient uptake of eight emergent species. Ecol Eng 7:59–93
Vymazal J (2005) Horizontal sub-surface flow and hybrid constructed wetlands systems for wastewater treatment. Ecol Eng 25(5):478–490
Vymazal J (2007) Removal of nutrient in various types of constructed wetlands. Sci Total Environ 31(380):48–65
Vymazal J (2011) Plants used in constructed wetlands with horizontal subsurface flow: A review. Hydrobiologia 674(1):133–156
Vymazal J (2013) The use of hybrid constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment with special attention to nitrogen removal: A review of a recent development. Water Res 47(14):4795–4811
Vymazal J (2018) Constructed wetlands for water quality regulation. In: Finlayson C et al (eds) The Wetland Book. Springer, Dordrecht 1313–1320 pp
Vymazal J, Kröpfelová L (2015) Multistage hybrid constructed wetland for enhanced removal of nitrogen. Ecol Eng 84:202–208
Wojciechowska E (2017) Potential and limits of landfill leachate treatment in a multi-stage subsurface flow constructed wetland – evaluation of organics and nitrogen removal. Bioresour Technol 236:146–154
Wojciechowska E, Gajewska M, Ostojski A (2016) Reliability of nitrogen removal processes in multistage treatment wetlands receiving high-strength wastewater. Ecol Eng 98:365–371
Wu S, Lei M, Lu Q, Guo L, Dong R (2016) Treatment of pig manure liquid digestate in horizontal flow constructed wetlands: effect of aeration. Eng Life Sci 16(3):263–271
Yalcuk A, Ugurlu A (2009) Comparison of horizontal and vertical constructed wetland systems for landfill leachate treatment. Bioresour Technol 18(100):2521–2526
Funding
Funds for this work were provided by Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET), Universidad Nacional del Litoral (UNL), and Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silvestrini, N.E.C., Hadad, H.R., Maine, M.A. et al. Vertical flow wetlands and hybrid systems for the treatment of landfill leachate. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 8019–8027 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04280-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04280-5